| A | B |
|---|
| Electron Configuration | The arrangement of electrons in an atom,  |
| Aufbau Principle | The principle that states that the structure of each successive element is obtained by adding one proton to the nucleus of the atom and one electron to the lowest-energy orbital that is available, 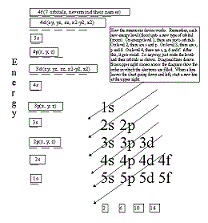 |
| Pauli Exclusion Principle | The principle that states tha two particles of a certain class cannot be in exactly the same energy state, 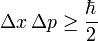 |
| Hund's Rule | The rule that states that for an atom in the ground state, the number of unpaired electrons is the maximum possible and these unpaired electrons have the same spin, 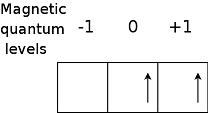 |
| Noble Gas | One of the elements in Group 18 of the periodic table (helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon); noble gases are unreactive,  |
| Noble-Gas Configuration | An outer main energy level fully occupied, in most cases, by eight electrons, 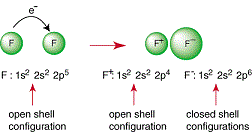 |
| Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle | The principle that states that determining both the position and velocity of an electron or any other particle simultaneously is impossible,  |
| Quantum Theory | The study of the structure and behavior of the atom and of subatomic particles from the view that all energy comes in tiny, indivisible bundles,  |
| Orbital | A region in an atom where there is a high probability of finding electrons, 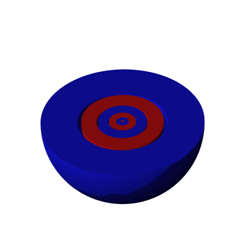 |
| Quantum Number | A number that specifies certain properties of electrons, 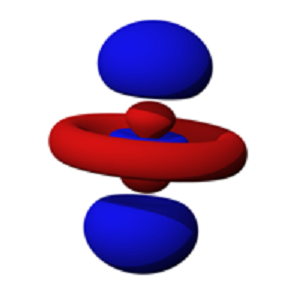 |
| Principal Quantum Number | The quantum number that indicates the energy and orbital of an electron in an atom, 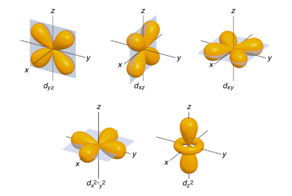 |
| Angular Momentum Quantum Number | The quantum number that indicates the shape of an orbital,  |
| Magnetic Quantum Number | The quantum number that corresponds to the alignment of the angular momentum component with a magnetic field, 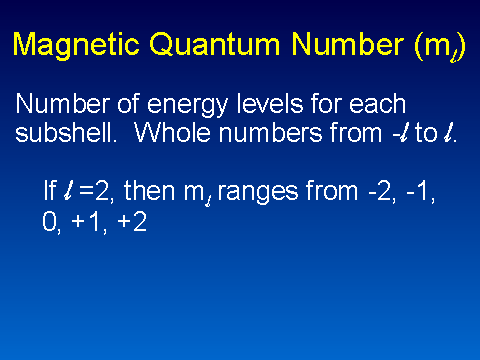 |
| Spin Quantum Number | The quantum number that describes the intrinsic angular momentum of a particle, 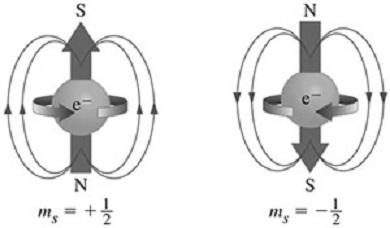 |
| Continuous Spectrum | The interrupted broad band of all colors (wavelengths) emitted by incandescent solids, 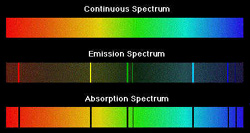 |
| Electromagnetic Radiation | The radiation associated with an electric and magnetic field; it varies periodically and travels at the speed of light,  |
| Electromagnetic Spectrum | All of the frequencies or wavelength of electromagnetic radiation, 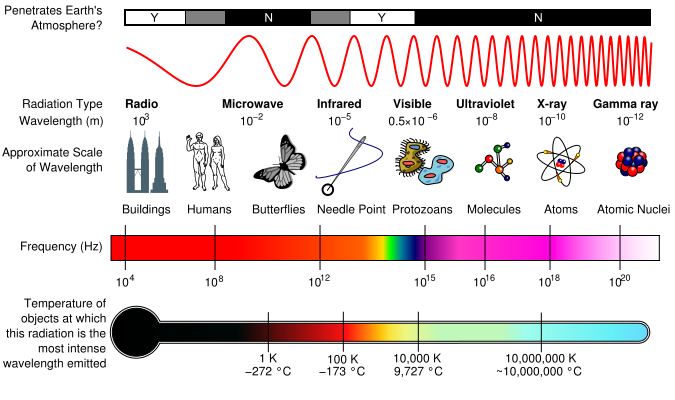 |
| Excited State | A state in which an atom has more energy than it does at its ground stare, 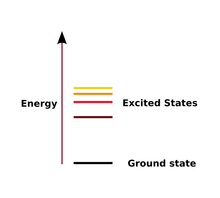 |
| Frequency | The number of cycles or vibrations per unit of time; also the number of waves produced in a given amount of time., 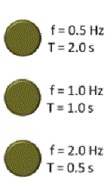 |
| Ground State | The lowest energy state of a quantized system, 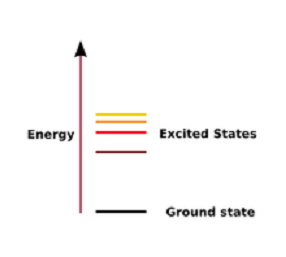 |
| Line-Emission | A diagram or graph that indicates the degree to which a substance emits radiant energy with respect to wavelength,  |
| Photoelectric Effect | The emission of electrons from a material when a light of certain frequencies shines on the surface of the material, 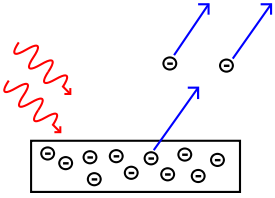 |
| Photon | A unit or quantum of light; a particle of electromagnetic radiation that has zero rest mass and carries a quantum of energy,  |
| Quantum | The basic unit of electromagnetic energy; it characterizes the wave properties of electrons, 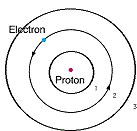 |
| Wavelength | The distance from any point on a wavelength to an identical point on the next wave, 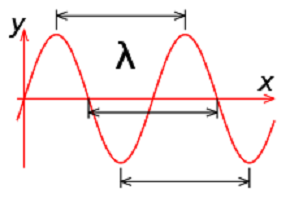 |