| A | B |
|---|
| what makes 2 geometric figures congruent? | 2 geometric figures are congruent if they have exactly the same size and the same shape |
| what REALLY makes 2 geometric figures congruent | When there is a correspondence between their angles and sides such that corresponding angles are congruent and corresponding sides are congruent |
| What are the 5 methods of finding congruent triangles? | Side-Side-Side, Side-Angle-Side, Angle-Side-Angle, Angle-Angle-Side, Hypotenuse Leg |
| Side-Side-Side Postulate | If 3 sides of a triangle are congruent to 3 sides of a triangle, then the triangles are congruent |
| Side-Angle-Side Postulate | If 2 sides and the included angle of a triangle are congruent to two sides and included angle of another triangle, then the triangles are congruent |
| Angle-Side-Angle Postulate | If 2 angles and the included side of a triangle are congruent to 2 angles and included side of another triangle, then the triangles are congruent |
| Angle-Angle-Side Postulate | If 2 angles and a non-included side of a triangle are congruent to the corresponding parts of another triangle, then the triangles are congruent |
| Hypotenuse Leg-Therorem | If the hypotenuse and a leg of a right triangle are congruent to the corresponding parts of another right triangle, then the triangles are congruent. |
| Perpendicular Bisector Theroem | If a point is on the perpendicular bisector of a segment, then that point is equidistant from the endpoints of the segment |
| Isosceles Triangle Thereom | If 2 sides of a triangle are congruent, then angles oppisite those sides are congruent |
| Concurrent Lines | 3 lines that intersect at the same point |
| Point of Concurrency | Point of intersection of the 3 lines |
| Perpendicular Bisector of a Triangle | A line, segment, or ray that is perpendicular to a side of a triangle at its midpoint; angle bisectors of a triangle are congruent |
| Circumcenter | Point of concurrency of perpendicular bisectors of a triangle |
| Incenter | Point of concurrency of the angle bisectors; all meet at one point |
| Median of a Triangle | Segment from a vertex to the midpoint of the opposite side; cut opposite sides in half |
| Centroid | Point of concurrency of the medians of a triangle |
| Altitude of a Triangle | Perpendicular segment from a vertex to its opposidte side; form/ creat a right angle |
| Orthocenter | Point of concurrency of the altitudes |
| How many altitudes are formed by the legs in a triangle? | 2 of the altitudes are formed by the legs in a right triangle |
| Isosceles Triangle Thereom | If 2 sides of a triangle are congruent, then the angles opposite those sides are congruent |
| Perpendicular Bisector Theroem | If a point is on the angle bisector of a segment, then that point is equidistant from endpoints of the segment |
| When does it matter what kind of triangle it is (6.7) | Point of concurrency of angle bisectors/medians are always INSIDE the triangle |
| When does it depend on the type of triangle it is? | Point of concurrency of angle bisectors/altitudes DEPENDS on the triangle |
| Circumcenter - Acute triangle | location is inside triangle,  |
| Circumcenter - Right triangle | location will be on the triangle,  |
| Circumcenter - Obtuse | location is outside the triangle,  |
| Orthocenter - Acute triangle | location is inside triangle, 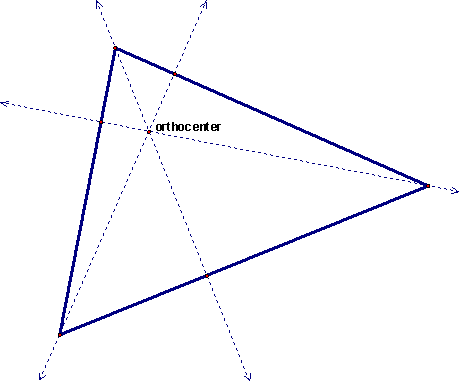 |
| Orthocenter - Right triangle | location will be on the triangle, 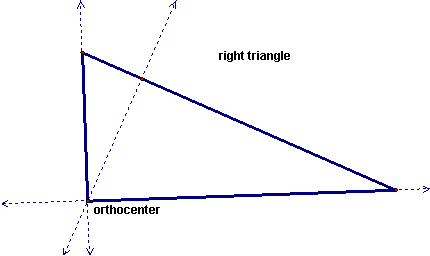 |
| Orthocenter - Obtuse triangle | location is outside the triangle |
| circumcenter2 | equidistant from the vertices; the center of a circle that is circumscribed around/about the vertices,  |
| incenter2 | equidistant to the sides of a triangle; the center of a circle inscribed about/around sides of a triangle, 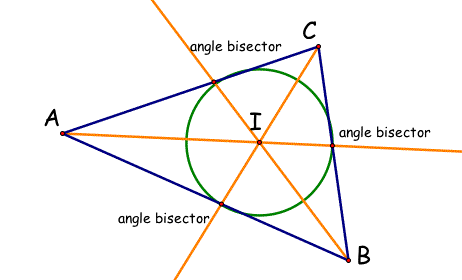 |
| centroid2 | 2/3 the distance from the vertex to the midpoint of the opposite side; 2:1 relationship, vertex to the centroid=2x, centroid to the side=x |