| A | B |
|---|
| Weathering | The breakdown of rocks into smaller fragments. |
| Types of weathering | 1- mechanical 2- chemical 3- biological |
| Mechanical weathering | Rocks break apart without changing their composition -- just become smaller rocks |
| Chemical weathering | Chemical composition of the rock is changed and a new substance is formed. |
| Biological weathering | Changes in rocks that are caused by the activities if living organisms. |
| Agents of mechanical weathering | Frost wedging, gravity, abrasion |
| Agents of chemical weathering | Acid rain, acids in living things, oxygen in the air and iron from pollution in the air make a process called oxidation causing rust |
| Agents of biological weathering | Plants and roots expanding cracks in rocks, animal digging and exposing more of the rock to weathering |
| Does more water in the air make weathering faster or slower? | The more water the FASTER the weathering. |
| In what climates does weathering happen faster? | Weathering is FASTER in HOT, WET climates. |
| In what climates does weathering happen slowly? | Weathering is SLOW in HOT, DRY climates. |
| The more surface of a rock that is exposed, the --------- the rock will weather. | The MORE surface of a rock that is exposed, the FASTER the rock will weather. |
| Give an example of a rock that weathers slowly. | Quartz weathers slowly. |
| Give TWO examples of rocks that weather quickly. | Rocks with Iron and Calcite weather quickly. |
| How is acid rain formed? | Acid rain is made when pollutants in the the atmosphere mix with rain. |
| What is erosion? | Erosion is the process of moving sediment by wind, water, ice, or gravity. |
| Erosion agents are... | Gravity, glaciers, wind, water, and people are all erosion agents...things that can cause erosion. |
| Surface area is... | the amount of rock that is exposed to weather. |
| Where does frost wedging occur? | Frost wedging occurs in areas where there is water and the temperatures are around the freezing point. |
| What is biological weathering by plants? | Biological weathering by plants is is when roots grow into cracks in a rock. |
| Root wedging | When plants grow in cracks in rocks and then they add pressure to the rock and make it split or break apart.,  |
| What is biological weathering by animals? | Biological weathering by animals is caused when animals dig into the soil or burrow underground. The create pockets for water to move further underground, causing weathering to happen faster than it normally would.,  |
| Exfoliation | Exfoliation is a weathering process that is causes rock layers to peel away. |
| Wind as a mechanical weathering agent... | Wind-blown sand or other particles chip away tiny bits of rock from the surface of exposed rock. This leaves rock with unusual shapes.,  |
| What kind of plants cause chemical weathering? | Moss, lichens, and other plants cause CHEMICAL weathering. |
| What moves sediment? | Running or flowing water moves sediment. |
| River | A river is a large, flowing body of water. |
| Stream | A stream is a small river. |
| Channel | The path that a river or stream follows is called a channel. |
| Where does sediment that is carried by running water end up? | Due to gravity, sediment carried by running water ends up at the lowest place it can reach, like a beach. Then the sediment is carried into the ocean water by the waves. |
