| A | B |
|---|
| 2 scientists that would study the geology of Mars | Geologist & Astronomer |
| 2 Scientists who would study underwater volcanoes | Geologist & Oceanographer |
| Meteorology | The study of the atmosphere & weather |
| Oceanography | The study of the oceans |
| Hypothesis | A possible explanation for an observed set of facts |
| Model | A representation of something that can not be viewed in its natural state |
| Revolve | To orbit something |
| Rotate | To spin on an axis |
| Approximate age of the Solar System | 4.6 Billion years old |
| % of atmosphere that is Nitrogen | 78% |
| % of atmosphere that is Oxygen | 21% |
| Geo- | prefix meaning Earth |
| Hydro- | prefix meaning Water |
| Bio- | prefix meaning Life |
| Atmos- | prefix meaning Vapor |
| Where most of the water on Earth is found | Oceans |
| Where most of the freshwater on Earth is found | Frozen in Glaciers & Icecaps |
| #1 Source of Useable Fresh Water | Groundwater |
| Hydrosphere (def) | The water of Earth's Surface |
| Water Cycle Synonym | Hydrologic Cycle |
| Most effective agent of erosion in wearing down Earth's surface | Running water (def) |
| 2 ways water wears down land | weathering & erosion |
| 3 Examples of items carried in suspendion by a river | Sands, Silts & Clays |
| Drainage Basin Synonym | Watershed |
| Drainage Basin (def) | The land area from which a stream or river gets its water |
| 3 Stages of Stream Development | Young Stream, Mature Stream, Old Stream |
| 7 Characteristics of a Young Stream | Flows swiftly, V-shaped valley, may have rapids, may have waterfalls, Erodes the stream bottom more than the sides, Has a high energy level due to the slope, Steep sides |
| Base Level of the Toms River | Barnegat Bay |
| 3 Characteristics of a Mature Stream | Flows less swiftly than a young stream, erodes along sides of stream & bottom, may form meanders |
| Meander (def) | A curve in a mature stream |
| Fastest part of an meander | Outside curve |
| Deepest part of a meander | Outside curve |
| Slowest part of a meander | Inside curve |
| Shallow part of a meander | Inside curve |
| Floodplain (def) | Broad, flat valley floor, carved by a meandering stream |
| 3 Characteristics of an Old Stream | Flows the slowest, flows through a broad flat plain, may have oxbow lakes |
| Oxbow Lakes (def) | Crescent shaped lake formed when a river meander gets cut off from the main river due to build up of sediments |
| Base level (def) | Level of the body of water into which a stream flows |
| Delta (def) | Level, fan shaped deposit at the mouth of a river |
| Why do deltas form? | The water slowed down as it hit its base level |
| % of Water on Earth that is Salt Water | 97% |
| Porosity (def) | % of a material's volume that is pore space |
| Porous (def) | Having many holes |
| 2 Things Porosity depends on | Particle shape & Sorting of Sediments |
| Shape of particles which creates the most pore space | Spherical |
| Shape of particles which creates the least pore space | Flat |
| Porosity of well sorted sediments | High Porosity |
| Porosity of poorly sorted sediments | Low Porosity |
| Two things that can decrease porosity | Natural cements & small sediments mixed with larger ones |
| Permeability (def) | The rate at which water & other liquids pass through pore space in rock |
| Effect on Permeability when grain size is increased | Permeability increases |
| Permeability of sand & gravel | High Permeability |
| Permeability of silts & clays | Low Permeability |
| Water Table (def) | The surface of the zone of saturation |
| Zone of Saturation (def) | Part of the ground where all pore space is full of water |
| Artesian Formation (def) | The arrangement of a permeable layer of rock sandwiched between two layers of impermeable rock |
| Aquifer (def) | Permeable layer of an artesian formation |
| Cap Rock (def) | Impermeable layer of an artesian formation |
| Rock that is usually the aquifer | Sandstone |
| Rock that is usually the cap rock | Shale |
| Plate Tectonics (def) | The study of the movement of Earth's plates. |
| Converging Boundary (def) | Type of plate boundary where O-O, O-C & C-C plates come together. |
| Rock of the Ocean Floors | Basalt |
| Rock of the Continents | Granite |
| Diverging Boundary (def) | Type of boundary where plates move apart. |
