| A | B |
|---|
| Electron Capture | Electron capture is a decay mode for isotopes that will occur when there are too many protons in the nucleus of an atom and insufficient energy to emit a positron; however, it continues to be a viable decay mode for radioactive isotopes that can decay by positron emission.,  |
| Parent Nuclide | In nuclear physics, a decay product (also known as a daughter product, daughter isotope or daughter nuclide) is the remaining nuclide left over from radioactive decay, 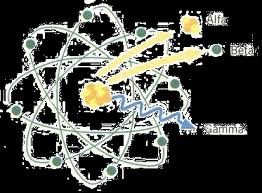 |
| Decay Series | In nuclear science, the decay chain refers to the radioactive decay of different discrete radioactive decay products as a chained series of transformations. ..., 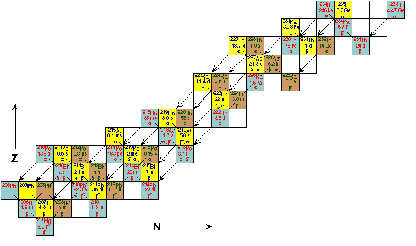 |
| Nuclear Reaction | Involves a change in the composition of a nucleus and can evolve or absorb an extraordinarily large amount of energy,  |
| Nuclear Fission | is a nuclear reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into smaller parts, 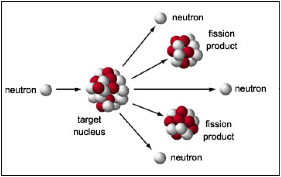 |
| Half-Life | Is the period of time it takes for a substance undergoing decay to decrease by half.,  |
| Radioactive Decay | Is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by emitting ionizing particles, 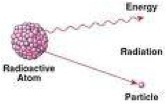 |
| Radioactive Nuclide | A nuclide that contains isotopes that decay and that emit radiation.,  |
| Radioactive Dating | Measurement of the amount of radioactive material (usually carbon 14) that an object contains; can be used to estimate the age of the object,  |
| Nuclear Shell Model | A model that represents nucleons as existing in different energy levels or shells in the nucleus.,  |
| Nuclear Radiation | The particles that are relased from the nucleus during radioactive decays, such as neutrons, electrons, and protons.,  |
| Transmutation | The alteration of one species into another.,  |
| Mass Defect | The difference between the mass of an atom and the um of the masses of the atom's protons, electrons, and neutrons., 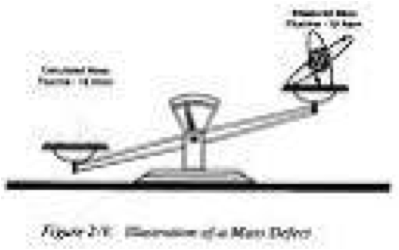 |
| Transuranium Element | The chemical elements with atomic numbers greater than 92,  |
| Nuclear Binding Energy | The difference between the total energy (= mc^2) of the bound nucleus, and the energies of the individual constituent particles (= sum of masses c^2).,  |
| Shielding | A radiation absorbing material that is used to decrease radiation leakage from nuclear reactors.,  |
| Film Badge | The film badge dosimeter, or film badge, is a dosimeter used for monitoring cumulative exposure to ionizing radiation. The badge consists of two parts: photographic film, and a holder. The film is removed and developed to measure exposure.,  |
| Critical Mass | The minimum mass of a particular fissionable nuclide in a given volume required to sustain a nuclear chain reaction.,  |
| Geiger-Miller Counter | The most commonly used portable radiation detection and measuring instrument,  |
| Rem | The quantity of ionizing radiation whose biological effect is equal to that produced by one roentgen of x-rays.,  |