| A | B |
|---|
popular sovereignty,  | The people vote to decide the issue of slavery (like in Kansas-Nebraska) |
Uncle Tom's Cabin,  | Book about slavery that convinced people in the North that it was wrong |
Compromise of 1850, 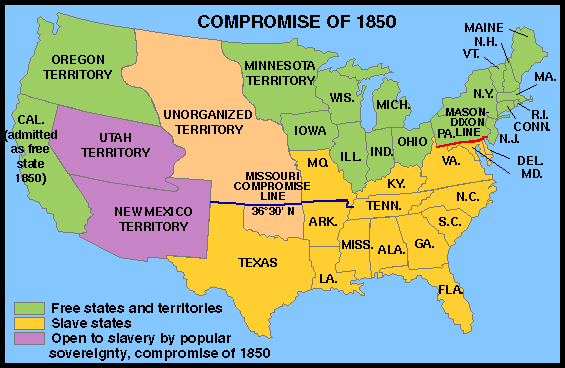 | Admitted California as a free state and included a new Fugitive Slave Act. |
Spoils System,  | The practice of hiring your supporters for government jobs |
Kansas-Nebraska Act, 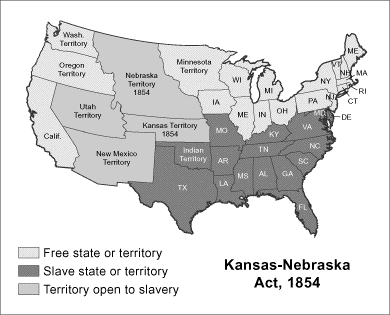 | Law that said slavery would be decided by popular sovereignty and led to violence (Bleeding Kansas) |
Mexican War, 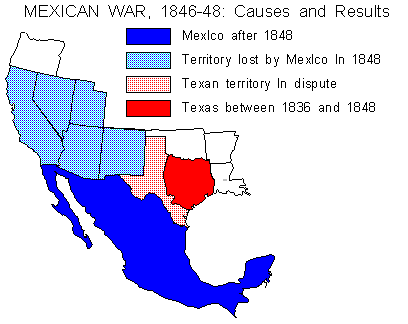 | War over Texas and Manifest Destiny that created problems over slavery in the new lands |
Kitchen Cabinet,  | Jackson's advisors that became a precedent for the EOP |
John Brown's Raid,  | Tried to lead a slave revolt spreading fear in the South |
The Bank War,  | Jackson destroyed the National Bank by vetoing it and then taking the money out leading to a depression |
Nullification,  | The belief that a state can ignore or cancel a law it does not agree with |
Indian Removal,  | Jackson forced Indians to move west of the Mississippi River leading to the death of thousands |
