| A | B |
|---|
| Absolute Zero | The lowest temperature theoretically attainable, 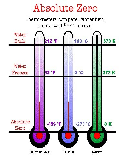 |
| Atmosphere of Pressure | The pressure exerted by the atmosphere at the earth's surface. It has an average value of 1 atmosphere,  |
| Avogadro's Law | The principle that equal volumes of all gases (given the same temperature and pressure) contain equal numbers of molecules, 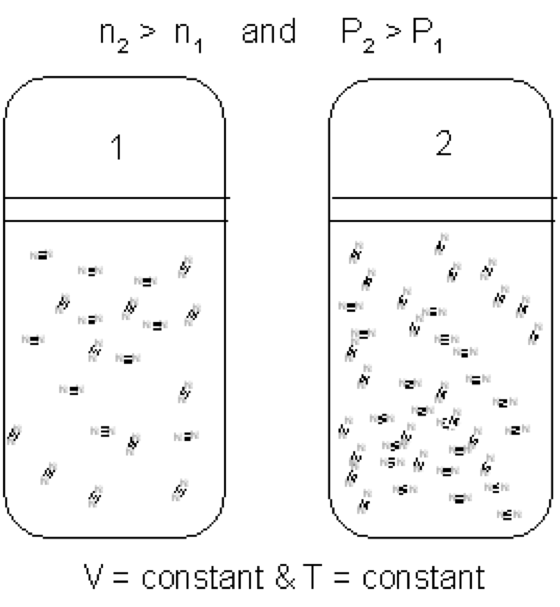 |
| Barometer | Any instrument that measures atmospheric pressure.,  |
| Boyle's Law | The principle that, for relatively low pressures, the pressure of an ideal gas kept at constant temperature varies inversely with the volume of the gas.,  |
| Charles's Law | (Also known as the law of volumes) Is an experimental gas law which describes how gases tend to expand when heated., 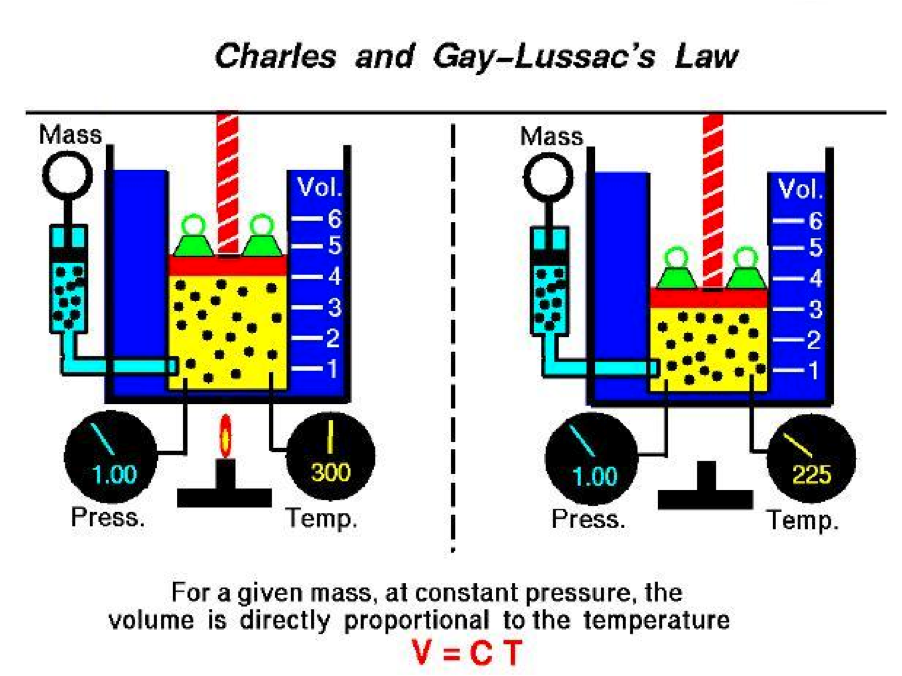 |
| Combined Gas Law | A combination of Boyle's law and Charles's law which states that the product of the volume and pressure of an ideal gas divided by its temperature is constant, 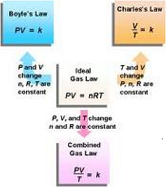 |
| Daltons Law of Partial Pressure | In chemistry and physics, Dalton's law (also called Dalton's law of partial pressures) states that the total pressure exerted by a gaseous mixture is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of each individual component in a gas mixture.,  |
| Gay-Lussac’s Law | The principle that gases react together in volumes (measured at the same temperature and pressure) that bear a simple ratio to each other and to the gaseous products. (also known as charle’s law), 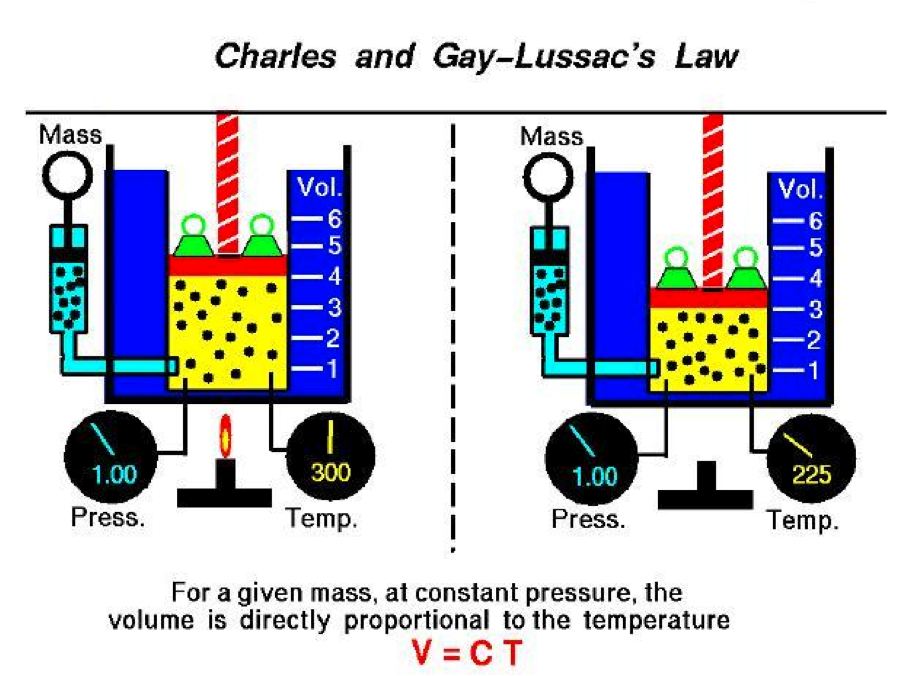 |
