| A | B |
|---|
| Crystalline Solids | A solid material, whose constituent atoms, molecules, or ions are arranged in an orderly repeating pattern extending in all three spatial dimensions., 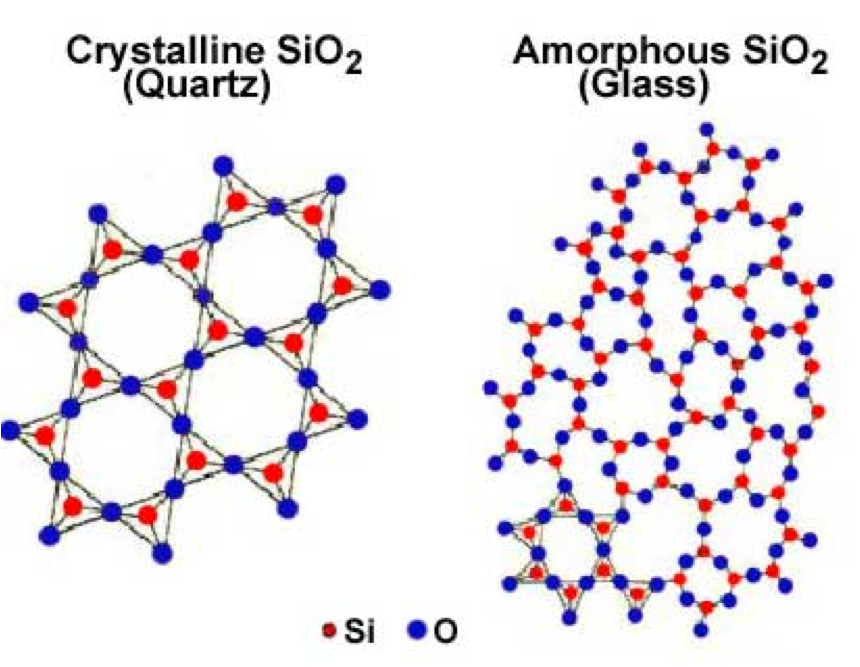 |
| Crystal | A solid formed by the solidification of a chemical and having a highly regular atomic structure.,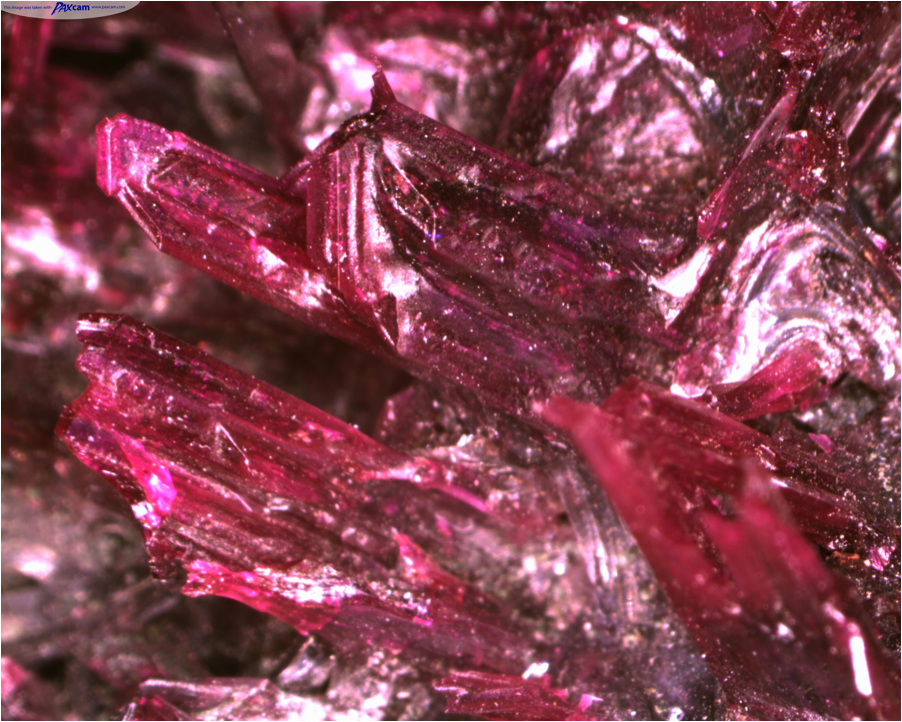  |
| Amorphous Solids | A solid which has a disordered atomic structure., 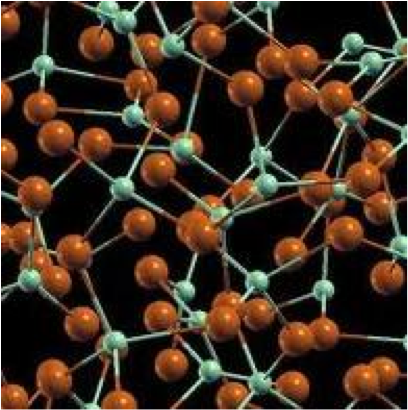 |
| Melting | To reduce to a liquid state by using warmth or heat.,  |
| Volatile Liquid | Is one which evaporates easily,  |
| Boiling | Is the rapid vaporization of a liquid, which occurs when a liquid is heated to its boiling point, the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid is equal to the pressure exerted on the liquid by the surrounding environmental pressure,  |
| Equilibrium | Is the condition of a system in which competing influences are balanced.,  |
| Equilibrium Vapor Pressure | The vapor pressure of a system in which two or more phases of water coexist., 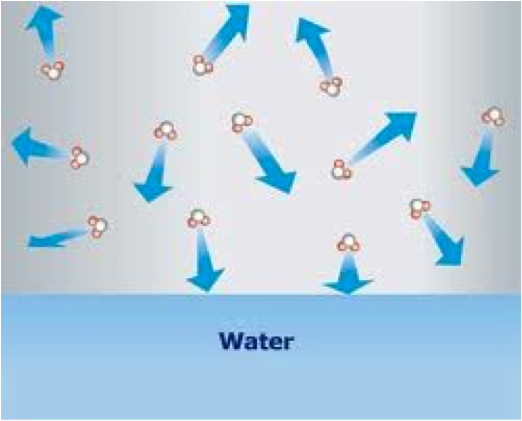 |
| Capillary Action | Surface tension that results in the elevation or depression of liquids in capillaries.,  |
| Vaporization | Transition of matter from a solid or liquid phase into a gaseous phase.,  |
| Boiling Point | Is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals the external pressure surrounding the liquid.,  |
