| A | B |
|---|
| Activity Series | An invaluable aid to predicting the products of replacement reactions. It also can be used as an aid in predicting products of some other reactions., 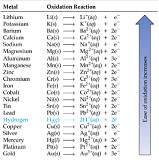 |
| Balanced Equation | Shows how mass is conserved because it shows how atoms are conserved., 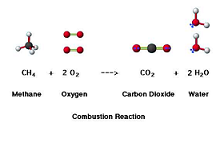 |
| Catalyst | A substance that initiates or accelerates a chemical reaction without itself being affected something that causes an important event to happen,  |
| Chemical Equation | A symbolic representation of a chemical reaction., 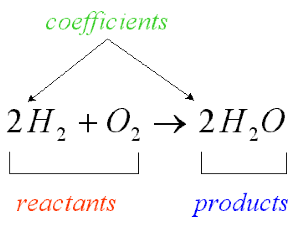 |
| Coefficents | The ratio of the change in length or volumen of a body to the original lengthor volume for a unit change in temperature.,  |
| Combination Reaction | Is a general category of a chemical reaction in which two or more reactants are chemically bonded together to produce a single product. Also called a synthesis reaction.,  |
| Combustion Reaction | Combustion or burning is the sequence of exothermic chemical reactions between a fuel and an oxidant accompanied by the production of heat and conversion of chemical species. The release of heat can result in the production of light in the form of either glowing or a flame, 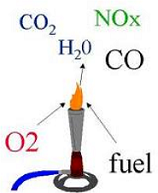 |
| Complete Ionic Equation | A chemical equation may be described as a chemical reaction or a means of writing out and describing such a phenomenon., 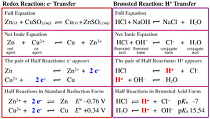 |
| Decomposition Reaction | Separation of a substance into two or more substances that may differ from each other and from the original substance,  |
| Double-Replacement Reaction | A chemical reaction between two compounds where the positive ion of one compound is exchanged with the positive ion of another compound, 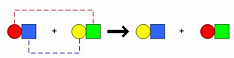 |
| Net Ionic Equation | Chemical equation for a reaction which lists only those species participating in the reaction.,  |
| Single Replacement Reaction | A type of oxidation-reduction chemical reaction when an element or ion moves out of one compound and into another., 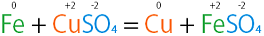 |
| Skeleton Equation | A chemical equation that is not balanced, with an unequal number of atoms on each side of the reaction.,  |
| Spectator Ion | The Na+ and SO4 ^2? ions are spectator ions since they remain unchanged on both sides of the equation. They simply "watch" the other ions react, hence the name. They are present in total ionic equations to balance the charges of the ions.,  |