| A | B |
|---|
| Boyle's law | The pressure of an ideal gas at constant temperature varies inversely with the volume, 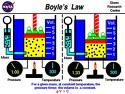 |
| Charle's law | The volume of a fixed mass od gas is directly proportional to its kelvin temperaturemif the pressure is kept constant, 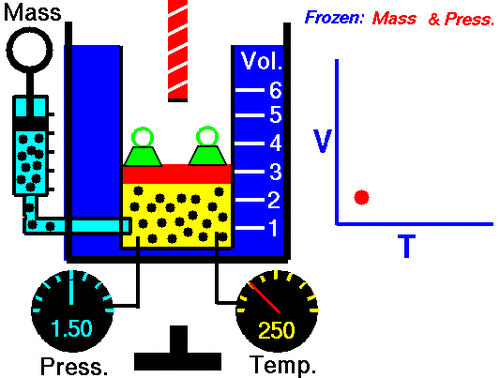 |
| Combined Gas Law | The las that describes the relationship among the pressere, temperature, and volume of an elclosed gas, 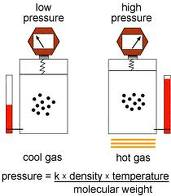 |
| Compressibilty | A measure of how much the volume of matte decreases unde pressure,  |
| Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures | at constant volume and temperature, the total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the component gases, 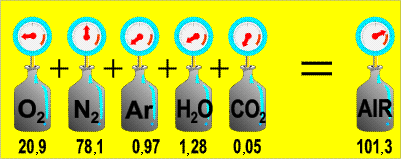 |
| Diffusion | the tendency of molecules to move toward areas of lower concentration until the concentration is uniform throughout, 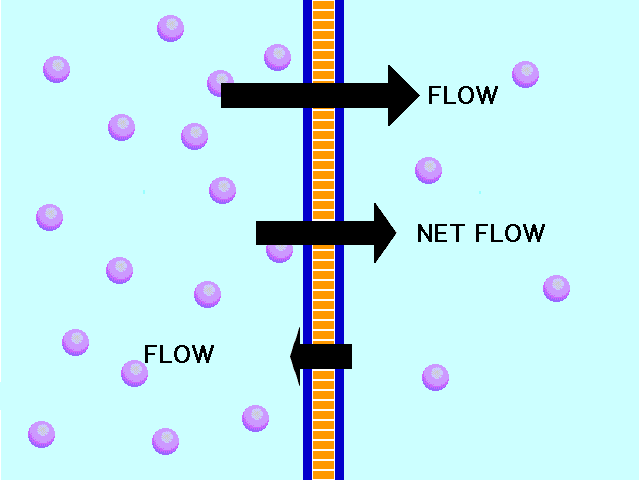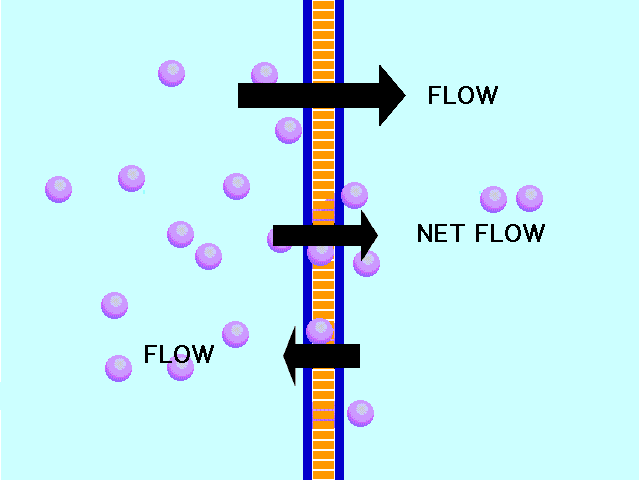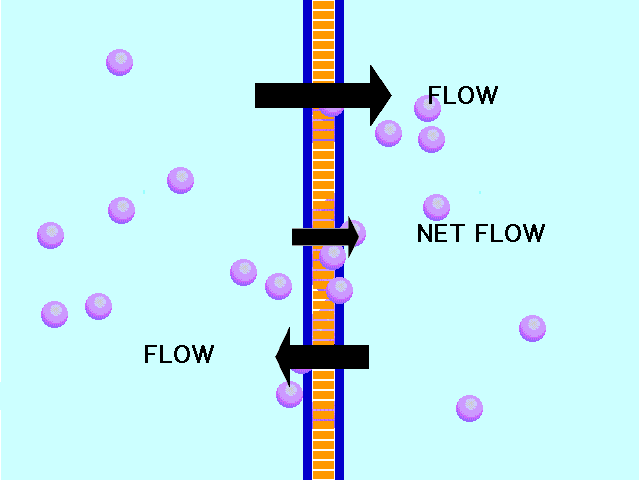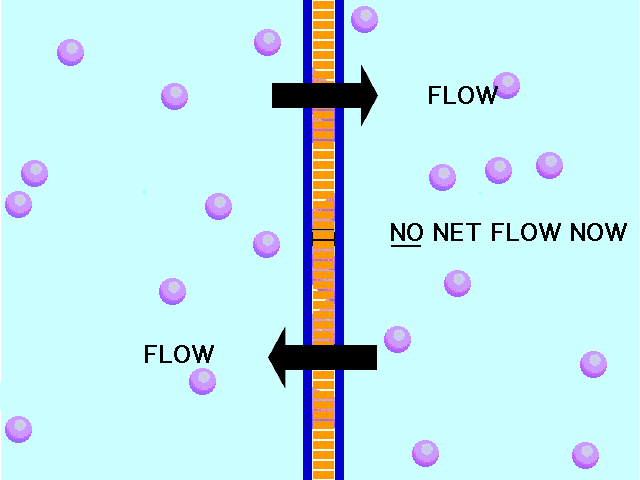 |
| Effusion | The process that occurs when a gas escapes through a tiny hole in its container, 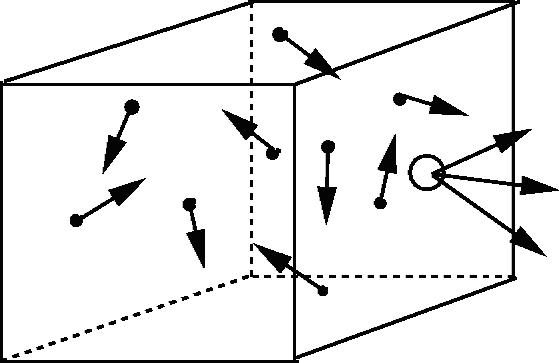 |
| Gay-Lussac's law | The pressure of a gas is directly proportional to the kelvin temperature if the volume is constant,  |
| Graham's law of effusion | The rate of effuison of a gas is inversley proportional to the square root of its molar mass; this relationship is also true for the diffusion of gases, 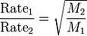 |
| ideal gas constant | The constant in the ideal gas law with the symbol R and the value 8.31, 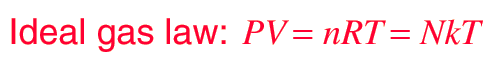 |
| ideal gas law | The relationship PV=nRT, which describes the behavior of an ideal gas, 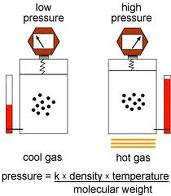 |
| partial presuure | The contribution each gas in a mixture of gases makes to the total pressure, 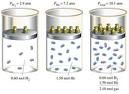 |