| A | B |
|---|
| What does LD stand for? | "Lethal Dose" |
| What is LD50 ? | the amount of a material, given all at once, which causes the death of 50% (one half) of a group of test animals. The LD50 is one way to measure the short-term poisoning potential (acute toxicity) of a material. The LD50 is defined as the amount of chemical that when ingested, injected, or applied to the skin of a test animal. |
| What does LC stand for? | "Lethal Concentration". |
| What is LC50? | LC values usually refer to the concentration of a chemical in air but in environmental studies it can also mean the concentration of a chemical in water. For inhalation experiments, the concentration of the chemical in air that kills 50% of the test animals in a given time (usually four hours) is the LC50 value. For airborne and dissolved in water. |
What is the Lethal Dose for this Chemical?, 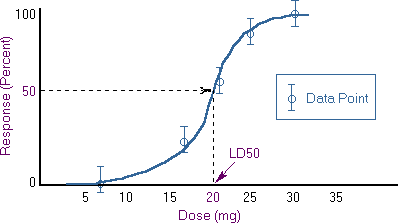 | 20mg (20 milligrams) |
What is the Lethal Dose for this chemical?, 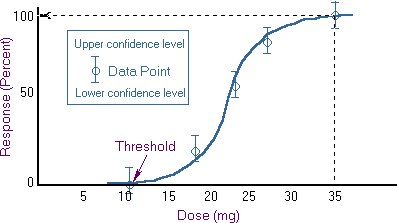 | ~ 22.5 mg |
What is the Lethal Dose for this chemical? (The x-axis is measured in grams), 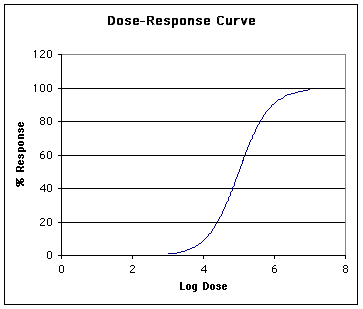 | 5 g (grams) |
Which is most toxic A or B and why?,  | A is more toxic because this toxic is lethal to 50% of the population at lower doses. |
| How is LD50 Measured? (Units?) | The LD50 is typically expressed in milligrams of test substance per kilogram of body weight. mg(toxin)/kg(weight of animal) |
| How is LC50 Measured (units)? | The LC50 is typically reported as an airborne concentration (parts per million, mg per cubic meter, etc.) over a specified time period (example: 10 ppm; 4 hours). |
| The lower the value of the LD50 and LC50 the _________ the substance | The lower the value of the LD50 and LC50 the more toxic the substance |