| A | B |
|---|
| Estimation Challenge | A problem for which it is difficult, or even impossible, to find an exact answer. |
magnitude estimate, 
| A rough estimate. A magnitude estimate tells whether an answer should be in the tens, hundreds, thousands, and so on.,  |
| maximum | The largest amount; the greatest number in a set of data. |
| mean | The sum of a set of numbers divided by the number of numbers in the set. The mean is often referred to simply as the average. |
| median | The middle value in a set of data when the data are listed in order from smallest to largest or vice versa. If there is an even number of data points, the median is the mean of the two middle values. |
| minimum | The smallest amount; the smallest number in a set of data. |
| partial-sums addition | A method, or algorithm, for adding in which sums are computed for each place (ones, tens, hundreds, and so on) separately and are then added to get a final answer.,  |
| place value | A number system that values a digit according to its position in a number. In our number system, each place has a value ten times that of the place to its right and one-tenth the value of the place to its left. |
| range | The difference between the maximum and minimum in a set of data. |
| reaction time | The amount of time it takes a person to react to something. |
| trade-first subtraction | A method, or algorithm, for subtracting in which all trades are done before any subtractions are carried out., 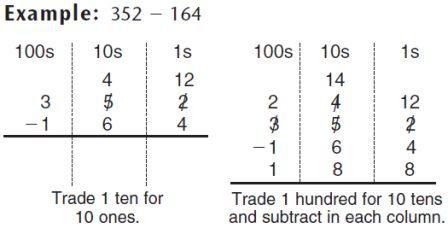 |