| A | B |
|---|
#1, 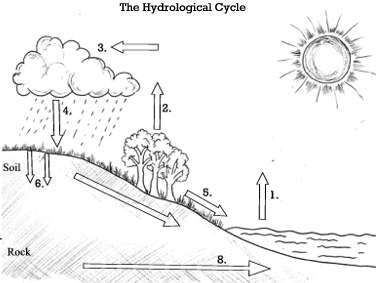 | evaporation |
#2,  | transpiration |
#3,  | condensation |
#4,  | precipitation |
#5,  | surface runoff |
#6,  | infiltration |
#8,  | movement of groundwater |
| characteristic of materials such as clay and granite that do not allow water to pass through them | impermeable |
| characteristic of materials such as sand and gravel that allow water to pass easily through them | permeable, 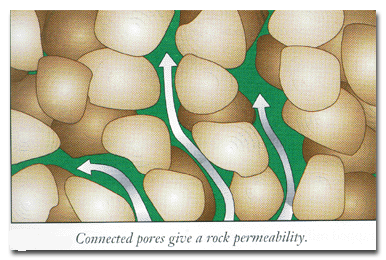 |
| a layer of permeable rock or soil in which the cracks and pores are completely filled with water | Zone of Saturation (saturated), 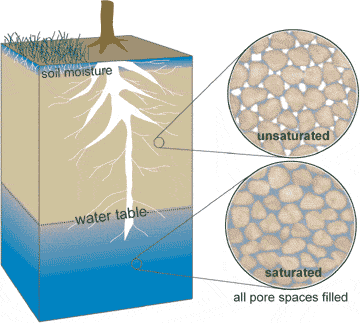 |
| a layer of rock and soil above the water table in which the pores contain air as well as some water | Zone of Aeration (unsaturated),  |
| the top of the groundwater, or the depth to the top of the Zone of Saturation | water table, 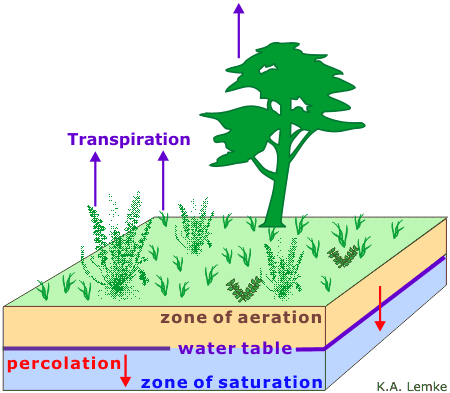 |
| an underground layer of saturated rock or soil that holds water | aquifer, 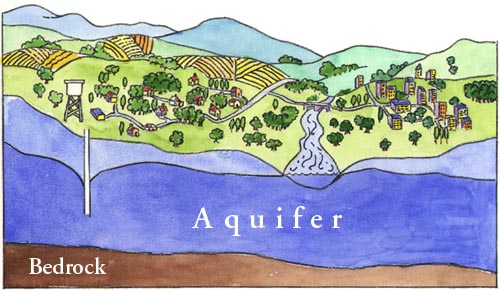 |
| ultimate source of energy to keep the water cycle going | sun |
| water that flows over the earth's surface and moves into nearby rivers, lakes, streams or drains | runoff |
| water soaking into the earth's surface and moving through soil or porous layers of rock | infiltration |
| the invisible, gaseous form of water | water vapor, 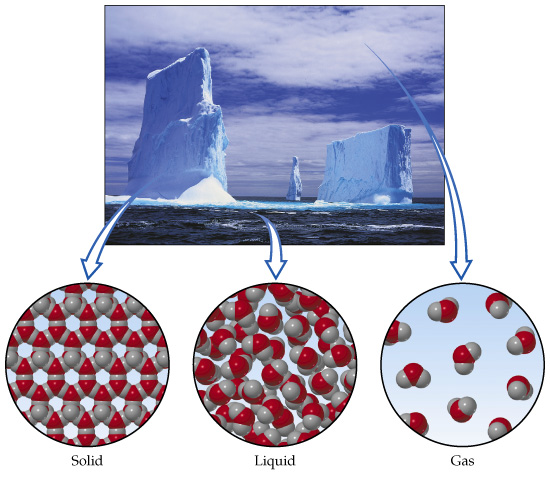 |
| water deep underground that completely fills the cracks and pores in underground soil and rock layers | groundwater, 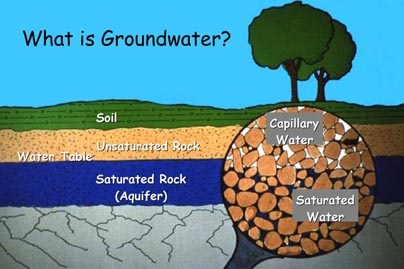 |
| the continuous process by which water moves from the Earth's surface to the atmosphere and back, passing through the living and non-living parts of the environment | water cycle |
| process by which water vapor in the air changes into the liquid state, forming visible water droplets (forms clouds in the air) | condensation,  |
| the process by which liquid water changes into invisible water vapor gas | evaporation, 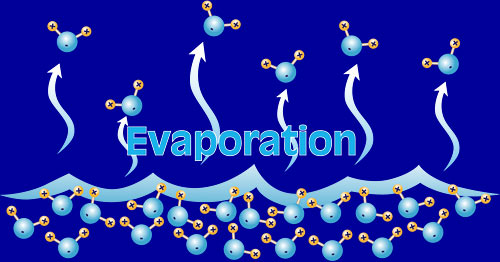 |
| the process by which water vapor evaporates through small pores in the surface of plant leaves | transpiration, 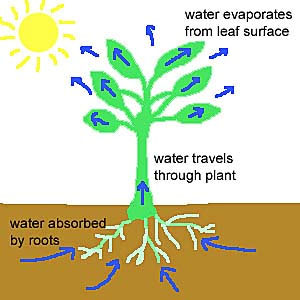 |
| forms of water such as rain, snow, sleet or hail that fall from clouds and reach the earth's surface | precipitation |
| tiny openings in and between particles of rock and soil that may contain air or water | pores (porous materials can hold water), 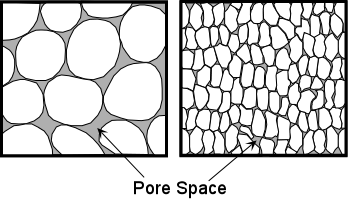 |