| Molar Enthalpy of Vaporization | The amount of heat necessary to boil (or condense) 1.00 mole of a substance at its boiling point, 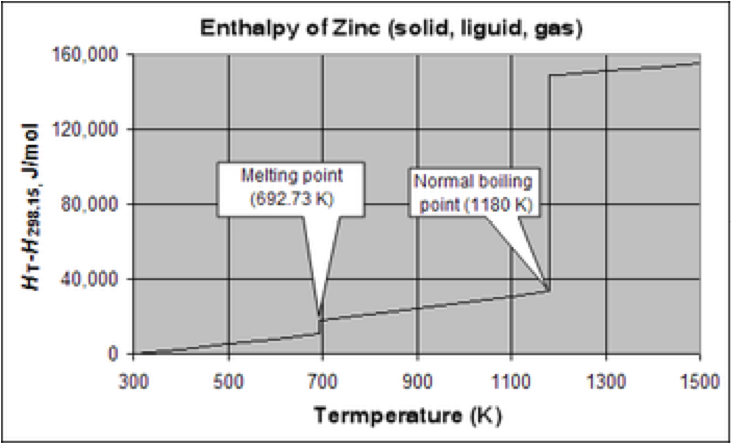 |
| Critical Pressure | The pressure of a pure element or compound at a critical point., 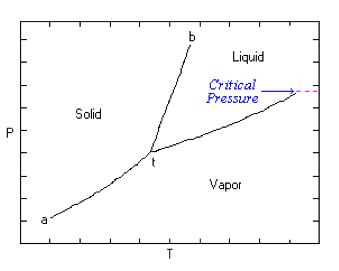 |
| Critical Point | The point at which a substance in one phase, as the liquid, has the same density, pressure, and temperature as in another phase, as the gaseous.,  |
| Critical Temperature | The temperature above which a gas cannot be liquefied, no matter how much pressure is applied., 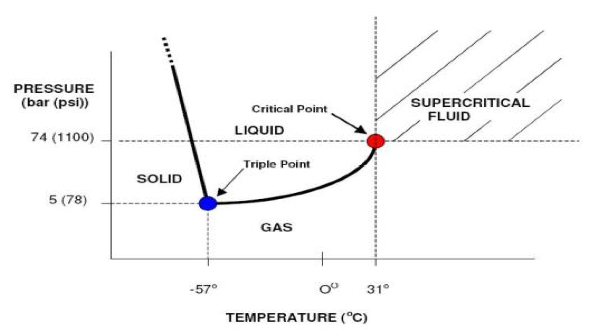 |
| Fluid | A state of matter, such as liquid or gas, in which the component particles (generally molecules) can move past one another. Fluids flow easily and conform to the shape of their containers.,  |
| Surface Tension | A property of liquids such that their surfaces behave like a thin, elastic film.,  |
| Phase | Any distinct time period in a sequence of events,  |
| Condensation | The process by which matter transitions from a gas (or vapor) phase into a liquid phase, 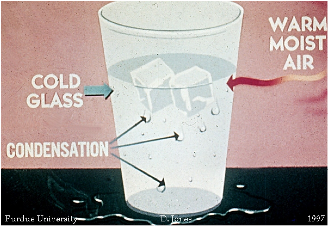 |
| Kinetic-Molecular Theory | The theory that gases are made up of a large number of small particles (atoms or molecules), all of which are in constant, random motion. .., 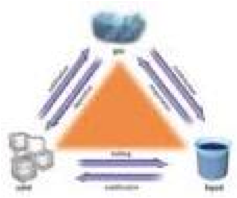 |
| Ideal Gas | A hypothetical gas with molecules of negligible size that exert no intermolecular forces, 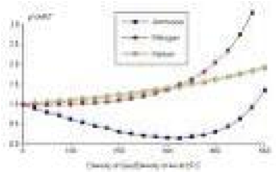 |