Nullification Crisis over tariffs,  | Jackson forced South Carolina to pay the tariff by threatening to use the military |
tariff,  | A tax on imports |
Andrew Jackson,  | President that increased power and scared conservatives |
Conservatives,  | Believed the states and the people should have the power |
Liberals,  | Wanted the national government to have the power |
Election of 1824,  | Election that led to two new parties and universal white male suffrage |
suffrage,  | The right to vote |
reform movement,  | People work together to fix a problem |
Second Great Awakening,  | Movement that made people believe they could do good things and go to heaven leading to reform |
| money | The reason the first settlers came to the South |
| religion | The reason the first settlers came to the North |
| environment | The reason both the North and the South developed their economies |
| Senate | Part of the United States Congress based on equal representation |
| House of Representatives | Part of the U.S. Congress based on population |
Industrial Revolution,  | A total change in the way things were made |
urbanization,  | People moved to cities in the North during the Industrial Revolution increasing population and power |
immigration,  | People came from other countries during the Industrial Revolution increasing population and power |
| power | Main cause of the Civil War - the South wanted the states to have it and the North wanted the National government to have it. |
| slavery | Main cause of the Civil War: the South needed it and the North was against it |
| Abolitionist Movement | The movement to end slavery |
canals, 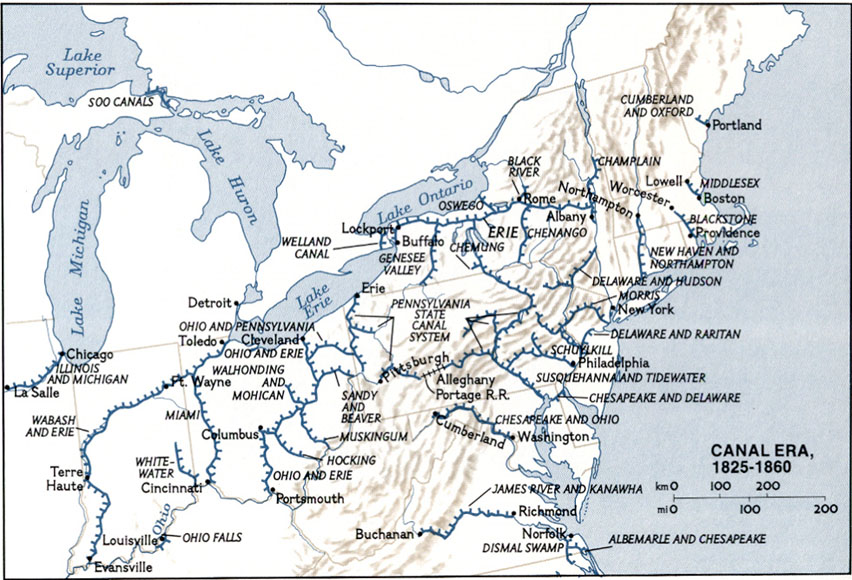 | Man made waterways that connected the North and the West |
railroads, 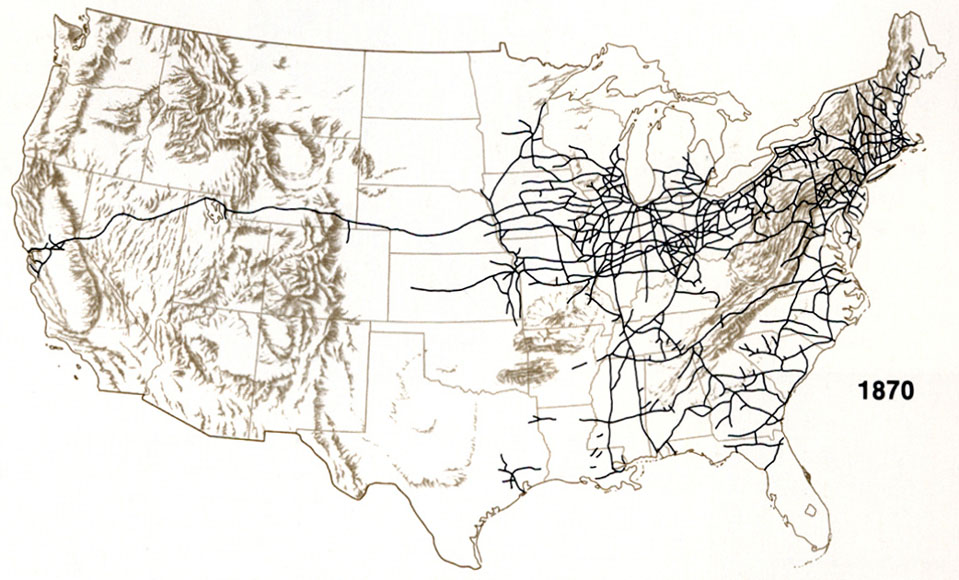 | Tracks for trains that connected places on ground especially in the North and West |
Erie Canal, 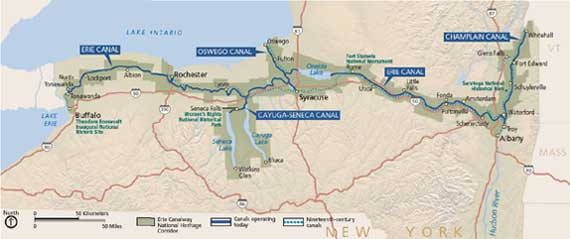 | Waterway that connected the West to the North and made New York the most important city |
cotton gin,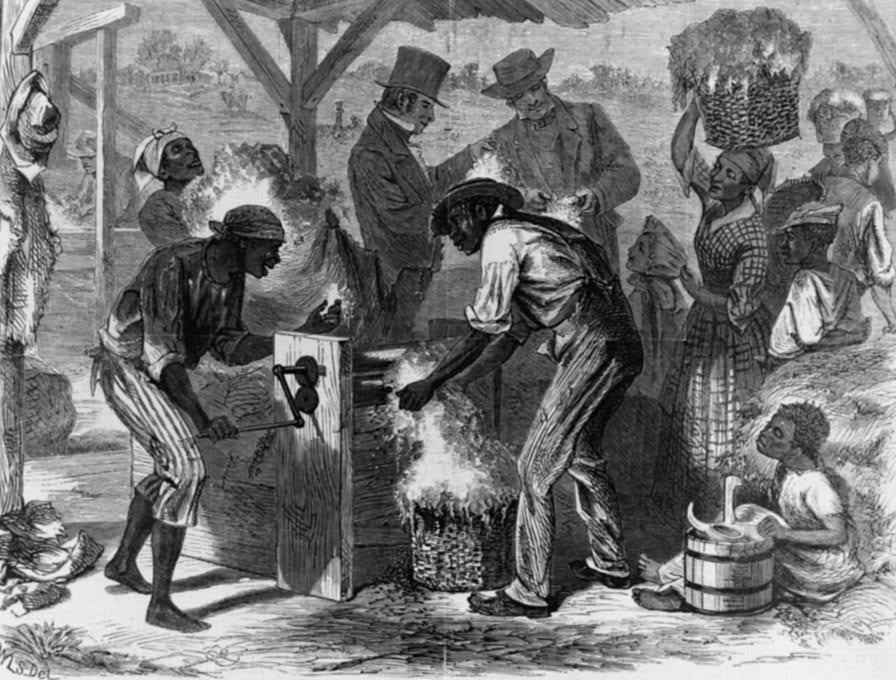  | Made harvesting cotton easier and increased the demand for slaves |
Planters (Cottonocracy),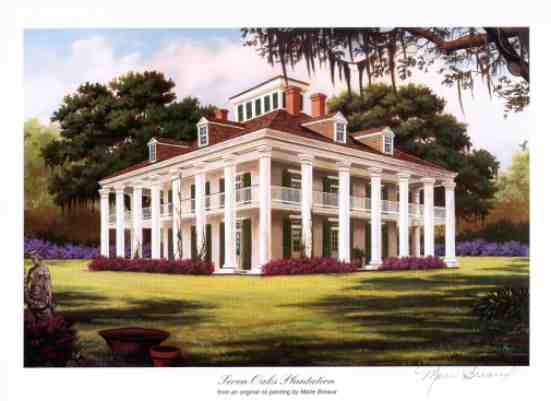  | Only 3 percent of the southern population but they owned most of the slaves and had most of the money and power |