| Subduction Boundary (def) | Type of boundary where trenches are formed. |
| Alfred Wegener | German Scientist who developed Theory of Continental Drift |
| Harry Hess | Scientist from Princeton who developed the Theory of Sea Floor Spreading |
| Sliding Boundary (def) | Type of boundary where plates move past each other but not toward or away from each other: site of many earthquakes |
| Formations found at a diverging O-O boundary | Ocean Ridge and rift zone where magma is rising |
| Formations found at a subducting O-O boundary | Trench & Volcanic Island Arc |
| Formations found at a subducting O-C boundary | Trench & Continental Volcanic Mountain Chain |
| Formation formed at a collision boundary | Mountains |
| 2 Catastrophic Events associated with plate boundaries | Earthquakes & Volcanoes |
| Causes diverging plate boundaries | Hot, rising convection currents |
| Causes converging plate boundaries | Cooler, sinking convection currents |
| 3 Pieces of Evidence for Continental Drift | 1. Fossils of Mesosaurus found only in SA and Africa, 2. Continents seem to fit together like pieces of a puzzle, 3. rock core samples from SA & Africa match by type of rock, thickness of the layers and order the layers are in. |
| Pangaea (def) | Super continent described by Wegener |
| Pacific Ring of Fire | Largest belt of earthquakes & volcanoes in the world |
| 3 Specific Examples of the formation made at a C-C boundary | Himalayas, Ural Mts. & Southern Appalachian Mts. |
| 2 Specific examples of the formations made at an O-O boundary | Mariana Trench & Mariana Islands, Aleutian Trench & Aleutian Islands |
| 2 Specific examples of formations made at an O-C boundary | Andes Mountains & Peru-Chile Trench, Cascade Mountain Range & the Juan de Fuca trench |
| Deepest trench in the world | Mariana trench |
| Longest trench in the world | Peru-Chile trench |
| Specific example of a formation made by a diverging plate boundary | Mid Atlantic ridge or East Pacific Rise |
| Cause of the formation of Iceland | Divergence of the Mid Atlantic Ridge |
| Specific example of a sliding plate boundary | San Andreas Fault in CA |
| Area in North America where the craton is exposed at the surface of the ground | Canadian Shield |
| 2 Pieces of Evidence for The Theory of Sea Floor Spreading | Age Evidence - (rock closest to an ocean ridge is the youngest and gets older at the same rate on either side of the ridge), & rocks bands of equal width and magnetic polarity are found in matching patterns on both side of the mid ocean ridge |
| 2 Causes of Plate Tectonics | Convection currents & Differences in rock density |
| Convection Currents (def) | Cycle of hotter material rising and cooler material sinking that is one cause of Plate Tectonics |
| Rock Density Differences (def) | Rock that is more dense (ocean floor) sinks and rock that is less dense rises or stays on top of an area of subduction |
| Hot Spots (def) | Areas where magma from deep in Earth's mantle has melted through the crust to form several volcanoes |
| Ex. of Islands formed by a hot spot | Hawaiian Islands |
| Oldest Volcano in Hawaii | Kauai |
| 3 most abundant gases released by a volcano | Water vapor, Carbon dioxide & Sulfur gases |
| Location of Mt. St. Helens | Washington State, USA |
| Date Mt. St. Helens Erupted | May 18th, 1980 |
| Rift Eruptions (def) | Occur where two plates diverge |
| Caldera (def) | Formed when the top of a volcano collapses into the partially emptied magma chamber, producing a large opening |
| Ex. of a caldera | Crater Lake in Oregon |
| Plutons (def) | Igneous rock intrusion that cools inside other rock |
| 5 Ex. of Plutons | Sill, Dike, Laccolith, Batholith, Volcanic neck |
| Sill (def) | Horizontal intrusion that forms when magma squeezes into horizontal cracks |
| Batholith (def) | Largest igneous intrusion, forms when magma cools underground before reaching the surface |
| Laccolith (def) | Domed sill that has pushed up the rock above it |
| Volcanic neck (def) | The hard solid vent of a volcano left behind after the cone erodes |
| Dikes (def) | Vertical intrusion that cuts across layers, rock types don't match |
| Ex. of a laccolith | Stone Mt. Georgia |
| 2 Ex. of Volcanic necks | Ship Rock & Devil's Tower |
| Epicenter (def) | Point on the Earth's surface directly above where the earthquake happened underground |
