 |
Java Games: Flashcards, matching, concentration, and word search. |
 |
 |
Lewis_CaseSt_Ch54_Terms
A glossary explaining terms used in the Chapter 54 Case Study. A printable List of Terms is found under the Flashcard choice.
|
| A | B |
|---|
| Combination estrogen-progestin replacement therapy | When estrogen is combined with progestin (another hormone), it is called combination estrogen-progestin replacement therapy. For postmenopausal women, taking estrogen in combination with progestin does not increase the risk of endometrial cancer. |
| Endometrial Ablation | Endometrial ablation is a surgical procedure performed to treat abnormal uterine bleeding due to benign non-cancerous conditions. Endometrial ablation destroys the lining tissues of the uterus, known as the endometrium.since cancer cells may have grown into the deeper tissues of the uterus and would not be removed by the procedure. Endometrial ablation is only performed on a nonpregnant woman who does not plan to become pregnant in the future. It should not be performed if the woman has an active infection of the genital tract. Endometrial ablation is not a first-line therapy for heavy bleeding and should only be considered when medical and hormonal therapies have not been sufficient to control the bleeding. |
| Endometrium | The uterine lining; the cells that line the uterus (the womb); the inner layer of the uterus. This tissue is shed monthly in response to the hormonal changes of the menstrual period. The endometrium then grows back and slowly gets thicker and thicker until the next period when it is once again sloughed off. |
| Estrogen | Estrogen is a hormone made by the body. It helps the body develop and maintain female sex characteristics. Estrogen can affect the growth of some cancers, including endometrial cancer. |
| Estrogen-only hormone replacement therapy | Estrogen may be given to replace the estrogen no longer produced by the ovaries in postmenopausal women or women whose ovaries have been removed. This is called hormone replacement therapy (HRT), or hormone therapy (HT). The use of hormone replacement therapy that contains only estrogen increases the risk of endometrial cancer. For this reason, estrogen therapy alone is usually prescribed only for women who do not have a uterus. |
| Hereditary Non-Polyposis Colon Cancer (HNPCC) | A hereditary cancer syndrome which carries a very high risk of colon cancer and an above-normal risk of other cancers (uterus, ovary, stomach, small intestine, biliary system, urinary tract, brain, and skin). The HNPCC syndrome is due to mutation in a gene in the DNA mismatch repair system, usually the MLH1 or MSH2 gene or less often the MSH6 or PMS2 genes. Families with HNPCC account for about 5% of all cases of colon cancer and the highest risk with HNPCC is for colon cancer. A person with HNPCC has about an 80% lifetime risk of colon cancer. Two-thirds of these tumors occur in the proximal colon. Women with HNPCC have a 20-60% lifetime risk of endometrial cancer. |
| Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) or Hormone Therapy (HT) | Estrogen may be given to replace the estrogen no longer produced by the ovaries in postmenopausal women or women whose ovaries have been removed. This is called hormone replacement therapy (HRT), or hormone therapy (HT). |
| Hysterectomy | A surgical operation to remove the uterus and, sometimes, the cervix. |
| Lynch Syndrome | See: Hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer. |
| Multipara | Had given birth to multiple infants. |
| Neoplasm | A tumor. An abnormal growth of tissue. The word neoplasm is not synonymous with cancer. A neoplasm may be benign or malignant. The word neoplasm literally means a new growth, from the Greek neo-, new + plasma, that which is formed, or a growth = a new growth. |
| Non-polyposis | Describes a condition of no polyps |
| Nulliparity | Has not given birth to a viable infant. |
| Oophorectomy | The removal of one or both ovaries by surgery. Also known as an ovariectomy. |
| Polyposis | Describes a condition of many polyps |
| Primipara | Is experiencing first live birth. |
| Salpingo-oophorectomy | Removal of the fallopian tubes and ovaries. |
| Subtotal hysterectomy | Removal of the body of the uterus without removing the cervix is referred to as a subtotal hysterectomy. |
| Total hysterectomy | Removal of the entire uterus and the cervix is referred to as a total hysterectomy. |
| Unopposed estrogen therapy | Estrogen therapy without progesterone |
| Cervix | The cervix is the lower, narrow part of the uterus (womb). The uterus, a hollow, pear-shaped organ, is located in a woman's lower abdomen, between the bladder and the rectum. The cervix forms a canal that opens into the vagina, which leads to the outside of the body. |
| Cervical cancer | Cancer of the entrance to the womb (uterus). The cervix is the lower, narrow part of the uterus (womb). The uterus, a hollow, pear-shaped organ, is located in a woman's lower abdomen, between the bladder and the rectum. The cervix forms a canal that opens into the vagina, which leads to the outside of the body. |
| Cancer | An abnormal growth of cells which tend to proliferate in an uncontrolled way and, in some cases, to metastasize (spread). |
| Metrorrhagia | Uterine bleeding at irregular intervals, particularly between the expected menstrual periods. Metrorrhagia may be a sign of an underlying disorder, such as hormone imbalance, endometriosis, uterine fibroids or, rarely, cancer of the uterus. Metrorrhagia may cause significant anemia. See also: Menometrorrhagia; Menorrhagia. |
| Menorrhagia | Excessive uterine bleeding occurring at the expected intervals of the menstrual periods. The bleeding from the uterus starts on schedule but is heavier than usual and may last longer than usual. Menorrhagia may be a sign of an underlying disorder, such as hormone imbalance, endometriosis, uterine fibroids or, rarely, cancer of the uterus. Menorrhagia may cause significant anemia. See also: Menometrorrhagia; Metrorrhagia. |
Read the Chapter 54 Case Study., 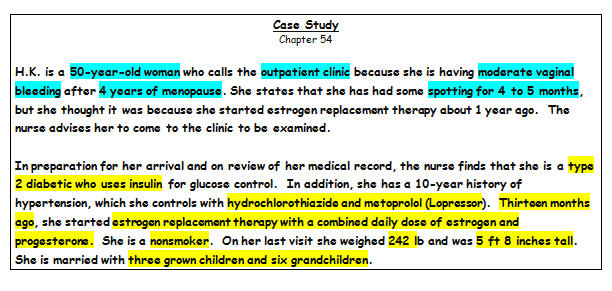 |  |
Number 1-5 on scratch paper and identify each as a) Cervical, b) Endometrial, or c) Both. Then flip the card over to check your answers.,  | B, B, A, A, B,  |
Number 6-11 on scratch paper and identify each as a) Cervical, b) Endometrial, or c) Both. Then flip the card over to check your answers.,  | A, B, A ,B, B, A,  |
Choose, A, B, C, or D.,  | D,  |
Choose, A, B, C, or D.,  | D,  |
|
 |
 |
|
|
|
| |