| A | B |
|---|
| Function of mucins | lubrication, coat cell surfaces, provide adhesion |
| Strongly sulfated acidic mucins (C.T) | Keratin sulfate,heparin,heparin sulfate, dermatin sulfate |
| Two types of Nonsulfated Acidic Mucins | Sialomucins, Hyaluronic Acid |
| Alcian blue pH 0.5 stains | Strongly sulfated(C.T), Mast cells |
| Mucicarmine stains | Nonsulfated sialomucins |
| Metachromatic Dyes pH 2.0 stains | Strongly sulfated(C.T), weakly sulfated sulfomucins |
| Colloidal Iron stains | Strongly sulfated(C.T such as heparin sulfate) |
| Two Metachromatic Dyes which demonstrate Mast cells | Alcian Blue, Aldehyde Fuchsin |
| Which dyes stain Weakly Sulfated Goblet Cells | PAS, Alcian Blue pH 2.5, Metachromatic pH 2.0, Colloidal Iron |
| Neutral Mucins are stained by | PAS |
| Nonsulfated Sialomucins in the Epithelium are NOT stained by | Alcian Blue pH 0.5, Metachromatic pH 2.0 |
| Three types of sugars | Monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides |
| Tests that demonstrate homoglycans | PAS, PAS/DIASTASE, Best Carmine, Bauer-Feulgen |
| Glycogens fixative of choice | Rossmans |
| Carbohydrates that do not require fixation | Starch, Cellulose, Chitin |
