| A | B |
|---|
| The DNA "ladder" has a backbone made of | deoxyribose sugar and phosphate. |
Identify the phase of mitosis.,  | Prophase |
| DNA replication takes place during | S phase of interphase (2nd part of interphase). |
| Two sister chromatids are connected by the | centromere. |
| When mRNA is decoded to produce amino acids, it is called | translation. |
| The 2 strands of DNA run in opposite directions, so DNA is | antiparallel. |
| Amino acids are carried to the ribosome for translation by | transfer RNA (tRNA). |
Use the RNA-codon chart to find the amino acid the following DNA sequence codes for: TAC, 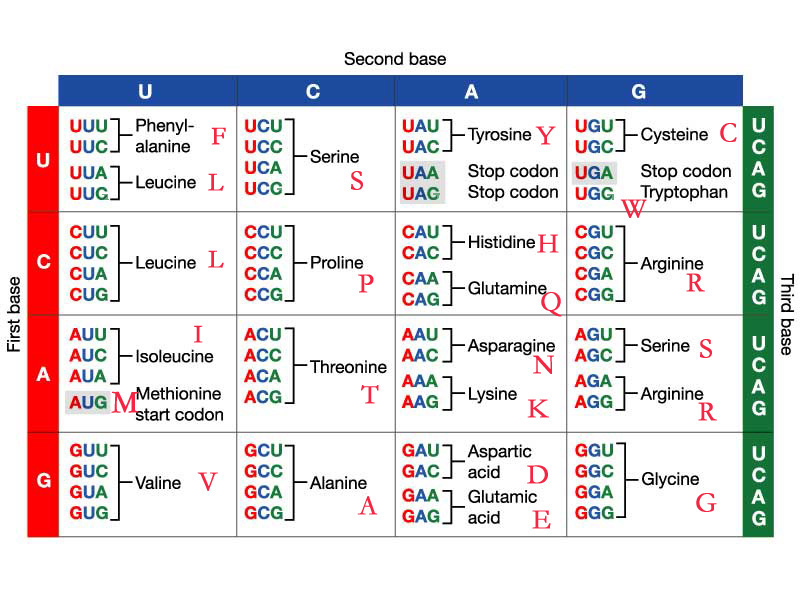 | Start Codon (Met) |
| In DNA replication, having thymine on the original strand means the new strand will have | adenine. |
| A mutation that causes the DNA to be "read" at a different point and usually shortens the sequence is called a | frameshift mutation. |
| Different forms of a gene are called | alleles. |
| When 2 traits often occur together, the genes are thought to be | linked. |
| When offspring show a phenotype that is somewhere in between the 2 parents it is called | incomplete dominance. |
Is this individual male or female? Are there any genetic abnormalities?, 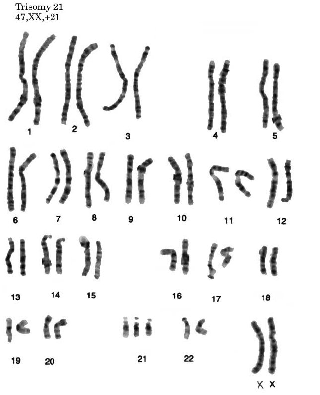 | Female (XX); Down Syndrome (3 copies of #21) |
| When offspring have a phenotype that shows part of both parents' phenotypes (black and white stripes) it is called | codominance |
| When genes are "shuffled" during meiosis to produce different, uncommon combinations it is called | crossing over. |
| T/F: All organisms have the same genetic code. | True |
| When making recombinant DNA, the "sticky ends" are sealed by | DNA ligase. |
| Eco R1 is an example of a | restriction enzyme. |
| In an electrophoresis gel, the shortest piece of DNA will be found | closest to the negative (starting) point. |
| Heritable variation is necessary for | evolution. |
| The wing of a bat and the arm of a human are examples of | homologous structures. |
| The speciation of animals (development of new species) usually begins with | geographic isolation. |
| Natural selection requires | genetic variation, overproduction, and differential success in surviving/reproducing. |
| The Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium is an idealized model that says | gene frequencies remain constant unless affected by a disturbance. |
| The migration of genes between populations (gene pools) is known as | gene flow. |
| Archaea and Eubacteria are both | prokaryotes. |
| The wing of a bat and the wing of a butterfly are examples of | analogous structures. |
| When 2 different species mate at different times of the year, it is known as | temporal isolation. |
Tyrannosaurus is most closely related to, 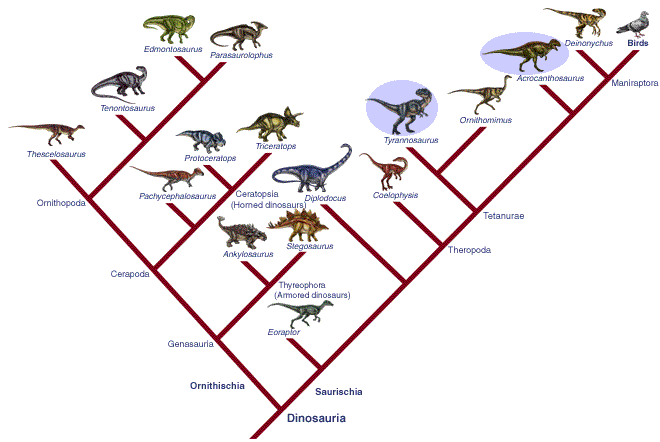 | Ornithomimus |