| A | B |
|---|
| atom | the smallest unit of an element that maintains the chemical properties of that element,  |
| atomic mass unit | a unit of mass that describes the mass of an atom or molecule; it is exactly 1/12 of the mass of a carbon atom with mass number 12, 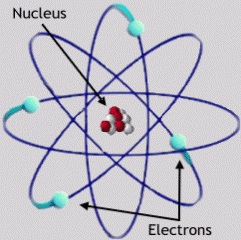 |
| average atomic mass | the weighted average of the masses of all naturally occuring isotopes of an element, 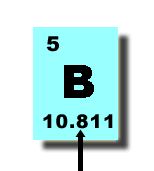 |
| avogardo's number | 6.02x10^23, the number of atoms or molecules in one mole,  |
| isotope | an atom that has the same number of protons as the other atoms of the same element do but that hasa different number of neutrons, 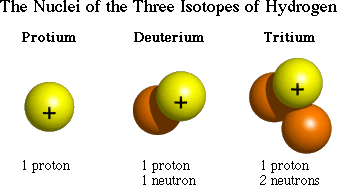 |
| law of conservation of mass | the law that states that mass cannot be created or destroyed in ordinary chemical and physical changes |
| law of definite proportions | the law that states that a chemical compound always contains the same elements in exactly the same proportions by weight or mass, 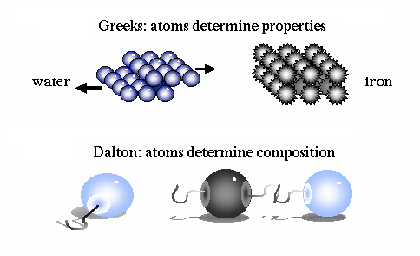 |
| law of multiple proportions | the law that states that when two elements combine to form two or more compounds, the mass of one element that contains with a given mass of the other is in the ratio of small whole numbers, 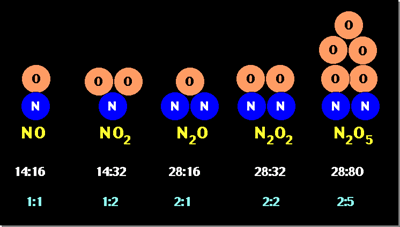 |
| mass number | the sum of the numbers of protons and neutrons that make up the nucleus of an atom,  |
| molar mass | the mass in grams of 1 mol of a substance, 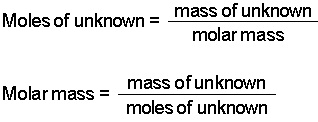 |
| mole | the SI unit used to measure the amount of a substance whose number of particles is the same as the number of atoms of carbon in exactly 12 g of carbon-12, 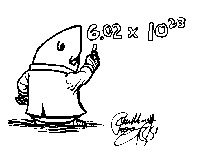 |
| nuclear forces | the interaction that binds proton and nuetrons, protons and protons, and nuetrons and nuetrons together in a nucleus, 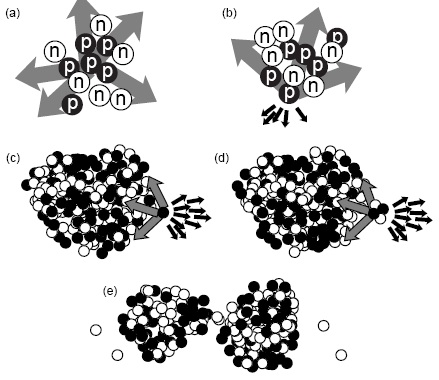 |
| nuclide | an atom that is identified by the number of protons and nuetrons in its nucleus,  |