| A | B |
|---|
| accuracy | a description of how close a measurement is to the true value of the quantity measured,  |
| conversion factor | a ratio that is derived from the equality of two different units and that can be used to convert from one unit to the other, 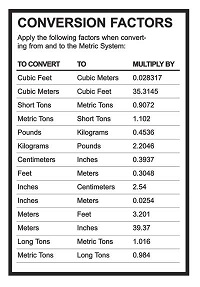 |
| density | the ratio of the mass of a substance; often expressed as grams per cubic centimeter for solids and liquids and as a gram per liter for gases,  |
| Derived Unit | a unit of measure that is a combination of the other measurements,  |
| dimensional analysis | a mathematical techniques for studying dimensions of physical quantities,  |
| directly proportional | the relationship between two variables whose ratio is a constant value, 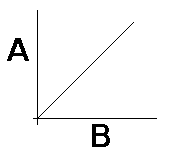 |
| Hypothesis | a testable statement, 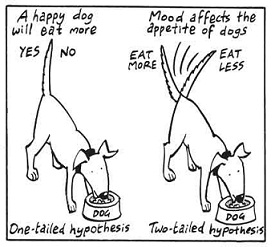 |
| inversely proportional | the relationship between two variables whose product is constant,  |
| Model | in science it is more than a physical object; it is often an explanation of how phenomena occur and how data or events are related.,  |
| percentage error | a figure that is calculated by subtracting the accepted value from the experimental value, dividing the difference by the accepted value, and then multiplying by 100, 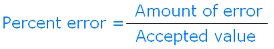 |
| precision | the exactness of a measurement,  |
| Quantity | something that has magnitude, size, or amount |
| Scientific Method | A logical approach to solving problems by observing and collecting data, formulating hypotheses, testing hypotheses, and formulating theories that are supported by data.,  |
| scientific notation | a method of expressing a quantity as a number multiplied by 10 to the appropriate power,  |
| System International | International Systems of Units, which is the measurement system accepted worldwide, 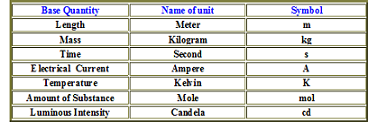 |
| significant figures | a prescribed decimal place that determines the amount of rounding off to be done based on the precision of the measurement,  |
| System | a specific portion of matter in a given region of space that has been selected for study during an experiment or observation. |
| Theory | Is a broad generalization that explains a body of facts or phenomena,  |
| volume | a measure of the size of a body or region in the three-dimensional space. |
| Weight | a measure of the gravitational force excreted on an object; its value can change with the location of the object in the universe,  |