| A | B |
|---|
| Analytical Chemistry | The subdivision of chemistry dealing with the qualitative and quantitative determination of chemical components of substances., 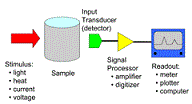 |
| Applied Chemistry | The application of the theories and principles of chemistry to practical purposes.,  |
| Biochemistry | The science dealing with the chemistry of living matter., 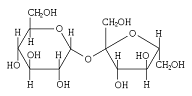 |
| Biotechnology | The use of living organisms or other biological systems in the manufacture of drugs or other products or for environmental management, as in waste recycling: includes the use of bioreactors in manufacturing, microorganisms to degrade oil slicks or organic waste, genetically engineered bacteria to produce human hormones, and monoclonal antibodies to identify antigens.,  |
| Chemistry | The science that deals with the composition and properties of substances and various elementary forms of matter. Compare element,  |
| Experiment | A test, trial, or tentative procedure; an act or operation for the purpose of discovering something unknown or of testing a principle, supposition, etc.: a chemical experiment; a teaching experiment; an experiment in living.,  |
| Hypothesis | A proposition assumed as a premise in an argument., 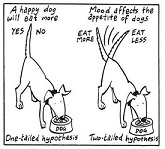 |
| Inorganic Chemistry | The branch of chemistry dealing with inorganic compounds., 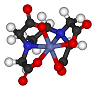 |
| Macroscopic | Visible to the naked eye. Compare microscopic,  |
| Matter | Anything that takes up space and has mass.,  |
| Microscopic | So small as to be invisible or indistinct without the use of the microscope: microscopic organisms. Compare macroscopic.,  |
| Observation | An act or instance of noticing or perceiving.,  |
| Organic Chemistry | Is a sub-discipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation (by synthesis or by other means) of carbon-based compounds, hydrocarbons, and their derivatives,  |
| Physical Chemistry | The branch of chemistry dealing with the physical properties of chemical substances,  |
| Responding Variable | Is the variable that will change as a result of the change in the manipulated variable. |
| Scientific Law | A phenomenon of nature that has been proven to invariably occur whenever certain conditions exist or are met; also, a formal statement about such a phenomenon,  |
| Scientific Method | A logical, systematic approach to the solution of a scientific problem; steps include making observations, testing hypotheses, and developing theories,  |
| Technology | The means by which a society provides its members with those things neededand desired,  |
| Theory | A well-tested explanation for a broad set of observations,  |
| Manipulated Variable | The variable that is changed during an experiment; also called independent variable,  |
| Pollutant | A material found in air, water, or soil that is harmful to humans and other organisms,  |
| Pure Chemistry | The pursuit of chemical knowledge for its own sake,  |
| Responding Variable | The variable that is observed during an experiment; also called dependent variable,  |