| Where will weathering happen faster: in a tropical rainforest or in a dry desert? | Weathering happens faster in HOT, WET places, so weathering will happen faster in a tropical rainforest. |
| Name the factors that affect how fast a rock might weather. | Water, climate, plants, animals, minerals, and the amount of surface area all affect how fast a rock weathers. |
| What is deposition? | Deposition is the process of depositing sediment after it has been moved by water, wind, ice, or gravity. |
| Which moves a rock faster: fast-moving water or slow-moving water? | Fast-moving water can move big pieces of rock. Slow-moving water can only move tiny pieces of sediment. |
| How is sediment sorted by water. | When running water slows down, the pieces of rock and sediment being carried settle. First the largest pieces settle to the bottom, then the medium sized pieces, and then the smallest particles. So, the heaviest settle further down on the bottom and the lighter particles are on the top. |
| Graded bedding | At the bottom of a river, graded bedding is the way sediment settles -- large pieces on the bottom, medium sized pieces next, and then the smallest particles on the top., 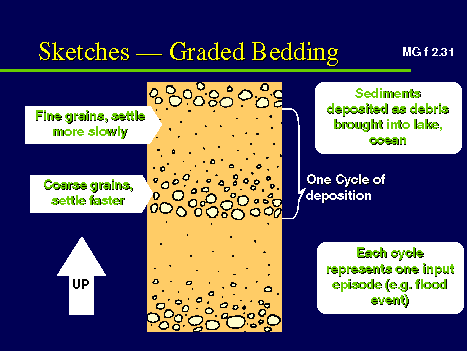 |
| Direction of younging | The order in which sedimentary rock layers are formed, from larger to finer particles. |
| Cross bedding | A pattern of alternating beds of sediment that often form as wind and water deposit the sediments. |
| U-shaped glacial valley | Valleys made when glaciers scraped through land areas.,  |
| Rock flour | The fine powder that results from abrasion by glaciers. Rock flour makes the water look tourquoise.,  |
| Glaciers | Formed by the accumulation of snow over hundreds or thousands of years. |
| Give an example of evidence of glaciers in the United States thousands of years ago. | Evidence of glaciers in the US is found in the rocky soil in New England.,  |
| Mass wasting | The downhill movement of large amounts of rock and sediment due to the force of gravity. |
| Landslide | A large mass of soil or rock that slides down a volcano or mountain.,  |
| Rockfall | An event that results in a large amount of rock splitting off a landform. |
| Examples of wind erosion | Desert pavement and Loess are examples of wind moving particles of sediment from one place to another.,  |
| Mudflow | When a large amount of rock, sediment, plant material, and water flows down a mountain.,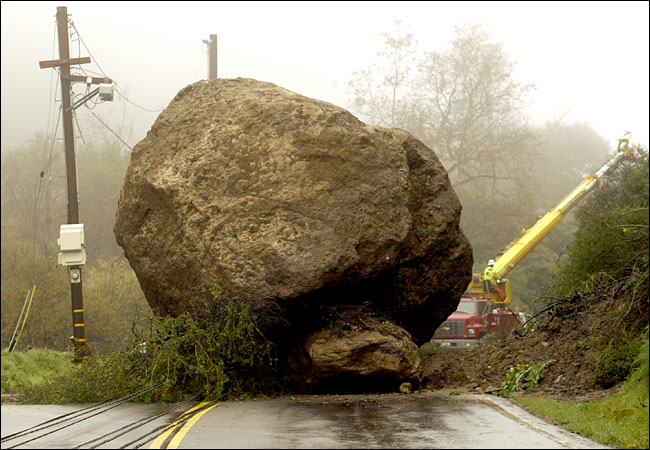  |
| Slumping | When soil particles become surrounded by water so that the ground slides or "slumps.", 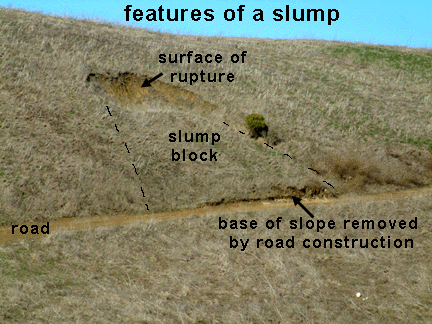 |
| Floodplain | Flat land alongside a river that often floods. |
| Meanders | S-shaped curves in a river,  |
| Braided stream | A stream that has many channels that criss-cross each other.,  |
| What makes a river meander? | Water flows at different speeds. The fastest flow is on the outside of each curve and the slowest flow is on the inside. Fast flowing water picks up particles and the slow-moving water drops the particles. |
| River valley | A river valley is created when rivers carve into mountains. |
| V-shaped valley | A valley formed by a river, not a glacier.,  |