| Surface Wave Synonym | L-wave |
| Surface Wave (def) | Waves that travel like ripples on a pond across Earth's surface; combination of P & S-waves; most destructive |
| Seismograph (def) | Instrument that detects & records earthquakes |
| Seismologist (def) | Scientist who studies earthquakes |
| Earthquake (def) | Shaking of Earth's crust due to vibrations made from rocks breaking |
| Layers of the Earth from the outsid in | Crust, Mantle, Outer Core, Inner Core |
| Focus (def) | Point in Earth's interior where earthquake energy is released |
| Magnitude (def) | measure of the energy released by an earthquake |
| P-wave (def) | Waves that move through Earth by causing particles in rocks to move back & forth; fastest seismic waves; first waves to arrive at a seismic station; formed by compressional and tension forces |
| Tsumamis (def) | Ocean waves generated by earthquakes |
| Seismic Wave (def) | Energy waves that move outward from the earthquake & make the ground quake. |
| Secondary Wave (def) | Waves that move though the Earth causing particles to move at right angles to the direction of the wave; S-waves; second fastest; body waves; only travel through solids |
| Order of arrival at a seismic station for P, S & L waves | P first, S second, & L last |
| Seismic Waves that travel through Solids, & Liquids | P-waves |
| Material/s S-waves can travel through | Solids |
| Slowest Seismic wave | L-wave |
| Fastest Seismic wave | P-waves |
| Seismic waves used to calculate distance to the epicenter | P & S waves |
| # of Stations that must provide seismogram readings to locate the epicenter of an earthquake | 3 |
| How does the size of the earthquake damage area change based focus depth increasing? | It increases |
| San Andreas Fault | Area of frequent earthquakes due to the Pacific plate trying to move past the North American plate. Shear forces involved at a transform(sliding) plate boundary |
| Inner Core | Earth layer composed of solid iron & nickel |
| Outer Core | Earth layer composed of liquid iron & nickel |
| Mantle | The thickest Earth layer; layer found below the crust; composed of silicon, oxygen, magnesium, & iron |
| Crust | The thinnest Earth layer; only layer man has dug or drilled into |
| Oblate Spheroid (def) | The shape of the Earth; flattened at the poles bulging at the equator |
| Cause of Earth's Shape | Earth's Rotation |
| Mass (def) | The amount of matter in an object |
| Volume | The amount of space taken up by an object |
| Weight | The pull of gravity on a given mass |
| Density | The amount of matter in a given space |
| Formula for Density | D=m/v |
| Average Human Body Temperature in Celsius | 37 degrees Celsius |
| Average Human Body Temperature in Fahrenheit | 98.6 degrees F |
| Boiling Point of water in Fahrenheit | 212 degrees F |
| Freezing point of water in Fahrenheit | 32 degrees F |
| Freezing point of water in Celsius | 0 degrees C |
| Boiling point of water in Celsius | 100 degrees C |
| 1ml = ___ cubic centimeters | 1ml= 1cubic centimeter |
| Metric Prefix meaning one hundred | Hecto |
| Metric Prefix meaning one thousand | Kilo |
| Person credited with the first use of the displacement method of determining the volume of an irregularly-shaped obj. | Archimedes |
| If a box has a mass of 2g & a volume of 1250ml, what is the density? | .0016 g/ml |
| Instrument used to measure mass | Balance |
| Instrument used to measure volume | Meter stick or graduated cylinder |
| Instrument used to measure length | Meter stick |
| 12.3 hl = ____cl | 123,000 cl |
| An irregularly shaped obj. is placed in a graduated cylinder. Without the obj. the cylinder reads 15 ml, with the obj. it reads 25 ml. What is the volume of the obj? | 10 ml |
| If the volume of an obj. is 4 ml & the density is 3g/ml, what is the mass? | 12 g |
| 2 cities used by Eratosthenes to calculate Earth's circumference | Syene & Alexandria |
| 1st Greek to successfully estimated the Earth's Circumference | Eratosthenes |
| Scientific Method (def) | Series of planned steps scientists use to solve problems |
| Control(def) | The standard or unchanged portion of an experiment |
| Variable | The changeable factor in an experiment |
| Mass (def) | The amount of matter in an object |
| Volume | The amount of space taken up by an object |
