| A | B |
|---|
| deposits found at the bottom of undisturbed pile of strata is older than the one above it | law of superposition |
| sequential order of events, you don't know specific age/time of events | relative dating |
| rocks are deposited in horizontal layers unless disturbed by an outside force | law of original horizonality |
| geologic processes of today are same as in past, and will be same in future | law of uniformitarianism |
| geologist who proposed idea of uniformitarianism | Hutton |
| evidence of life preserves in a rock, at least 10,000 years old | fossil |
| rate at which a radioactive element decays is called its …. | half-life |
| igneous intrusions are younger than the layers they intrude | law of cross cutting relationships |
| you know the numerical age of rocks/objects | absolute dating |
| a gap in the geologic record | unconformity |
| bone, shell, pollen grains are what type of fossil | fossil remains of a living thing |
| worm burrow, footprints, leafprints are what type of fossil | fossil evidence |
| soft parts of organisms do not usually form fossils because they undergo | decay |
| dinosaur footprint is what type of fossil | trace fossil |
| empty space left in rock that clearly represents shape/size of organism | mold |
| in order to form a fossil, how should an organism be treated | be buried quickly in sediment |
| whole insects like wasps, mosquitoes are often found preserved in what substance | amber |
| Whole organisms have been found in La Brea Pits trapped in what substance | tar |
| whole organisms have been found frozen in Siberia trapped in what substance | ice |
| as sediments are deposited in layers, they are usually deposited in what orientation | horizontally |
| this law helps a geologist decide relative age of a sedimentary rock | law of superposition |
| technique used to date age of recently fossilized living things | carbon 14 dating |
| In radioactive dating, we measure the amount of the decay element; age of object can be learned from the … | half-life |
| changes in rocks after deposition | unconformity |
| an intrusion is older or younger than the rock layers through which it passes | younger |
| another term for preserved body of an organism (not fossil) | original remains |
| region with sinkholes, caves, caverns has what type of topography | karst |
| Mineral resources in VA are used for | construction of roads, buildings, gravel, cement |
| why cities like Richmond, Fredericksburg, Alexandria are located on rivers where they are | fall line |
where the Coastal Plain meets the Piedmont, 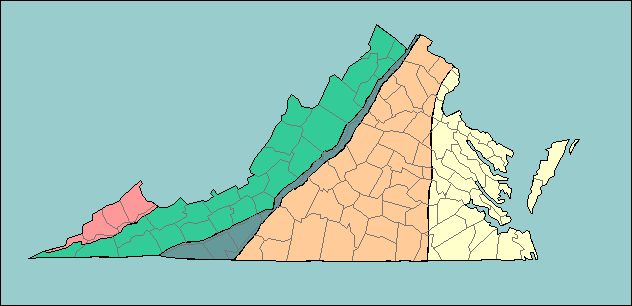 | fall line |
Western Henrico County where we live is located in what region, 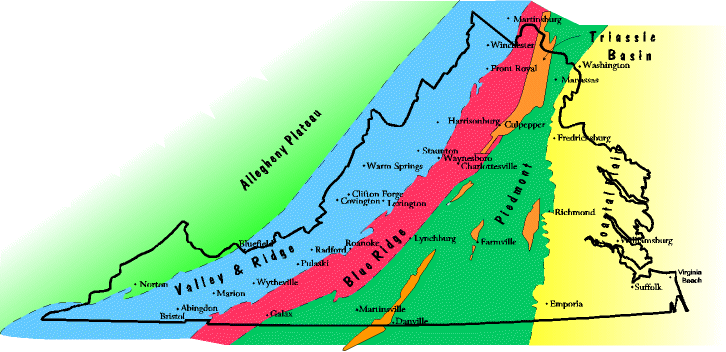 | Piedmont |
this region of VA represents the lowest, flattest regions of the state, made of sediments from eroded mountains,  | Coastal Plain |
2 regions of VA that are mountainous,  | Blue Ridge, Valley and Ridge |
These two regions of VA meet to form the Fall Line,  | Coastal Plain, Piedmont |
| Dinosaurs lived during this era | Mesozoic |
| We live in this era | Cenozoic |
| Horses evolved during this period | Tertiary |
| We live in this period | Quaternary |
| This is the oldest era | PreCambrian |
| The largest division of geologic time is | Epoch |
| a break or crack in earth's surface along which there is movement is called | fault |
| most earthquakes occur where | along plate boundaries/edges |
| An earthquake that registers 2.6 on the Richter Scale is how severe? | mild |
| large ocean waves caused by an earthquake are called | tsunami |
| breaking of rocks in the crust due to buildup of pressure are called | earthquakes |
| a bend in a layer of rock is called | folding |
| The San Andreas Fault is an example of this type of fault | lateral fault |
| The scale used to measure the strength of an earthquake | Richter Scale |
| Faults and earthquakes are studied by this type of scientist | seismologist |
| number of seismic stations required to locate an earthquake's epicenter | three |
| method used to locate an earthquake's epicenter using information from three stations | triangulation |
| if a rock fractures and then moves, it is called | fault |
center of earthquake below ground is called, 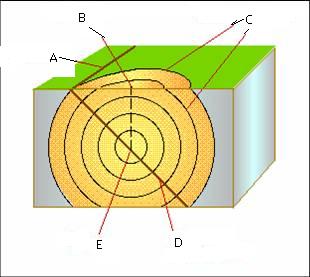 | focus |
point on surface of earth directly above focus of earthquake,  | epicenter |
Name from oldest to youngest,  | D, C, B, A, F, E |