| A | B |
|---|
| This class of drug increases the force of contraction and slows the heart rate so is effective for CHF and atrial fibrillation | Cardiac glycosides |
| This drug is considered a positive inotrope and a negative chronotrope | Cardiac glycosides |
| Due to its inotropic effect, this drug will increase cardiac output and improve kidney perfusion | Cardiac glycosides |
| Too little of this electrolyte may predispose to digixin toxicity | Potassium |
| What these symptoms indicate: anorexia, nausea, bradycardia, visual disturbances | Digoxin toxicity |
| The normal digoxin level | 0.5-2.0 |
| These drugs treat angina by dilating coronary arteries and decrease cardiac workload and 02 demand by relaxing peripheral veins and arterioles | Nitrates |
| This drug is mainly used as an antianginal, but is an adjunct for CHF and hypertension | Nitrates |
| A drug that reduces venous return will _____ preload | Decrease |
| A drug that decreases peripheral vascular resistance is said to ______ afterload | Decrease |
| Antihypertensives will have what effect on afterload? | Decreased |
| This drug is often given sublingual, but is also available in oral, topical and IV forms. | Nitrates |
| How many doses of SL Nitro may be given? | 3 doses 5 minutes apart |
| Headache and hypotension are common side effects of this drug | Nitrates |
| Beta blockers may be classified as having these 3 effects | Antianginal, antidysrhythmic, and antihypertensive |
| These drugs decrease the effects of the SNS by blocking the release of catecholamines so will decrease HR and BP | Beta blockers |
| The desired effect of beta blockers is to block which receptor? | Beta 1 |
| Why are beta blockers used with caution in asthma patients? | Blockage of beta 2 receptors causes bronchoconstriction |
| Instruct patients to rise slowly with these meds | Antihypertensives |
| Calcium channel blockers have these 3 effects | Antianginal, antidysrhythmic, antihypertensive |
| This drug slows conduction through the AV node, relaxes coronary arteries, decreases contractility and workload,and relaxes smooth muscle so will decrease HR and BP and decrease chest pain | Calcium channel blockers |
| Monitor HR and BP before these meds | Beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, alpha adrenergic blockers |
| These drugs stimulate alpha 2 receptors to decrease SNS activity and decrease catecholamines | Alpha 2 agonists |
| Blocking stimulation of alpha 1 receptors in the vasculature will result in _______ | Vasodilation |
| These drugs may decrease LDL and increase HDL | Alpha adrenergic blockers |
| ACE Inhibitors are classified as this | Antihypertensives |
| These drugs block the release of aldosterone resulting in sodium and water excretion and K retention. They also cause vasodilation. | ACE Inhibitors |
| This drug may be accompanied by hyperkalemia | ACE Inhibitors |
| These drugs act on the distal tubule to excrete sodium, chloride and water | Thiazide diuretics |
| These drugs act on the ascending Loop of Henle | Loop diuretics |
| These drugs may result in hypokalemia | Thiazide and loop diuretics |
| The normal K level | 3.5-5.0 mEq/L |
| The "olols" | Beta blockers |
| The "prils" | ACE Inhibitors |
| Often prescribed for patients on thiazide or loop diuretics | K supplement |
| Potassium rich diet advised for patients on which meds? | Digoxin, Thiazide and Loop diuretics |
| Watch for hypotension and dizziness with which meds? | All antihypertensives |
| This drug inhibits the sodium-potassium pump which increases intracellular colcium and causes cardiac muscle fibers to contract more efficiently | Cardiac glycosides |
| Avoid getting this medication on your fingers | Nitroglycerin |
| Not first line treatment for hypertension- often used with diuretics, calcium channel blockers, or ACE Inhibitors | Alpha drugs |
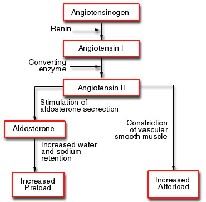 | Renin angiotensin aldosterone,  |