| Weight | The pull of gravity on a given mass |
| Latitude (def) | Angular distance in degrees north or south of the equator |
| Latitude of the North Pole | 90 degrees N |
| Latitude of the South Pole | 90 degrees S |
| Synonym for Latitude | Parallels |
| Latitude of the Equator | 0 degrees lat. |
| Longitude (def) | Angular distance in degrees east or west of the prime meridian |
| Synonym for Longitude | Meridians |
| Distance in miles from one line of latitude to the next | 70 miles |
| How many minutes are in a degree? | 60 minutes |
| How many seconds are in a minute? | 60 seconds |
| Latitude of the Tropic of Cancer | 23.5 degrees N |
| Latitude of the Tropic of Capricorn | 23.5 degrees S |
| Latitude of the Arctic Circle | 66.5 degrees N |
| Latitude of the Antarctic Circle | 66.5 degrees S |
| How does distance between Longitude lines change as you approach the poles? | The lines of Longitude get closer together toward the poles. |
| Longitude of the Prime Meridian | 0 degrees long. |
| Longitude of the International Date Line | 180 degrees long. |
| Place where the Prime Meridian is located. | Greenwich, England |
| Contour Lines (def) | Lines that connect points of equal elevation |
| Elevation (def) | Height above sea level |
| Topographic Map (def) | Map showing the shape & elevation of the Earth's surface. |
| Contour Interval (def) | The difference in height between two adjacent contour lines |
| Index Contours (def) | Every 5th line is darkened & labeled with the elevation |
| Map Legend (def) | Explains what the symbols used on the map mean |
| Hachures (def) | Lines drawn on a contour line to show a depression |
| Map Scale (def) | The relationship between the distance on the map & the actual distance on the Earth's surface. |
| Synonym for Map Legend | Map Key |
| Magnetic Declination (def) | The difference in the angle between true north & magnetic north |
| USGS stand for | United States Geological Survey |
| How are contour lines drawn to show a steep slope? | Contour lines are drawn close together. |
| Geosynchronous | Having an orbit with a fixed period of 24 hours |
| Bench Mark | Location whose exact elevation is known & is noted on a brass or aluminum plate permanently in the ground; abbrev. BM |
| Geosynchronous Satellite Examples | Weather Satellites & Communication Satellites |
| Matter (def) | Anything that has mass & takes up space |
| Organic matter (def) | Matter that was once living or is still alive |
| Inorganic matter (def) | Matter that has never been living |
| Physical properties of matter (def) | Characteristics that do not change the type of matter |
| Examples of Physical properties of matter | Color, shape, texture, hardness, density, ductility, buoyancy, solubility, &phase changes |
| Phase Change (def) | Change between the states of matter; solid to liquid, solid to gas, liquid to solid, liquid to gas, gas to liquid, gas to solid |
| Freezing point of water | 0 degrees C, 32 degrees F |
| Boiling point of water | 100 degrees C, 212 degrees F |
| Temperature at which water is most dense | 4 degrees C |
| Atom (def) | Smallest part of an element that has all the characteristics of that element; know as the building blocks of matter |
| Parts of an atom | Proton, Neutron, Electron |
| Positively charged particle in an atom | Proton |
| Negatively charged particle in an atom | Electron |
| Neutral particle in an atom | Neutron |
| 2 particles found in the nucleus of an atom | Protons & Neutrons |
| Center of an atom | Nucleus |
| Element (def) | Matter that contains only one type of atom |
| 4 Examples of Elements | Sodium (Na), Chlorine (Cl), Gold (Au), Silver (Ag) |
| John Dalton (def) | English chemist who stated the concept of the Particle Model |
| Compound (def) | Matter containing two or more chemically combined elements & having physical properties different from each of the elements in it |
| Molecule (def) | 2 or more atoms chemically combined; The smallest particle of a compound that still keeps all the properties of that compound |
| 3 Example of compounds | Water, Carbon dioxide, Salt (Halite) |
| Atomic # (def) | The number of protons in the nucleas of an atom |
| Mass # synonym | Atomic mass or Atomic weight |
| Mass # (def) | The number of protons & neutrons in the nucleus of an atom |
