| A | B |
|---|
| Vacuum Molding | Uses sand mold held together by vacuum pressure rather than by a chemical binder- The term "vacuum" refers to mold making rather than casting operation itself |
| Advantages and Disadvantages of Vacuum molding | Advantages of vacuum molding: Easy recovery of the sand, since no binders. Sand does not require mechanical reconditioning done when binders are used. Since no water is mixed with sand, moisture‑related defects are absent. Disadvantages: Slow process. Not readily adaptable to mechanization. |
| Expanded Polystyrene Process | Uses a mold of sand packed around a polystyrene foam pattern which vaporizes when molten metal is poured into mold. Mold does not have to be opened into cope and drag sections, 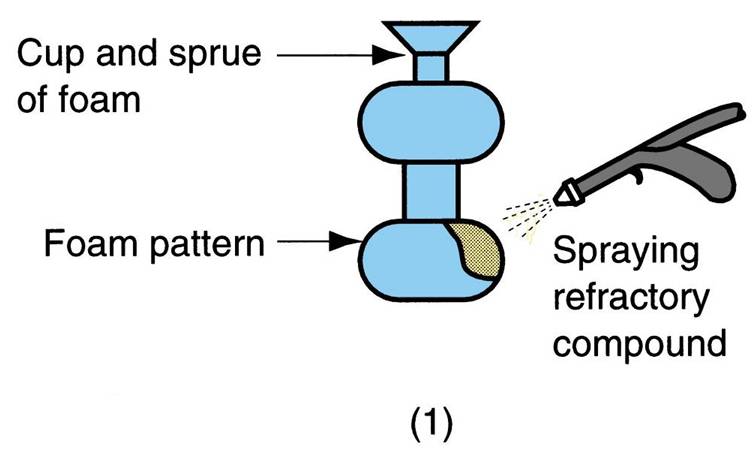 |
| Expanded Polystyrene Process Other names | lost‑foam process, lost pattern process, evaporative‑foam process, and full‑mold process, 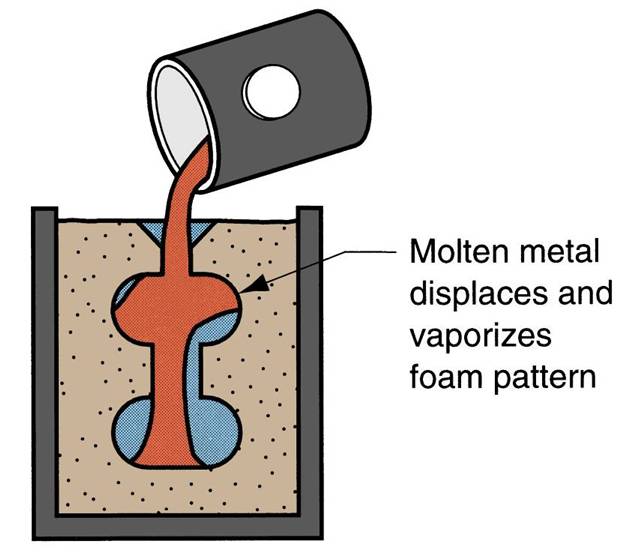 |
| Polystyrene foam pattern includes (4) | sprue, risers, gating system, and internal cores (if needed) |
| Disadvantages of Expanded Polystyrene Process | A new pattern is needed for every casting. Economic justification of the process is highly dependent on cost of producing patterns. |
| Advantages of Expanded Polystyrene Process | Pattern need not be removed from the mold. Simplifies and speeds mold‑making, because two mold halves are not required as in a conventional green‑sand mold. |
| Investment Casting (Lost Wax Process) | A pattern made of wax is coated with a refractory material to make mold, after which wax is melted away prior to pouring molten metal. It is a precision casting process - capable of producing castings of high accuracy and intricate detail, 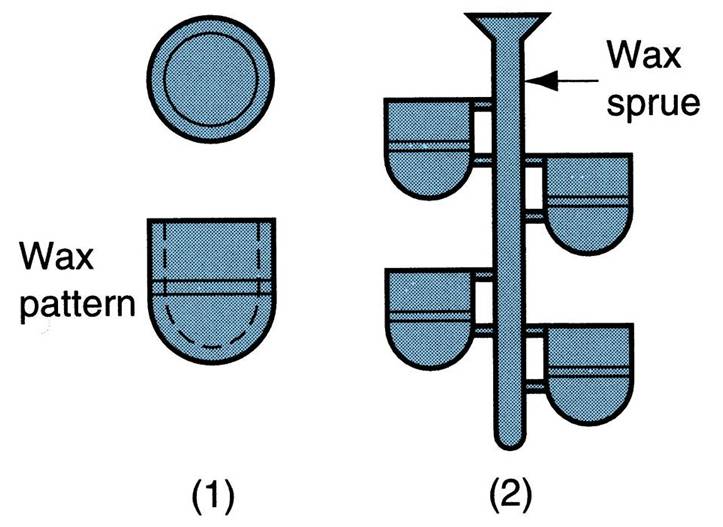 |
| Steps in investment casting: | (1) wax patterns are produced, (2) several patterns are attached to a sprue to form a pattern tree (3) the pattern tree is coated with a thin layer of refractory material, (4) the full mold is formed by covering the coated tree with sufficient refractory material to make it rigid (5) the mold is held in an inverted position and heated to melt the wax and permit it to drip out of the cavity, (6) the mold is preheated to a high temperature, the molten metal is poured, and it solidifies (7) the mold is broken away from the finished casting and the parts are separated from the sprue, 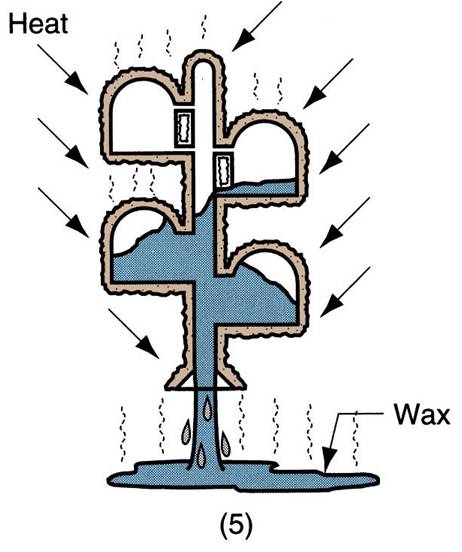 |
