| A | B |
|---|
| Disproportionation | Is used to describe two particular types of chemical reaction, 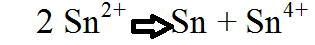 |
| Half Reaction | Either the oxidation or reduction reaction component of a redox reaction., 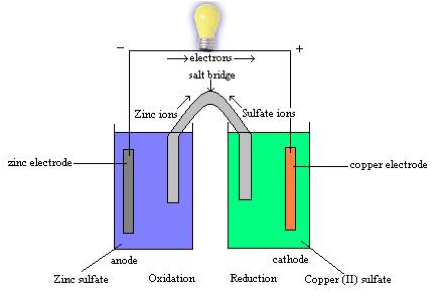 |
| Oxidation | Is the loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion., 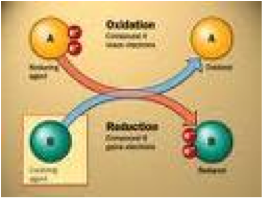 |
| Oxidation-reduction reaction | A reaction in which electrons are transferred from a donor (the reducing agent) to an acceptor molecule (the oxidizing agent)., 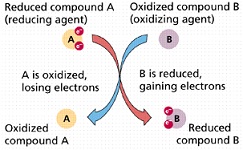 |
| Oxidized | To increase the positive charge or valence of (an element) by removing electrons.,  |
| Oxidizing Agent | Can be defined as either: a chemical compound that readily transfers oxygen atoms, or a substance that gains electrons in a redox chemical reaction In both cases, the oxidizing agent becomes reduced in the process., 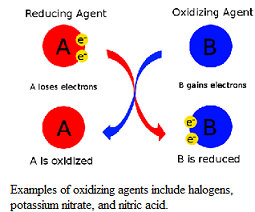 |
| Redox reaction | Any chemical reaction which involves oxidation and reduction, 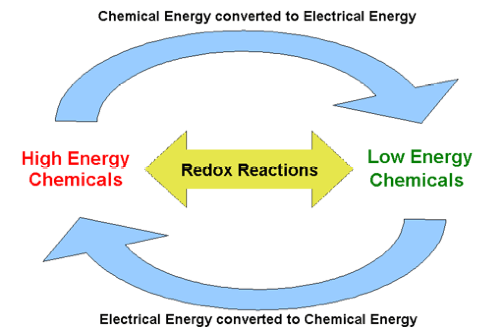 |
| Reduced | To decrease the valence of an atom by adding electrons., 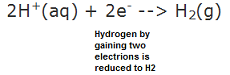 |
| Reducing agent | A substance capable of bringing about the reduction of another substance as it itself is oxidized, 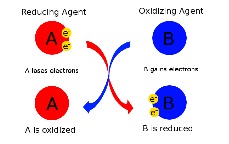 |
| Reduction | A decrease in positive valence or an increase in negative valence by the gaining of electrons., 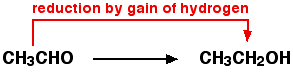 |