| Ion (def) | An electrically charged atom; formed when an atom either loses or gains an electron |
| Charge of a metal ion | + because metals tend to lose electrons |
| Charge of a nonmetal ion | - because nonmetals tend to gain electrons |
| Isotope (def) | Atom that has a different # of neutrons in the nucleus & therefore have a different mass # than the original atom; some are unstable & radioactive |
| 2 Examples of Ions | Na+ & Cl- |
| 2 Examples of Isotopes | Uranium 235 & Carbon 14 |
| 2 types of chemical bonds | Ionic & Covalent |
| Ionic Bond (def) | The force of electrical attraction between oppositely charged ions |
| Covalent Bond (def) | Attachment of atoms formed by sharing electrons |
| Type of bond holding NaCl (salt) together | Ionic |
| Examples of covalently bonded molecules | CO, Water, Carbon Dioxide, Nitrogen Gas |
| Generator (def) | Converts mechanical energy to electricity when a magnet with a coiled wire around it spins |
| Turbine (def) | Converts the Kinetic energy of a liquid or gas to mechanical energy |
| Silicates (def) | Family of minerals that all contain silicon & oxygen; contain silica tetrahedrons |
| Most abundant family of minerals found in Earth's crust | Silicates |
| 2 ex of silicate minerals | Feldspar, Quartz |
| Most abundant of all minerals | Feldspar |
| Hardness of Feldspar | 6 |
| Hardness of Quartz | 7 |
| Fracture type shown in Quartz | Conchoidal |
| 2nd most abundant mineral in Earth's crust | Quartz |
| Cleavage of Calcite | 3 cleavages; Rhombohedral |
| Chemical formula of Calcite | CaCO3 (the 3 is written as a subscript) |
| Hardness of Calcite | 3 |
| Family of minerals that reacts to the acid test | Carbonates |
| Shape of Calcite | Rhombus |
| Shape of Halite | Cubic |
| Streak color of Pyrite | Greenish black |
| Streak color of Gold | Gold |
| Fracture type found in Obsidian & Quartz | Conchoidal |
| # 1 on Mohs Scale of Hardness | Talc |
| #3 on Mohs Scale of Hardness | Calcite |
| #6 on Mohs Scale of Hardness | Feldspar |
| #7 on Mohs Scale of Hardness | Quartz |
| #10 on Mohs Scale of Hardness | Diamond |
| Mineral with a salty taste | Halite |
| Chemical formula of Halite | NaCl |
| Least reliable mineral property for identifying a mineral | Color |
| Cleavage (def) | The ability of a mineral to break along a flat surface or crystal face |
| Gas released by the acid test | Carbon dioxide |
| % of Earth's crust that is silicate minerals | 90% |
| Silica Tetrahedron (def) | The repeating structural unit of a silicate mineral; One silicon atom surrounded by four oxygen atoms. |
| What is determined by the rate of cooling of magma? | The crystal size of a mineral |
| Native mineral (def) | Mineral composed of single elements |
| 5 examples of native minerals | Gold, Silver, Copper, Diamond, & Sulfur |
| Renewable Resource (def) | resource replaced in nature as fast or faster than it is used |
| Nonrenewable Resource (def) | resource that exists in a fixed amount and is used up faster than it is replaced |
| Examples of Renewable Resources | Oxygen, Solar Energy, Carbon Dioxide |
| Examples of Nonrenewable Resources | All Metals, Sand, Gravel, Sulfur |
| The 4 R's of Conservation | Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, Respond |
| Fossil Fuels (def) | Fuel formed from the remains of plants and animals |
| 3 Examples of Fossils Fuels | Coal, Oil, Natural Gas |
| 4 Examples of Hydrocarbons | Gasoline, Diesel Fuel, Propane, Motor Oil |
| Salinization (def) | Condition caused by the evaporation of irrigation water, which leaves too much mineral matter on the soil surface, inhibiting plant growth |
| Eutrophication (def) | Phosphates & nitrates from fertilizers & detergents enter lake water & lead to the unusual growth of some algae, aerobic bacteria eat dead algae and oxygen for larger needed by larger fish is used up so fish die. |
| anaerobic (def) | Does not use oxygen |
| aerobic (def) | Uses oxygen |
| Best time to water your lawn | 5am - 10 am |
| pH of acid rain | 3 |
| pH of rain | 5.6 |
| Residual Soil (def) | Soil that has weathered directly from the bedrock beneath it; the bedrock is its parent material |
| Transported Soil (def) | Soil has been moved & doesn't match the bedrock beneath it |
| Parent Material (def) | Bedrock that is the source of soil |
| Humus | Organic material found in the topsoil |
