| A | B |
|---|
| flagella | long, whiplike "tail" used for movement |
| host | the organism a parasite lives on or in |
| zooplankton | animal-like protist |
| pseudopod | "false feet" used by paramecium |
| symbiosis | relationship between 2 organisms in which at least one benefits |
| commensalism | symbiosis where one benefits and the other is neither harmed nor helped |
| parasitism | symbiosis where one organism benefits and the other is harmed (dog and tick) |
| mutualism | symbiosis where both organisms benefit (bee and flower) |
| parasite | organism which lives on or in another organism (tick, flea) |
| diatoms | protists with a silica shell |
| cilia | small hair-like projections which help a cell move |
| unicellular | one-celled |
| silica | material diatoms use to make their beautiful shells |
| protista | kingdom of mostly unicellular eukaryotes |
| zoomastigina | phylum of protists with a flagella (mastigophora) |
| sporozoa | parasitic protists |
| phytoplankton | plant-like protists |
| eyespot | region of pigment which can detect light (euglena have them) |
| dinoflagellates | protists with flagella (cause red tides) |
| ciliophora | protists with cilia (paramecium and stentor) |
| anopheles mosquito | carries malaria protist |
| Euglenophyta | protist with a flagella |
| phaeophyta | kelps and brown algae |
| chlorophyta | green algae |
| bacillariophyta | diatoms |
| paramecium | 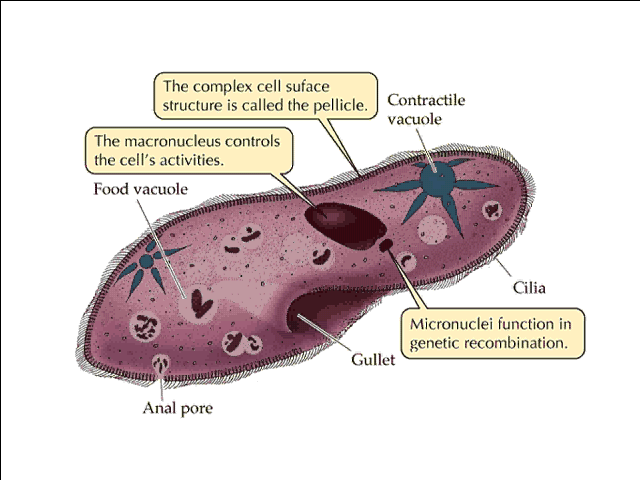 |
| euglena | 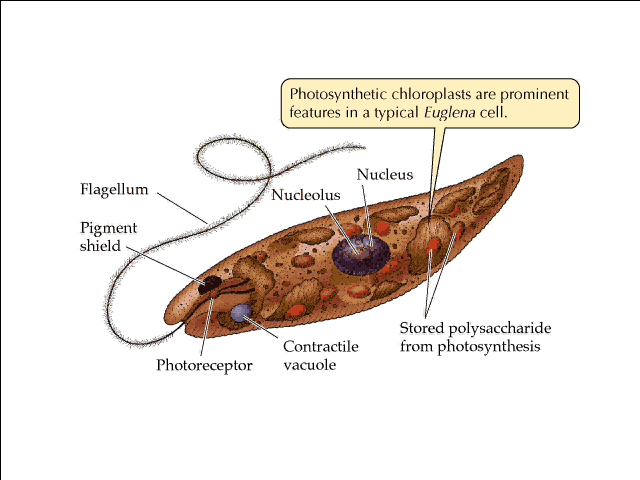 |
| volvox | 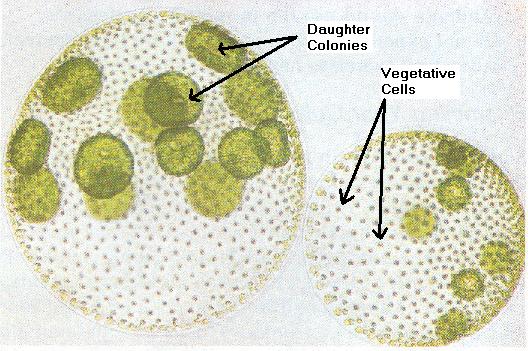 |
| amoeba | 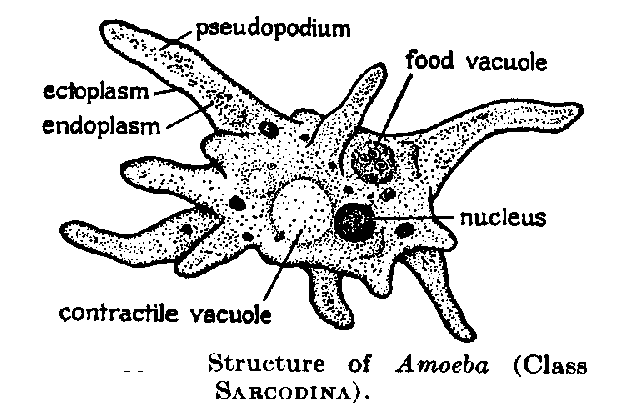 |
| vorticella |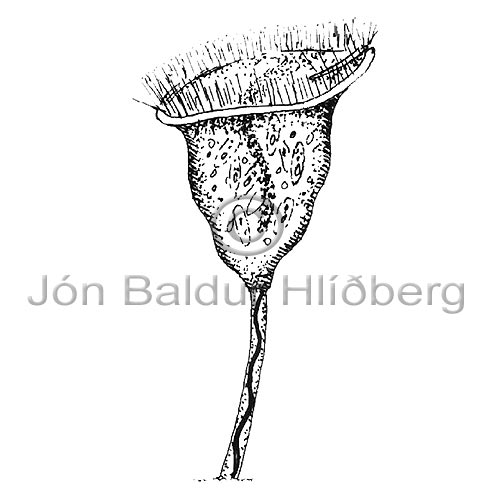  |
| stentor |  |