| A | B |
|---|
| periodic law | when the elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number there is a periodic repetition of their physical and chemical properties,  |
| metals | one of a class of elements that are good conductors of heat and electric current; metals tend to be ductile, malleable, and shiny,  |
| nonmetals | an element that tends to be a poor conductor of heat and electric current; nonmetals generally have properties opposite to those of metals,  |
| metalloid | an element that tends to have properties that are similar to those of metals and nonmetals,  |
| alkali metals | any metal in Group 1A of the periodic table, 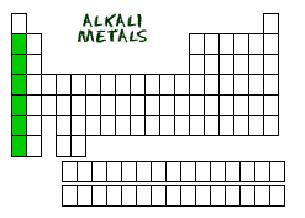 |
| alkaline earth metals | any metal in Group 2A of the periodic table, 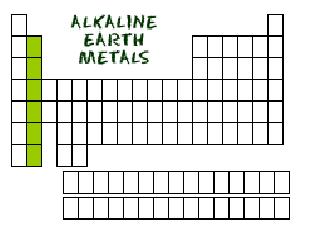 |
| halogens | a nonmetal in Group 7A of the periodic table,  |
| noble gases | an element in Group 8A of the periodic table; the s and p sublevels of the highest occupied energy level are filled,  |
| representative elements | as a group these elements display a wide range of physical and chemical properties. In their atoms the s and p sublevels in the highest occupied energy level are partially filled,  |
| transition metal | one of the Group B elements in which the highest occupied s sublevel and a nearby d sublevel generally contain electrons, 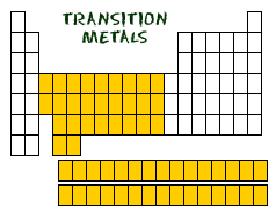 |
| inner transition metal | an element in the lanthanide or actinide series; the highest occupied s sublevel and nearby f sublevel of its atoms generally contain electrons; also called inner transition element,  |
| atomic radius | one-half the distance between the nuclei of two atoms of the same element when the atoms are joined,  |
| ion | an atom or group of atoms that has a positive or negative charge, 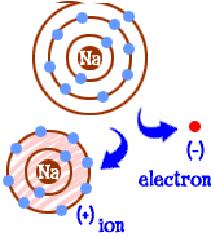 |
| cation | any atom or group of atoms with a positive charge,  |
| anion | any atom or group of atoms with a negative charge,  |
| ionization energy | the energy required to move an electron from an atom in its gaseous state,  |
| electronegativity | the ability of an atom to attract electrons when the atom is in a compound,  |