| Hydrolysis (def) | Type of chemical weathering in which water reacts with & changes the minerals present in a rock |
| Meaning of Hydro | Water |
| Erosion (def) | The removal of weathered matierals by winds, rain, glaciers or gravity |
| % of space frozen ice takes up compared to an equal amount of liquid water | 10% |
| Carbonic Acid (def) | Carbon Dioxide dissolved in water that can chemically weather rock such as limestone or the mineral calcite |
| Mass Movement (def) | The movement of soil, & rock fragments downslope due to the pull of gravity |
| 2 things used to classify types of mass movement | Size of the material & Speed of the movement of the material |
| Soil Profile (def) | A cross section of soil exposed by digging |
| A - Horizon Synonym | Topsoil |
| B - Horizon Synonym | Subsoil |
| C - Horizon (def) | Slightly Weathered parent material |
| B - Horizon contains | Clay & Minerals transported deeper by groundwater |
| rock (def) | mixture of minerals, glass, or organic matter bound together |
| Uniformitarianism | "the present geology is the key to the past geology" James Hutton |
| Granite (description) | Coarse texture, intrusive, light colored |
| igneous rock (def) | Rocks formed by the cooling and hardening of molten material from a volcano or from deep inside the Earth |
| intrusive (def) | Rocks that form below Earth's surface, formed from cooled magma |
| extrusive (def) | Rocks that form above Earth's surface from lava or volcanic ash |
| magma (def) | liquid rock underground |
| lava (def) | liquid rock above ground |
| 3 things that affect crystal size | 1. speed magma cools 2. amount of dissolved gas in magma 3. Space available for crystal formation |
| metamorphic rocks (def) | formed from existing rocks by the action of heat, pressure, and chemicals |
| Igneous Rock of the Ocean Floors | Basalt |
| Igneous Rock of the Continents, formed under mountains | Granite |
| Order of sediment deposit from the shore line | Pebbles & Gravels, Sands, Silts & Clays, 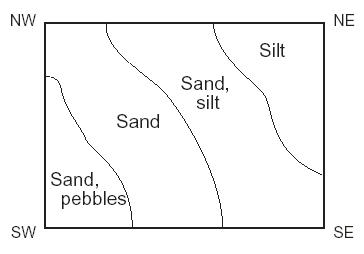 |
| Weathering (def) | The breakup of rock due to exposure to the atmosphere |
| Erosion (def) | The removal of weathered material |
| Rock gypsum | Soft Chemical Sedimentary rock made mostly of the mineral gypsum |
| Laccolith (Def) | Domed igneous intrusion |
| Batholith (Def) | Largest igneous intrusion |
| Sill (Def) | Horizontal Igneous Intrusion |
| Dike (Def) | Vertical Igneous Intrusion |
| Igneous Intrusion | When lava comes up through cracks in preexiting rock, 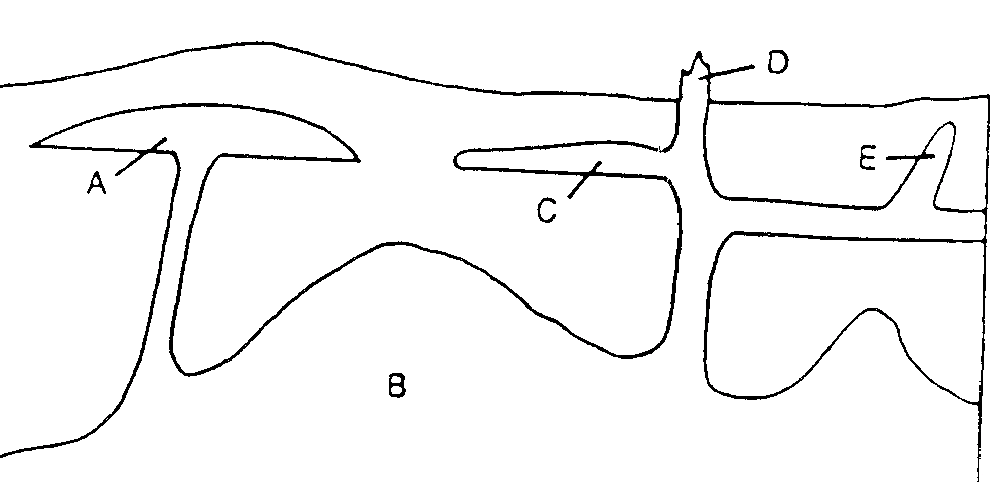 |
| Volcanic Neck | Left over hardened magma in the vent of a volcano |
| Fast cooling = ___ sized crystals | small |
| Slow cooling = ___ sized crystals | large |
| In a closed system the only thing that can enter & leave is | energy |
| 1 meter is closest to the standard measurement of | one yard |
| Salinity (def) | The amount of dissolved solids in seawater |
| Density (def) | The mass per volume of an object |
| Examples of Seamounts | The Hawaiian Islands |
| Main mineral of coral sands | calcite |
| Coral Atolls (def) | A ring-shaped island surrounding a seawater lagoon; formed as coral built up around an island as the island was sinking |
| El Nino (def) | A weakening of the tradewinds, causing a warming of the ocean surface off the western coast of South America that occurs every 4 to 12 years when upwelling of cold, nutrient-rich water does not occur. It causes die-offs of plankton and fish. |
| Gyres (def) | Large circular ocean patterns in each of the major ocean basins. |
| Wind (def) | Movement of air from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure created by the unequal heating of the land & oceans; force that drives ocean surface currents. |
| Ultimate cause of the direction of gyre flow in each hemisphere. | Earth's Rotation |
| Gulf Stream (def) | Warm, fast, deep, narrow current found in the western basin of the Atlantic Ocean |
| If salinity increases what is its effect on density? | Density increases; Salinity & Density are directly proportional |
| If temperature increases, what is its effect on density? | Density decreases; Temperature & Density are inversely proportional |
| 3 main gases dissolved in seawater | Nitrogen, Oxygen, & Carbon dioxide |
| 2 most abundant ions dissolved in seawater | Chloride & Sodium ions |
