 |
Java Games: Flashcards, matching, concentration, and word search. |
 |
 |
Needs revision Vocabulary - Computer Hardware
Vocabulary for computer hardware that you will be using in this class or at home. Good luck and learn how to use this.
|
| A | B |
|---|
Keyboard,  | A typewriter-like layer of keys used to enter text information into a computer. |
Central Processing Unit (CPU),  | The part of the computer hardware that controls all functions. |
Byte,  | The amount of storage required to hold one character. A set of 8 bits that means something to the computer, like a letter, number, or punctuation mark. For example, the byte 01001000 means a capital "H". |
| Megabyte | Equals 1,048,576 bytes, or 1024 kilobytes. The text of a six hundred page paperback book would require about one megabyte of ASCII storage. |
bit,  | A single number, either a 1 or 0, used for counting in the binary number system. A single bit can’t tell you much, so bits are usually gathered into groups of 8 to make a byte. For instance, 8 bits can tell your computer you mean a certain letter, number, or symbol like M, 9, o |
Hardware,  | The visible part of the computer system. |
| Kilobyte | is equal to 1,024 bytes; on a computer about the size of a half page of text (a very short story). |
| Gigabyte | is 1,073,741,824 bytes; The number of books it would take to fill the bed of a pickup; symphony in high-fidelity sound; broadcast quality movie. |
| Terabyte | is 1,099,511,627,776. Equal to 50,000 trees made into paper and printed. Equal to all books in the UT library. |
Return/Enter key,  | Key, that when pressed, moves the text insertion point to the start of the next line. |
Circuit board, 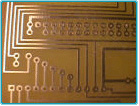 | The interconnection of a number of devices in one or more closed paths to perform a desired electrical or electronic function. A layer of a printed board containing conductors, including ground and voltage planes. |
Vacuum Tube,  | Tubes constructed of a glass or metal container that is vacuum sealed. The basic elements inside the tube are: the anode (or plate), the cathode, and the heater. Used in 1st generation computers. |
Transistors, 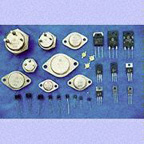 | At their most basic level, transistors may seem simple. But their development actually required many years of painstaking research. Before transistors, computers relied on slow, inefficient vacuum tubes and mechanical switches to work. Used in 2nd generation computers. Millions of transistors are in a microprocessor. |
Microprocessor,  | The microprocessor is the heart of any normal computer, whether it is a desktop machine, a server or a laptop. The microprocessor you are using might be a Pentium, a K6, a PowerPC, a Sparc or any of the many other brands and types of microprocessors, but they all do approximately the same thing in approximately the same way. A microprocessor -- also known as a CPU or central processing unit -- is a complete computation engine that is fabricated on a single chip. |
ROM,  | stands for read-only memory. A ROM chip is programmed with a permanent collection of pre-set bytes. The address bus tells the ROM chip which byte to get and place on the data bus. |
RAM,  | stands for random-access memory. RAM contains bytes of information, and the microprocessor can read or write to those bytes depending on whether the RD or WR line is signaled. One problem with today's RAM chips is that they forget everything once the power goes off. That is why the computer needs ROM. |
Operating System,  | The operating system defines our computing experience. It's the first software we see when we turn on the computer, and the last software we see when the computer is turned off. It's the software that enables all the programs we use. The operating system organizes and controls the hardware on our desks and in our hands. |
Monitor,  | Computer visual display device. |
Printer,  | An output device that produces print on paper. |
Mouse,  | A palm-size pointing input device used to control the cursor on a computer screen. |
CD-ROM Disk,  | Disk that can hold 700 megabytes of text, graphics, movies, sound, and computer data. Read by an optical laser. |
Disk Drive,  | Common auxiliary storage device that magnetically records data on the surface of a rotating disk. |
Disk/Diskette,  | A circular, flat surface on which data in the form a digital signal is recorded as magnetic impulses. |
Hard disk,  | Fixed storage device that holds large amounts of information (Typically 20 Gigabytes or more.) |
DVD Disk,  | Disk that can hold 3 Gigabytes of full movies, videos, or a complete library the size of a school. |
DVD Player,  | Machine that can play CD-ROM and DVD Disks |
Cursor,  | An indicator on a monitor, frequently a blinking rectangle or line, that indicates the point of insertion on a screen. |
Softtware,  | Electronic instructions that tell your computer what to do. Without software, a computer is like an airplane without a pilot. There are two types of software: operating system software and application software. |
|
 |
 |

|
|
|
Seventh Grade Language Arts |
Marion Local Middle School |
| Maria Stein, OH |
|
|
|
|
|
| |