| slave codes | Laws that limited the rights of enslaved Africans in the South |
| Nat Turner | Slave that led a violent revolt causing fear and harsher slave codes |
Underground Railroad, 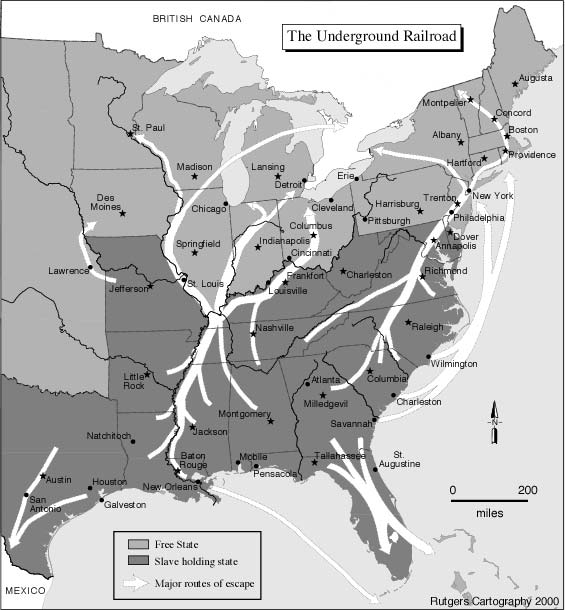 | System of people, houses, barns, etc that helped slaves escape to freedom |
Liberator,  | William Lloyd Garrison's anti-slavery newspaper |
Declaration of Independence,  | Document that led states in the North to outlaw slavery |
| politics and religion | The causes of reform |
Election of 1860, 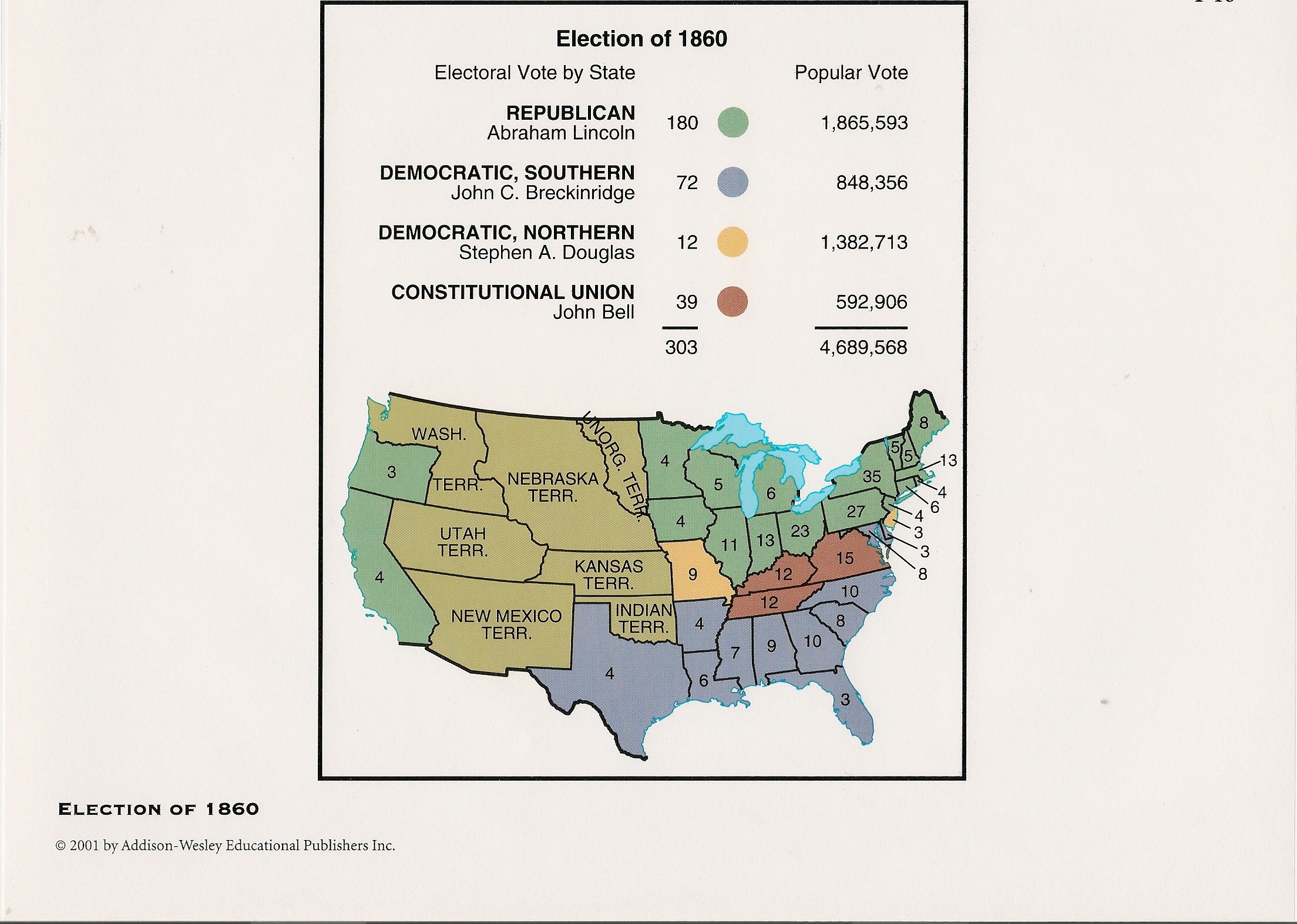 | Lincoln won the North and the West because the Democrats were split leading to secession |
secede (and secession), 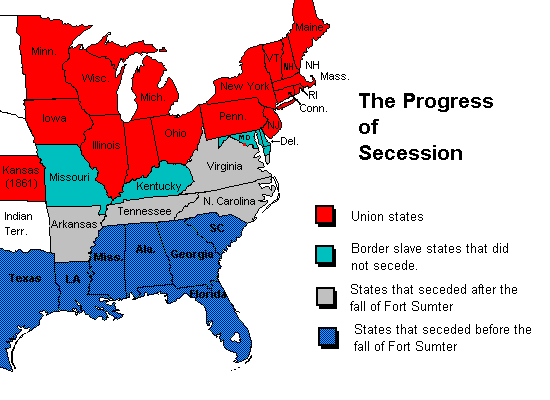 | To leave or break away like South Carolina did in 1860 |
Confederate States of America,  | The new nation formed by the South after secession |
Jacksonian Democracy,  | A new era where more people could vote and politicians did what the people wanted |
Manifest Destiny,  | The belief that the U.S. had the right and duty to expand to the Pacific Ocean (causing the Mexican War) |
Fugitive Slave Law (or Act),  | Law that demanded people help capture and return slaves |