| Average Salinity of Seawater | 34.5 parts per thousand |
| Factors that decrease salinity | Glaciers entering an ocean, rivers entering an ocean, heavy rainfall falling on an ocean |
| Factors that increase salinity | Sea ice forming, dry hot climates, |
| Major Source of dissolved minerals in the ocean | Weathering & Erosion of land |
| Thermometer (def) | Instrument used to measure temperature |
| Air (def) | Mixture of gases |
| Ozone (def) | Layer found in the Earth's atmosphere that protects the Earth from 99% of the Ultra Violet rays |
| Conduction (def) | Heat transfer by contact (touch) |
| Dew (def) | Formed when water vapor condenses after it has reached the dew point |
| Barometer (def) | Instrument used to measure pressure |
| Psychrometer (def) | Instrument that measures humidity by using a wet bulb/dry bulb thermometer |
| Greenhouse Effect (def) | Condition in which Earth is heated because carbon dioxide, water vapor & other gases let sunlight in, but trap infrared energy |
| Inventor of the barometer | Torricelli |
| Ionosphere (def) | Layer of the atmosphere that is a part of the Thermosphere & is full of charged atoms |
| Isotherms (def) | Lines on a map that connect points at the same temperature value |
| Hygrometer (def) | Instrument that measures humidity by using human hair |
| Inventor of the thermometer | Galileo |
| Wind Chill (def) | The cooling effect of the wind |
| Troposphere (def) | The lowest layer of the atmosphere; only layer where weather occurs; temperature decreases with altitude |
| Relative Humidity (def) | The % of air that is full of water vapor |
| Specific Humidity (def) | The exact amount of moisture in the air |
| Warmest part of the day | Between 3 & 4 pm |
| Coolest part of the day | Just before sunrise |
| Coldest month on average | January |
| Warmest month on average | July |
| Which heats faster & cools faster, land or water? | Land |
| Dew Point (def) | The temperature at which the air has reached its capacity and condensation occurs |
| Speed of Hurricane force winds | 73 + mph |
| Weather systems in the US usually move from | west to east |
| When is ozone a pollutant? | Ozone is a pollutant when it is in the troposphere. It is an irritant to your eyes & lungs |
| 5 Greenhouse gases | Carbon dioxide, water vapor, CFC's, Methane, Nitrous Oxides |
| 2 types of barometers | Aneroid barometer, & mercury barometer |
| Do condensing water molecules release or absorb heat energy? | Release |
| Which type of air hold more moisture, warm or cold? | Warm |
| Do evaporating water molecules release or absorb heat energy? | Absorb |
| 68 degrees F in Celsius = | 20 degrees Celsius |
| 90 degrees C in Fahrenheit = | 194 degrees Fahrenheit |
| Symbol for High pressure on a weather map | Blue H |
| Symbol for Low pressure on a weather map | Red L |
| Direction winds move around a low pressure system in the northern hemisphere | Counterclockwise |
| Direction wind blows around a high pressure system in the northern hemisphere | Clockwise |
| Temperature of are in a low pressure system relative to the air around it | Warmer |
| Temperature of are in a high pressure system relative to the air around it | Cooler |
| Winds spiral up and counterclockwise out for what type of pressure system? | Low pressure |
| Winds spiral down and clockwise in for what type of pressure system? | High pressure |
| Frost (def) | Frozen Condensation formed when the surface the water condenses on is freezing or below freezing |
| 3 Main Cloud Types | Cirrus, Stratus, Cumulus |
| # of inches of snow for every 1 inch of rain | 10 inches |
| The higher the air rises, the (more)(less) moisture it can drop | More |
| Windward (def) | Side of a mountain where rising air cools, water condenses and falls as rain |
| Leeward (def) | Side of a mountain where air is compressing and the sinking air is dryer. |
| 2 Chemical agents that cause of Acid Rain | Sulfates (from volcanoes & fuel burning) and nitrates (from car exhaust and industrial processes)) |
| 4 Dangers from Acid Rain | Changes pH of the soil, makes stone weather faster, kills plants & animals, & damages metals |
| Temperature Inversion (def) | Upside-down temperature condition occurring when surface air is colder than the air above. |
| 2 things that aid in destroying temperature inversions | Wind & sunlight |