| Advantages of investment casting: | Parts of great complexity and intricacy can be cast. Close dimensional control and good surface finish . Wax can usually be recovered for reuse . Additional machining is not normally required ‑ this is a net shape process. |
| Disdvantages of investment casting: | Many processing steps are required. Relatively expensive process. |
| Plaster Mold Casting | Similar to sand casting except mold is made of plaster of Paris (gypsum ‑ CaSO4‑2H2O). In mold-making, plaster and water mixture is poured over plastic or metal pattern and allowed to set. Plaster mixture readily flows around pattern, capturing its fine details and good surface finish. |
| Advantages of plaster mold casting: | Good accuracy and surface finish Capability to make thin cross‑sections |
| disadvantages of plaster mold casting: | Mold must be baked to remove moisture, which can cause problems in casting Mold strength is lost if over-baked Plaster molds cannot stand high temperatures, so limited to lower melting point alloys |
| Ceramic Mold Casting | Similar to plaster mold casting except that mold is made of refractory ceramic material that can withstand higher temperatures than plaster. Can be used to cast steels, cast irons, and other high‑temperature alloys |
| Advantages to Ceramic Mold Casting | Advantages (good accuracy and finish) also similar |
| Permanent Mold Casting Processes (definition) | Economic disadvantage of expendable mold casting: a new mold is required for every casting. In permanent mold casting, the mold is reused many times |
| Permanent Mold Casting Processes (types) | The processes include: Basic permanent mold casting Die casting Centrifugal casting |
| The Basic Permanent Mold Process | Uses a metal mold constructed of two sections designed for easy, precise opening and closing. Molds used for casting lower melting point alloys are commonly made of steel or cast iron. Molds used for casting steel must be made of refractory material, due to the very high pouring temperatures., 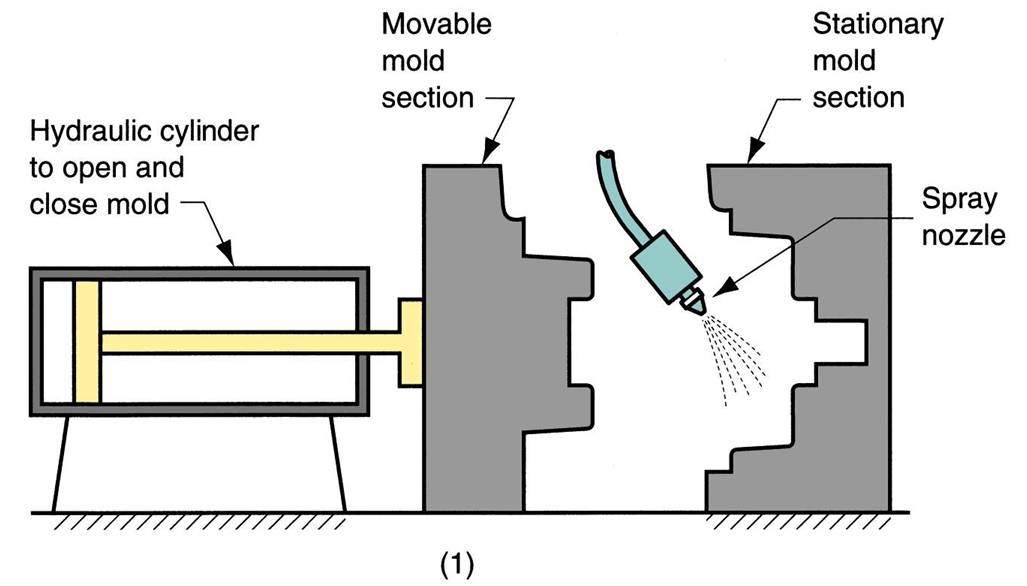 |
| Advantages of permanent mold casting | Good dimensional control and surface finish. More rapid solidification caused by the cold metal mold results in a finer grain structure, so castings are stronger |