Dred Scott v. Sandford, 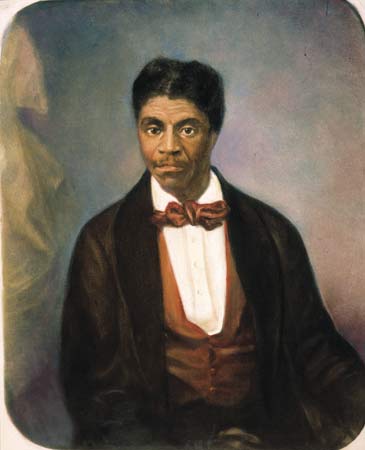 | Case where the Supreme Court ruled slaves had no rights and Congress had no right to outlaw slavery |
McCulloch v. Maryland,  | Case that gave the national government power (supremacy) over the states |
Gibbons v. Ogden, 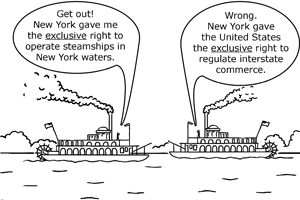 | Case that gave the national government power over interstate commerce |
interstate commerce,  | Trade or business between states |
Southern Social Structure, 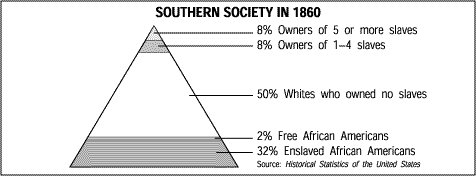 | Most southerners supported slavery even though they didn't own slaves |
Missouri Compromise, 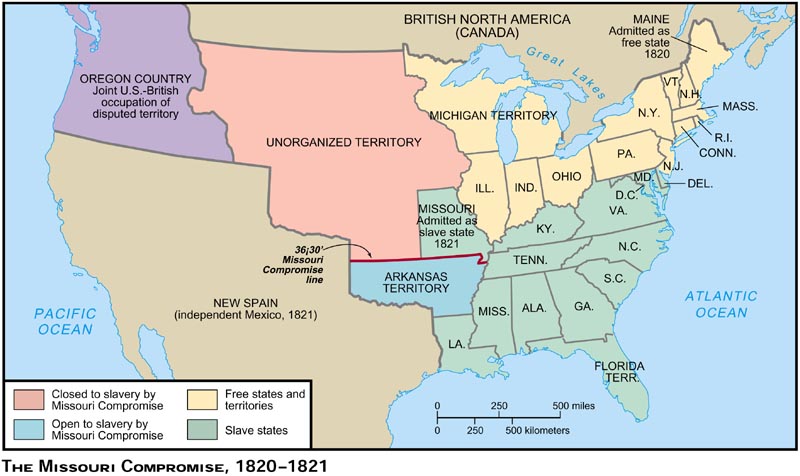 | Plan to keep the slave and free states equal in the Senate while drawing a line separating free and slave territory |
| Era of Good Feelings | A period where sectionalism replaced party fighting |
Monroe Doctrine,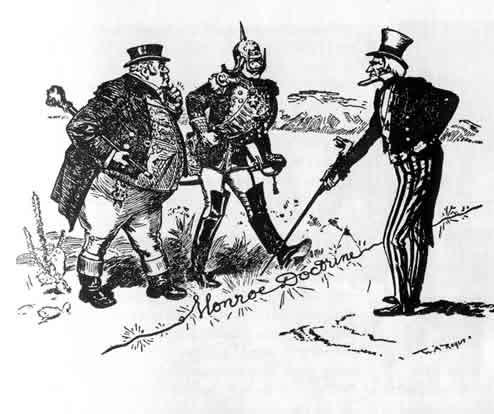  | Announcement that the U.S. would not allow any nations to take land in America allowing the U.S. to become a power |
| National Bank and tariff | Plan to fix the economy during the Era of Good Feelings leading to more sectionalism |
