| A | B |
|---|
| Evolution History | A timeline of major evolutioists that have change over time.,  |
| Geologic Time | The period of time covering the formation and development of the Earth, from about 4.6 billion years ago to today., 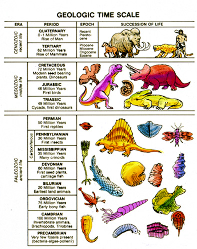 |
| Natural Selection | The process by which organisms that are better suited to their environment than others produce more offspring.,  |
| Extinction | A progressive decrease in the strength of a conditioned response, often resulting in its elimination, because of withdrawal of a specific stimulus.,  |
| Adaptation | A change in structure, function, or behavior by which a species or individual improves its chance of survival in a specific environment.,  |
| Homologous | Similar in structure and evolutionary origin but having different functions, as a human's arm and a seal's flipper., 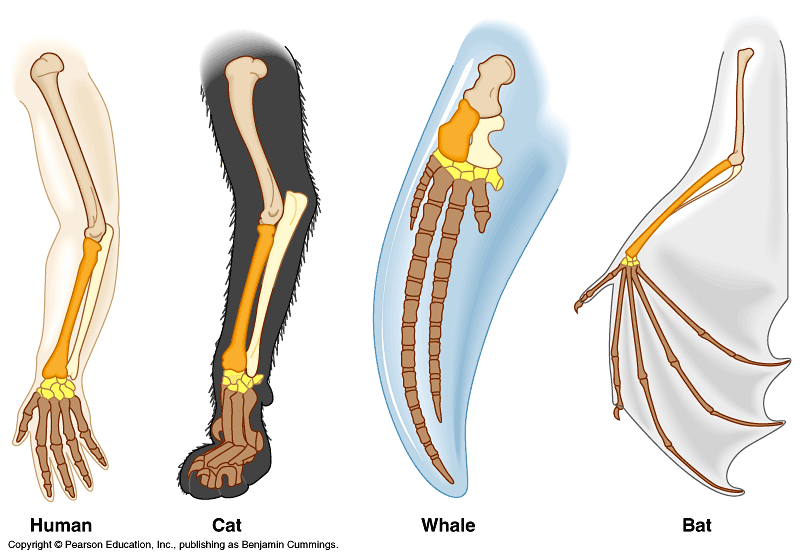 |
| Analogous | Similar in function but having different evolutionary origins, as the wings of a butterfly and the wings of a bird.,  |
| Phylogenic Tree | A tress also known as a phylogeny, is a diagram that depicts that line of evolutionary descent of different species, organisms, or genes from a common ancestor., 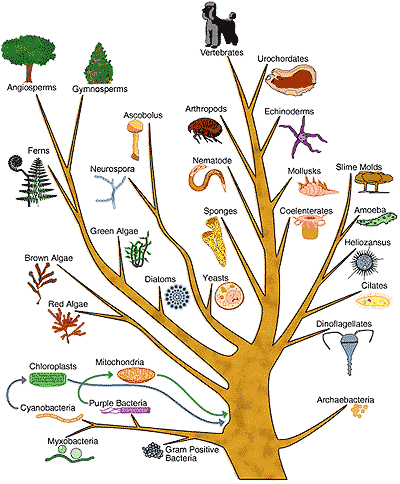 |
| Taxonomy | The scientific classification of organisms into specially named groups based either on shared characteristics or on evolutionary relationships as inferred from the fossil record or established by genetic analysis., 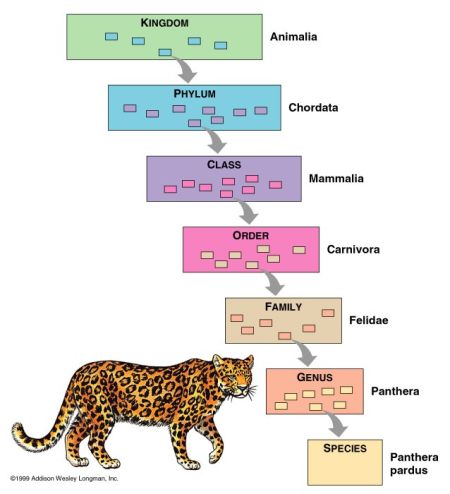 |
| Kingdom | The highest classification into which living organisms are grouped in Linnean taxonomy, ranking above a phylum., 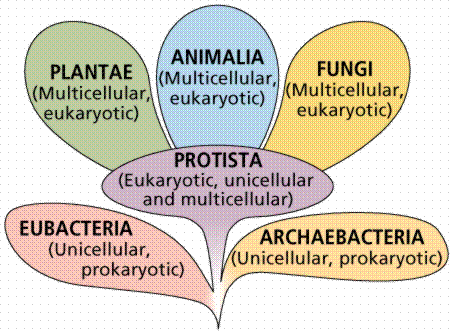 |
| Phylum | A group of organisms ranking above a class and below a kingdom.,  |
| Class | A taxonomic category of organisms ranking above an order and below a phylum or division., 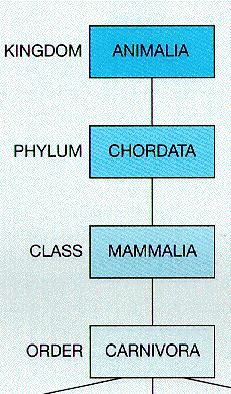 |
| Order | A group of organisms ranking above a family and below a class., 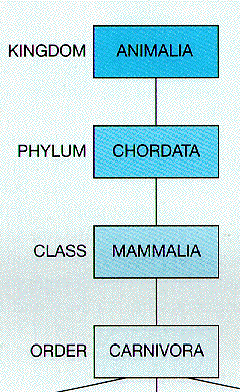 |
| Genus | A group of organisms ranking above a species and below a family., 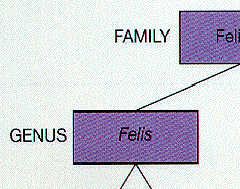 |
| Species | A group of organisms having many characteristics in common and ranking below a genus.,  |