| What results from the uneven heating of the Earth's surface? | Winds |
| Isobars that are close together signify areas were winds are (blowing faster) (blowing slower). | Blowing faster |
| Winds blow from (high) (low) pressure to (high) (low) pressure | From high pressure to low pressure |
| Anemometer (def) | Instrument that measures wind speed |
| Weather/Windvane (def) | Instrument that shows wind direction |
| How are winds named? | For the direction the wind comes from |
| What causes winds to curve to their right in the northern hemisphere? | Coriolis Effect |
| As altitude increase, what does temperature do? | Decreases |
| As altitude increases what does pressure do? | Decreases |
| As temperature increase, what does pressure do? | Decreases |
| Sea Breeze (def) | Cool breeze off of the ocean due to air on land heating up and rising away |
| Land Breeze (def) | Warm breeze off of the land due to cool air sinking over the land at night |
| Which direction does a Nor' easter blow? | Southwest |
| Front (def) | Boundary between two air masses; storms & precipitation occur here |
| What does a fully darkened station model circle represent? | A completely overcast sky |
| What does a flag (pennant) represent on a station model shaft? | 50 knots |
| What does one long feather on a station model shaft represent? | 10 knots |
| What does a short feather on a station model shaft represent? | 5 knots |
| Which direction does the shaft of a station model point? | Into the wind |
| Meteorologist (def) | Person who studies the weater |
| Station Model (def) | Symbols used by (NWS) the National Weather Service to depict current weather in one particular area |
| Station Model symbol that means rain | Dots |
| Station Model symbol that means fog | 3 Horizontal lines like an = sign with an extra line |
| Station Model symbol that means snow | Asterisk * |
| Weather Watch (def) | A cautionary statement issued by the NWS indicating that atmospheric conditions are favorable for the development of a particular weather or hydrologic phenomenon. |
| Weather Warning (def) | A cautionary statement issued by the NWS indicating that a specific hazardous weather or hydrologic event is imminent or actually occurring |
| Salinity (def) | The measure of the dissolved solids in sea water |
| Amount of dissolved solids typically found in 1000 parts of sea water | 35 parts per 1000, 3.5 parts per 100 |
| Turbidity Currents (def) | Underwater landslides |
| Cause of trans-Atlantic telegraph & telephone cables getting broken. | Turbidity Currents |
| 1st planet from sun | Mercury |
| 3rd planet from sun | Earth |
| A comet's tail always points | away from the sun |
| The same side of the Moon faces Earth because | Moon's rotation rate = the moon's revolution rate |
| The moon & sun rise in the east & set in the west because | Earth rotates from west to east |
| 3 names given to a rock in space, the rock burning in the atmosphere & the rock hitting Earth | Meteoroid, Meteor, Meteorite |
| Scientific explanation for the formation of the Universe | Big Bang Theory |
| Steps in the life cycle of our sun in order | Nebula, Protostar, Stable state, Red Giant, Planetary nebula, White dwarf, black dwarf |
| Advantage of Hubble telescope over ground based telescopes | Outside Earth's Atmosphere |
| Examples of Jovian planets | Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune |
| The name of our galaxy | Milky Way |
| Geocentric | Earth centered model of the solar system |
| Review how to read the H-R diagram in your astronomy notes | 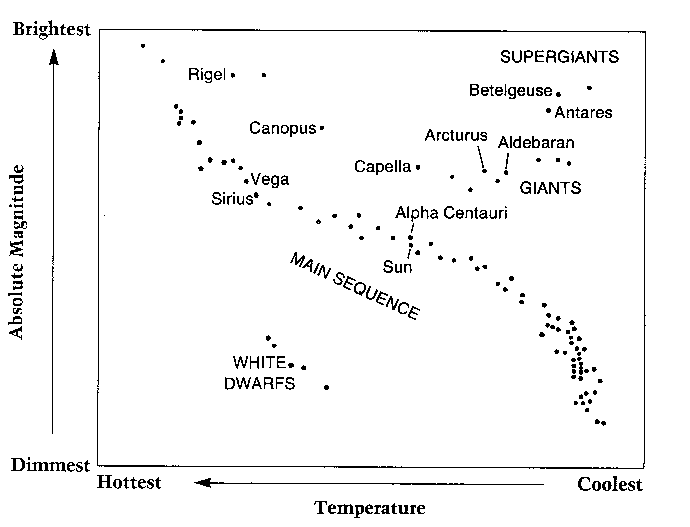 |
| Order of the moon phases from new to full | New, Waxing Crescent, 1st Quarter, Waxing Gibbous, Full Moon |
| An object will move in a straight line unless | external forces change it direction |
| Constellation containing the pointer starts used to find Polaris | Ursa Major |
| Cause of Tsunamis | Earthquakes |
| Moon phases for Spring tides | New & Full |
Name the igneous intrusion shown by letter A,  | Laccolith |
Name the igneous intrusion shown by letter C,  | Sill |
Name the igneous intrusion shown by letter E,  | Dike |
What is the elebation of A, 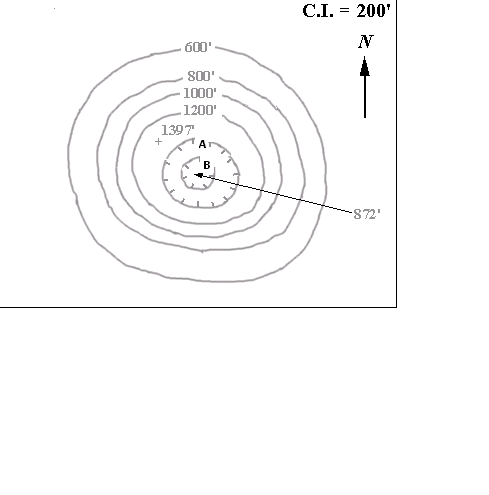 | 1200 ft. The 1st depression contour is always the same elevation as the last regular contour line. |