Trail of Tears,  | Jackson ignored the Supreme Court and Cherokees were forced to move off of their lands. 15,000 died during the journey. |
California,  | Gold was discovered and they applied to be a free state causing a huge debate over slavery |
Fort Sumter,  | The first battle of the Civil War happened because the Confederates tried to seize all forts |
sectionalism,  | Loyalty to a region or state instead of the nation |
Charles Sumner,  | Senator who was beaten almost to death by a Congressman over the slavery debate |
Bleeding Kansas,  | The violence that was a result of the Kansas-Nebraska Act (showing the failure of popular sovereignty) |
Abraham Lincoln,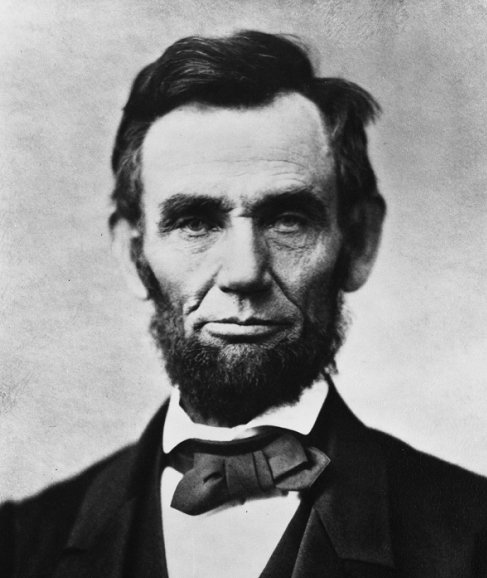  | Republican who was elected president in 1860 causing the South to secede |
Frederick Douglass,  | Runaway slave who spoke out against slavery and became one of the most important abolitionists |
Harriet Tubman,  | Runaway slave who became a conductor on the Underground Railroad and helped many slaves escape |
| Dred Scott | Slave who sued for freedom |
| John Brown | Killed people in Bleeding Kansas and tried to lead a slave revolt in Virginia |