| A | B |
|---|
 | Turner Syndrome |
 | Klinefelter syndrome |
 | Trisomy 21 female |
| chances increase with the age of the mother | Trisomy 21 |
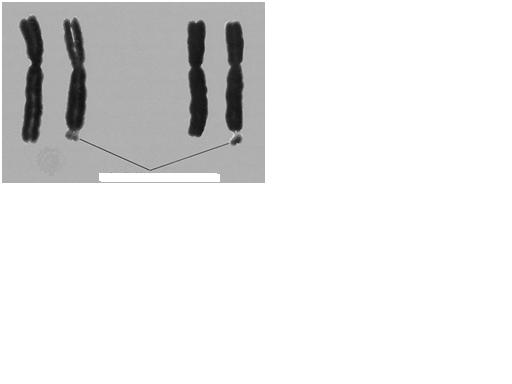 | Fragile X |
| Sex-linked from mother to son | Hemophilia |
| Tay-Sachs | Eastern European Jewish Population |
| extreme dwarfim | primordial dwarfism |
| autosomal dominant | 50% probability of offspring being affected |
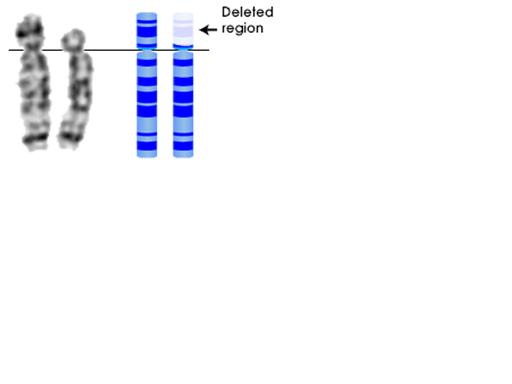 | Cri-du-Chat |
| Cry of the Cat | Severe mental retardation |
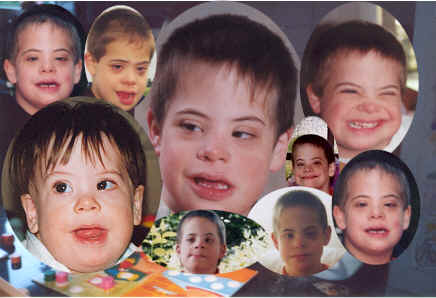 | Down's Syndrome |
| Dwarfism | Achondroplasia |
| Fatal in first year of life, affects Jewish population | Tay-Sachs |
| Affects mucous membranes, fatal by | cystic fibrosis |
| short arm of chromosome | p-arm of chromosome |
| metacentric | p and q arms essentially the same length |
| autosomal dominant disorder that causes neurological tumors | neurofibromatosis |
| Neurological degenerative disorder recognized in adulthood - fatal | Huntington's |
| African disorder | Sickle-cell anemia |
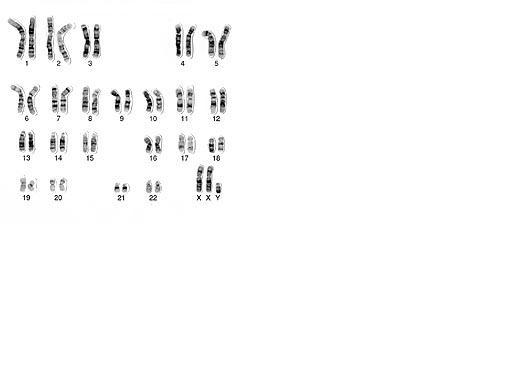
 | Normal male |
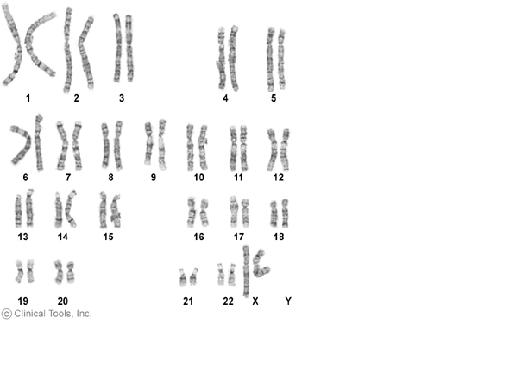 | Normal female |
| structural or numerical | the two major types of chromosomal abnormalities |
| structural abnormalities | Fragile X and Cri-du-Chat |
| enlarged limbs and facial features | Proteus syndrome |
| cystic fibrosis | disorder that affects the mucous membranes |
| progeria | premature aging disorder |