| A | B |
|---|
Articles of Confederation,  | The First Government of the United States where the states were stronger than the national government. It was too weak! |
Shays' Rebellion,  | Uprising in Massachusetts that showed how weak the Articles of Confederation was |
Constitutional Convention,  | Meeting called to revise the Articles of Confederation. They quickly decided to make a new government! |
Virginia Plan,  | The plan at the Constitutional Convention that gave power to the big states |
New Jersey Plan,  | Plan at the Constitutional Convention that gave power to the small states |
Great Compromise,  | Created a 2 house (bicameral) legislature. One house was based on population (for the big states) and the other was based on equal representation (for the small states) |
3/5's Compromise, 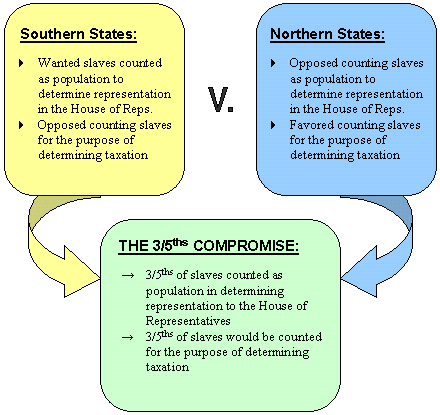 | Decision at the Constitutional Convention to count slaves as 3/5's of a person for population and taxes |
| Federal Representative Democracy | The type of government that the United States has! |
Federalists,  | People who were for the new Constitution and national government power |
Anti-Federalists,  | People who were against the new government and afraid of government power (because of the British) |
Bill of Rights,  | The Federalists agreed to include this list of freedoms. The anti-federalists agreed to ratify the Constitution because of this! |
| ratify | accept |
| precedent | example for others to follow |
| Federalist Papers | Arguments for the Constitution that were published in papers across the nation. |
Neutral,  | Not to take a side (Washington's Foreign Policy) |
Whiskey Rebellion,  | Washington stopped this; showing power and mercy |
| Hamilton's Plan | Pay all debt, a National Bank, and a tariff |
| Washington's precedents | 2 terms, cabinet, and neutrality |
| Federalists and Democratic Republicans | First two parties. Created because of arguments over power and Hamilton's Plan |
Alien and Sedition Acts,  | Laws passed so the Federalists could keep power |
Kentucky and Virginia Resolutions,  | Jefferson and Madison said the states had the right to ignore or cancel national government laws |
states' rights,  | The belief that states should have rights and powers not listed in the Constitution |
Embargo Act,  | Law that stopped all foreign trade |
Impressment,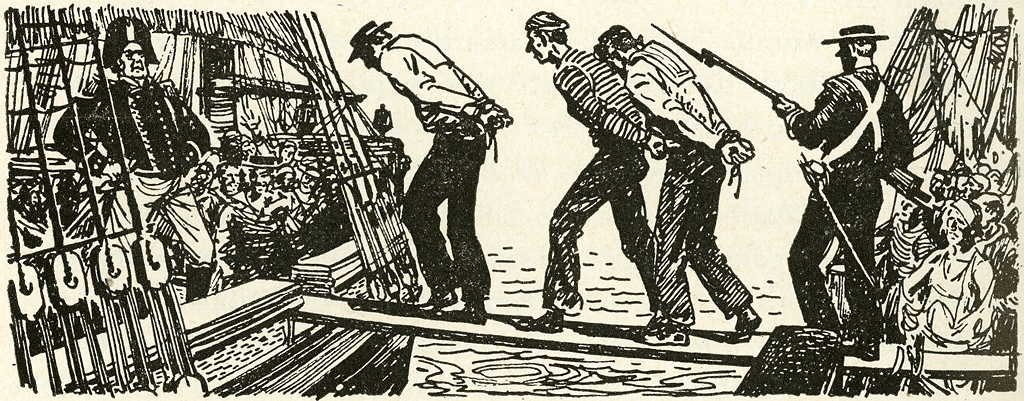  | Capturing sailors and forcing them to work |
judicial review,  | Courts rule acts of government unconstitutional |
Marbury v. Madison,  | Case that set precedent for judicial review |
Louisiana Purchase, 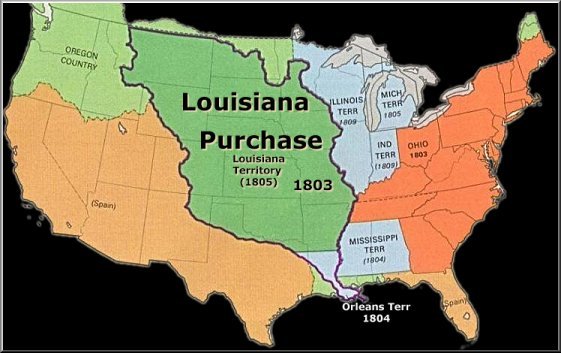 | Land bought from France that doubled the size of the U.S., caused problems over slavery, and increased the president's power |
Lewis and Clark,  | Led and expedition through Louisiana to the Pacific Ocean |
| John Marshall | Liberal Federalist Chief Justice who served for over 30 years on the Supreme Court |
War of 1812,  | War between the United States and Britain caused by impressment, ship seizing, and problems with the Indians |
Battle of New Orleans,  | Last battle that made it look like the U.S. won and made Jackson a hero. |
| Results of the War of 1812 | Abolitionist movement, Federalists Party destroyed, Jackson a hero, sectionalism increased, and Indians removed |