| A | B |
|---|
| point | Has no size, occupies no space. |
| line | Has length, but no width or thickness. |
| plane | Has length and width, but no thickness. |
| collinear | Points that are all on the same line. |
| coplanar | Points, lines, or shapes that are all in the same plane. |
| segment | A part of a line that contains 2 endpoints and all the points between them. |
| postulate | A statement (basic assumption) that is accepted without proof. |
| theorem | A statement that can be proved. |
| definition | A statement of the meaning of a word, phrase, or concept. |
| midpoint | A point that is equidistant from two other points. |
| congruent | Having equal measures. |
| bisector | A line, ray, segment, or plane that intersects a segment at its midpoint. |
| line | Extends indefinitely in 2 directions. |
| plane | Extends indefinitely in ALL directions. |
| plane | Can be represented by a flat surface. |
| ordered pair | (x, y) |
| ordered pair | Defines a specific point on the coordinate plane. |
| noncollinear | Points that are NOT all on the same line. |
| midpoint | M is the ________ of segment AB if M is between A and B, and AM=MB. |
| line | 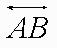 |
| segment | 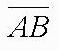 |
| distance between A and B | 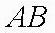 |
| Segment Addition Postulate | If Q is between P and R, then PQ + QR = PR. |
| Segment Addition Postulate | The sum of the measures of two adjacent, collinear segments equals the measure of the whole segment formed. |
| Midpoint Theorem | 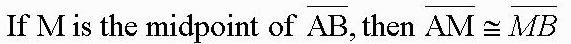 |
| Midpoint Formula | Average of the endpoints of a segment. |
| Midpoint Formula | 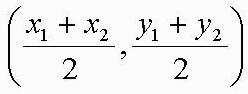 |
| Distance Formula | 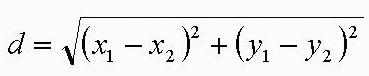 |
| Segment Addition Postulate |  |
| Distance Formula | A loooong square root sign with a plus sign in the middle, 2 sets of parentheses, each one squared, take the difference of the x's and the difference of the y's, ... |
| noncoplanar | Points that are NOT all on the same plane. |