| A | B |
|---|
| types of materials processed | metals, ceramics specifically glasses, polymers (PMC's) |
| 2 types of casting of metals | expendable mold casting and permant mold casting |
| types of processing of polymers | extrusion, injection molding, other molding processes and special processes for PMC's |
| Casting | Process in which molten metal flows by gravity or other force into a mold where it solidifies in the shape of the mold cavity |
| steps in casting | 1. melt the metal 2. pour it into a mold 3. let it freeze,  |
| Capabilities and Advantages of Casting | Can create complex part geometries, Can create both external and internal shapes, Some casting processes are net shape; others are near net shape, can produce large parts, some methods are suited to mass production |
| Disadvantages of Casting | Limitations on mechanical properties, Poor dimensional accuracy and surface finish for some processes; e.g., sand casting, Safety hazards to workers due to hot molten metals, Environmental problems |
| parts made by casting | big parts eg. engine blocks, machine frames, pipes, big statues. small parts eg. dental crowns, jewelry, frying pans |
| varieties of metals that can be cast | all varietis can be cast. ferrous and non ferrous |
| foundry | factory equipped for making molds, melting and handling molten metal, performing the casting process, and cleaning the finished casting |
| foundrymen | Workers who perform casting |
| what are molds made of? | sand, plaster, ceramic and metal |
| what should the size and shape of the cavity be? | actual size and shape must be slightly oversized to allow shrinkage of metals during solidification and cooling |
| 2 forms of molds | open - simply a container in shape of desired part. closed - mold geometry is more comples and requires a gating system leading into the cavity,  |
| expendable mold casting | uses expendable mold which must be destroyed to remove casting. materials include sand, plaster plus binders |
| permanent mold processes | uses permanent mold which can be used over and over. made of metal or less commonly a ceramic refractory material |
| advantages/disadvantes of expendable and permanent molding | expendable can make more intricate geometries. shapes in permanent molding are limited by need to open the mold. permanent molding are more economic in high production operations |
| halves of sand casting mold | cope - upper half of mold. drag - bottom half, 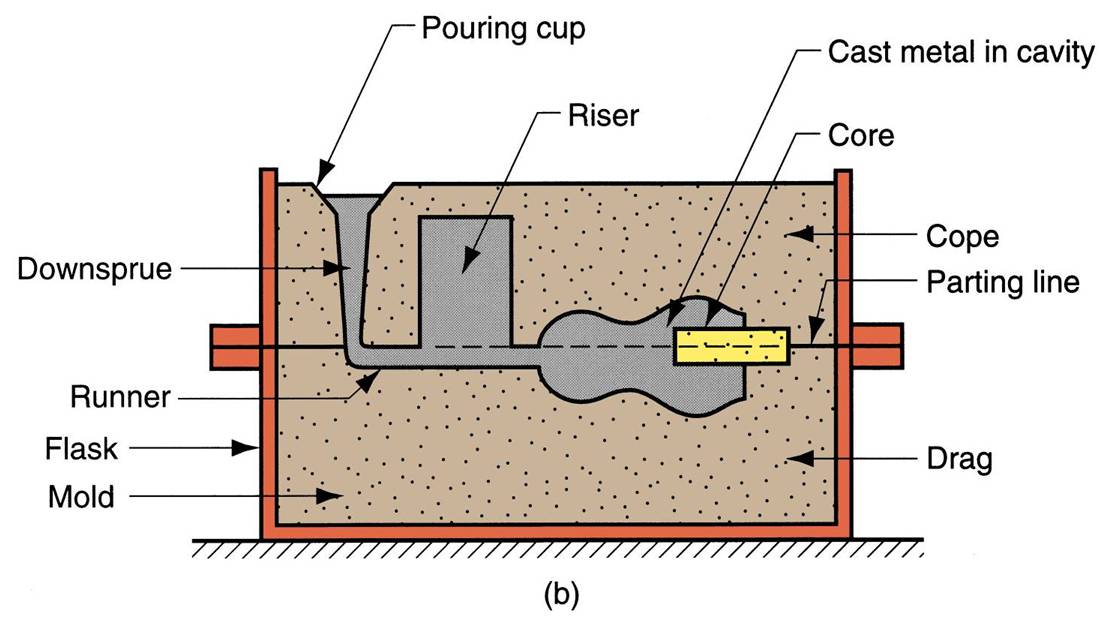 |
| flask | box which hold halves are contained |
| parting line | separate the 2 halves |
| Forming the Mold Cavity | Mold cavity is formed by packing sand around a pattern, which has the shape of the part. When the pattern is removed, the remaining cavity of the packed sand has desired shape of cast part. The pattern is usually oversized to allow for shrinkage of metal during solidification and cooling. Sand for the mold is moist and contains a binder to maintain its shape |
| cores | generally made of sand, used when casting has an internal surface, defines the interior geomerty of part,  |
| Gating System | Channel through which molten metal flows into cavity from outside of mold. consists of downsprue |
| downsprue | metal enters a runner leading to the main cavity |
| pouring cup | top of downsprue, minimize splash and turbulence as metal flows into downsprue |
| Riser | Reservoir in the mold which is a source of liquid metal to compensate for shrinkage of the part during solidification, The riser must be designed to freeze after the main casting in order to satisfy its function |