This section of small intestine can also be stained by?, 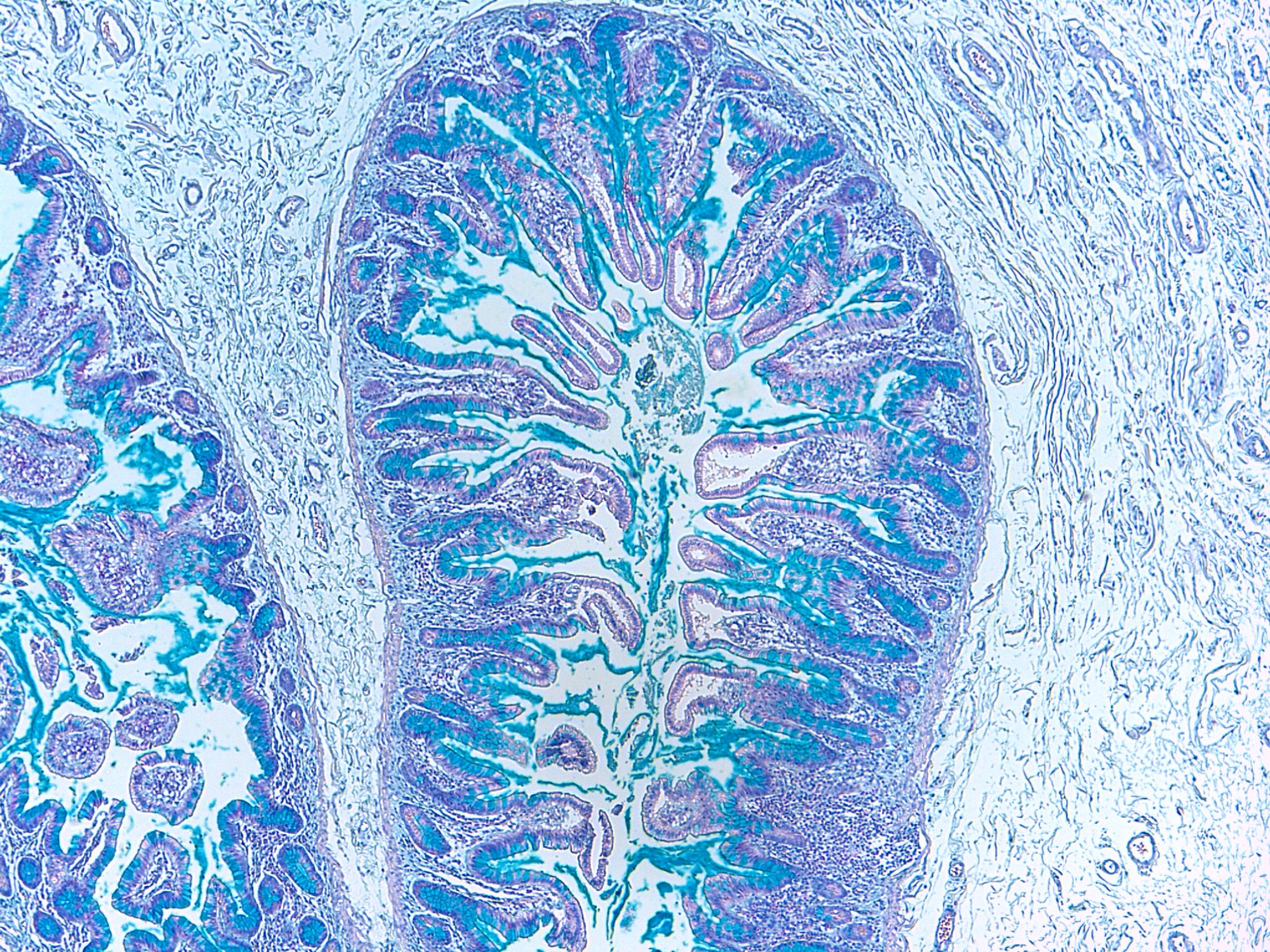 | Mucicarmine |
What is staining pink?, 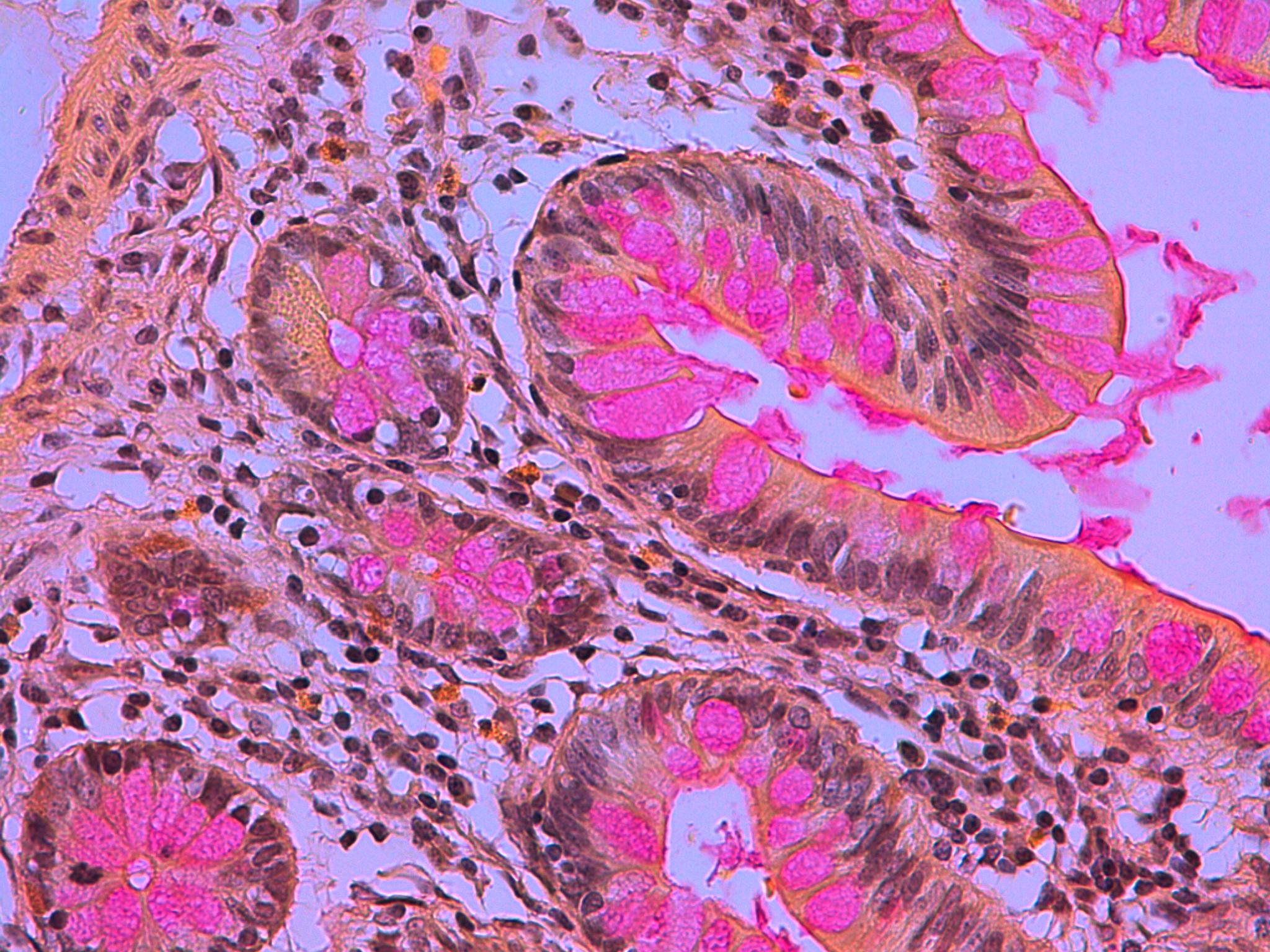 | Goblet cells |
What type of stain and tissue is this?, 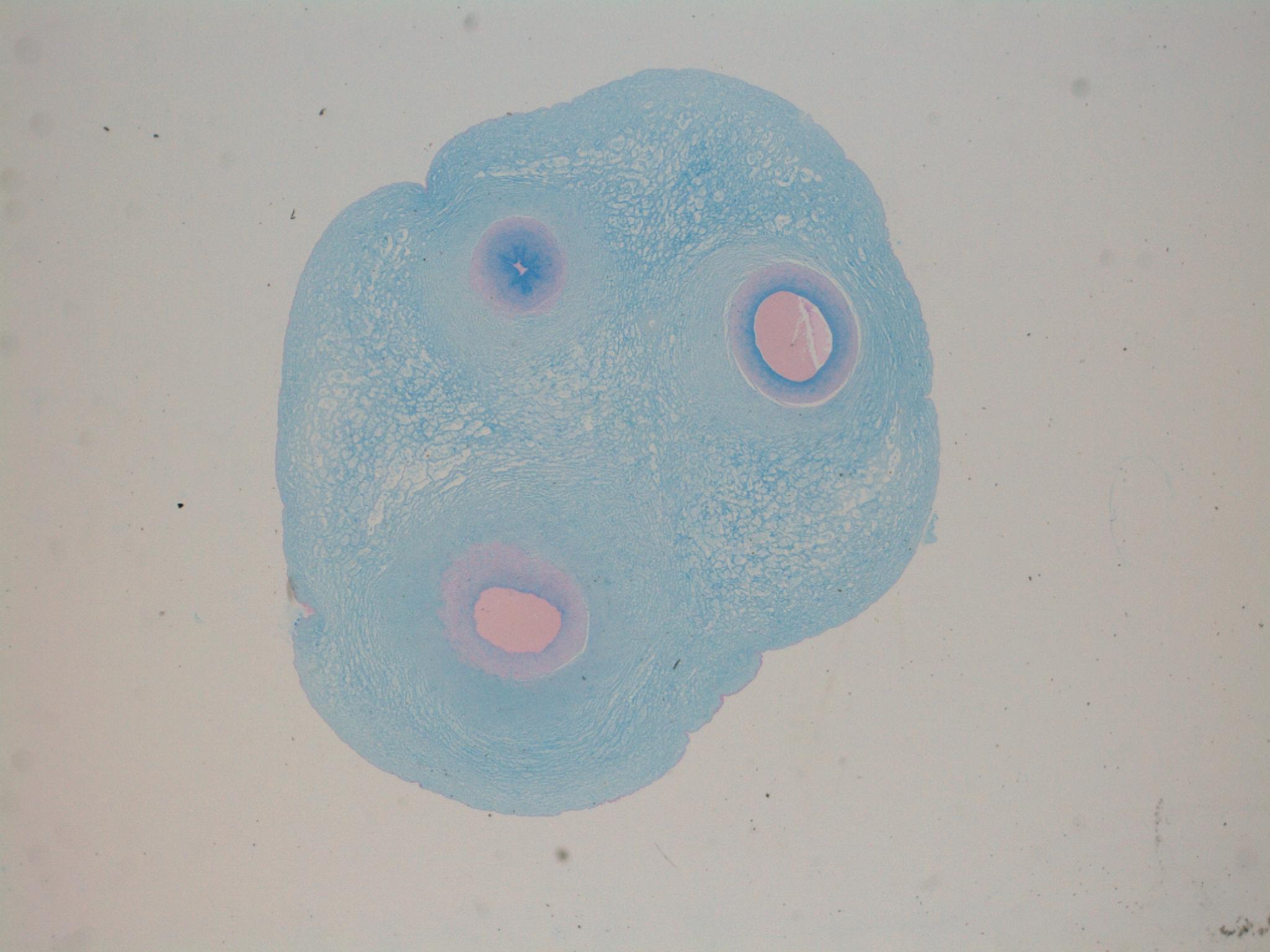 | Alcian Blue - Umbilical Cord |
What is staining brown-black, 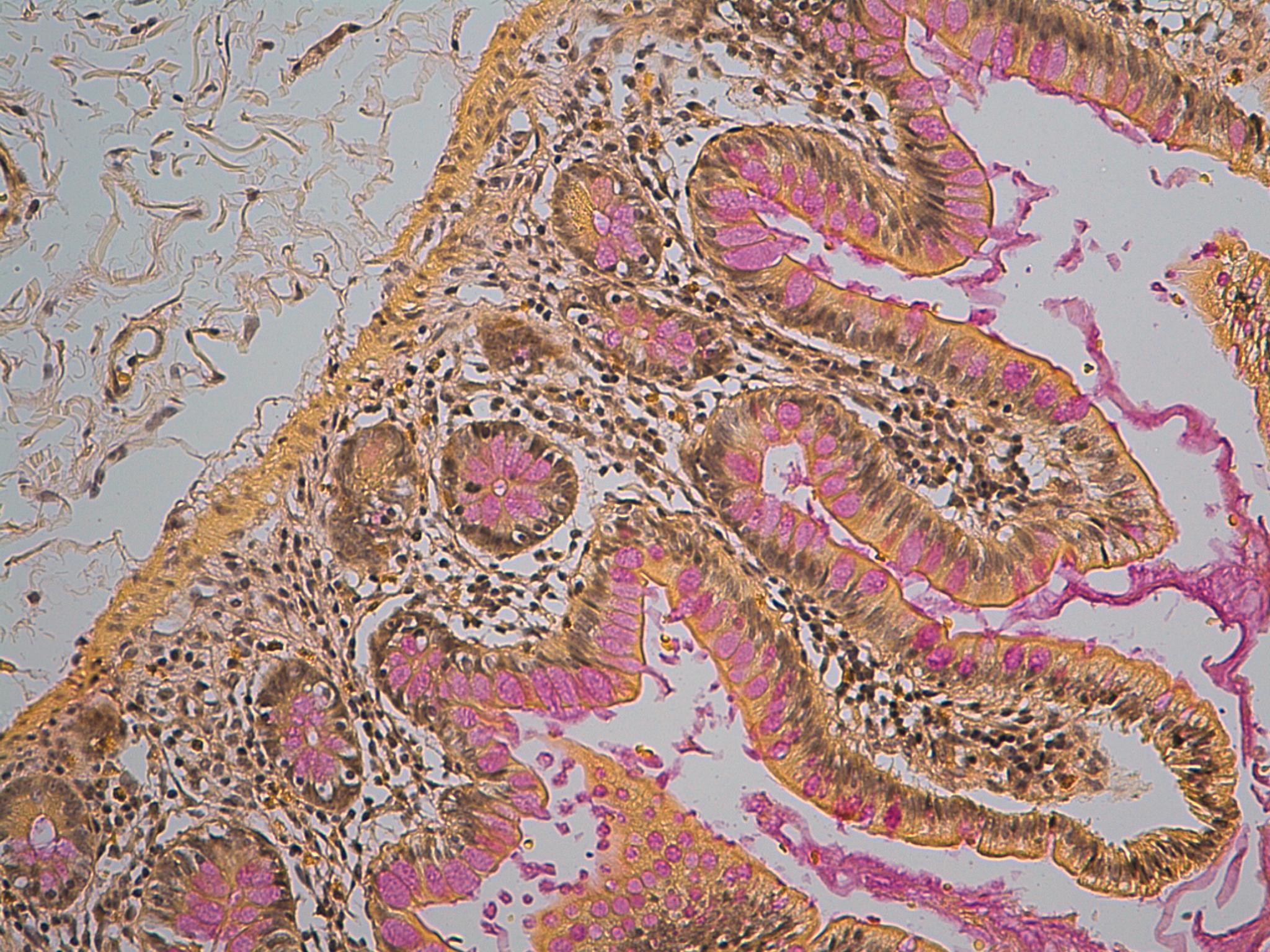 | Nuclei |