| Gay-Lussac’s Law of Combining Volume of a Gas | When gases react together to form other gases, and all volumes are measured at the same temperature and pressure:, 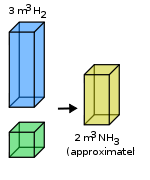 |
| Graham’s Law of Effusion | States that the rate of effusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its molecular weight., 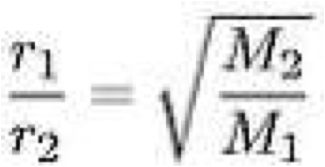 |
| Ideal Gas Constant | Is a physical constant which is featured in a large number of fundamental equations in physical sciences., 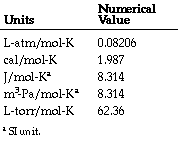 |
| Ideal Gas Law | As one in which all collisions between atoms or molecules are perfectly eleastic and in which there are no intermolecular attractive forces.,  |
| Millimeters of Mercury | A unit of pressure equal to 0.001316 atmosphere; named after Torricelli.,  |
| Newton | The Newton is the Standard International (SI) unit of force.,  |
| Partial Pressure | In a mixture of ideal gases, each gas has a partial pressure which is the pressure which the gas would have if it alone occupied the volume. The total pressure of a gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of each individual gas in the mixture., 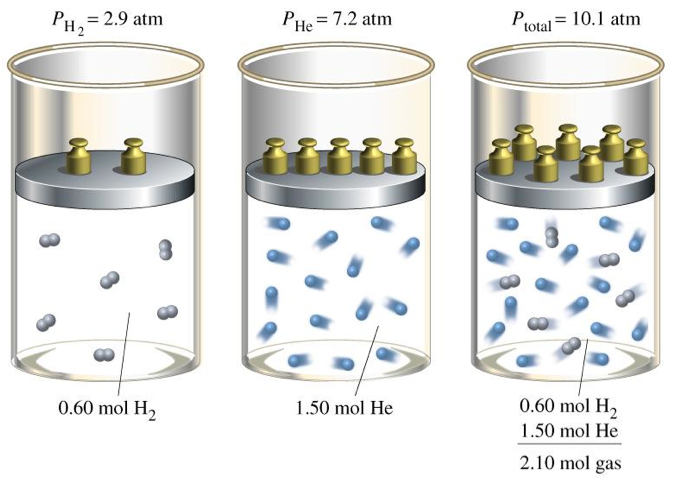 |
| Pascal | A unit of pressure equal to one newton per square meter,  |
| Pressure | Is defined as force per unit area., 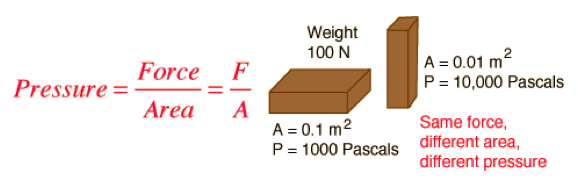 |
| Standard Molar Volume of Gas | 22.414 L at STP ("Standard temperature and pressure" of 273.15 K and 1 atm).,  |