| A | B |
|---|
| Calorimeter | A device used to measure the heat flow of a chemical reaction or physical change.,  |
| Calorimetry | Measurement of the amount of heat evolved or absorbed in a chemical reaction, change of state, or formation of a solution.,  |
| Chemical Potential Energy | Energy in the chemical bonds of matter., 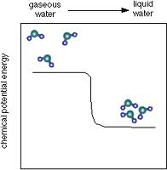 |
| Endothermic Process | Characterized by or causing the absorption of heat,  |
| Enthalpy | Equivalent to the sum of the internal energy of the system plus the product of its volume multiplied by the pressure exerted on it by its surroundings.,  |
| Exothermic Process | Releasing heat,  |
| Heat | The transfer of energy from one body to another as a result of a difference in temperature or a change in phase.,  |
| Heat Capacity | The ratio of the heat energy absorbed by a substance to the substance's increase in temperature.,  |
| Heat of Combustion | The amount of heat released per unit mass or unit volume of a substance when the substance is completely burned.,  |
| Heat of Reaction | The heat evolved or absorbed when one mole of a product is formed at constant pressure,  |
| Hess's Law of Heat Summation | The law states that the enthalpy change for a reaction that is carried out in a series of steps is equal to the sum of the enthalpy changes for the individual steps.,  |
| Law of Consevation of Energy | States that energy may neither be created nor destroyed. Therefore the sum of all the energies in the system is a constant., 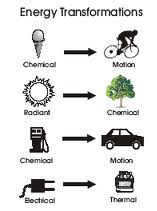 |
| Molar Heat of Condensation | Heat liberated by a unit mass of gas at its boiling point as it condenses into a liquid,  |
| Molar Heat of Fusion | Important part of energy calculations since it tells you how much energy is needed to melt each mole of substance on hand,  |
| Molar Heat of Solidification | The heat liberated by a unit mass of liquid at its freezing point as it solidifies: equal to the heat of fusion.,  |
| Molar Heat of Solution | The heat evolved or absorbed when one mole of a substance dissolves completely in a large volume of solvent,  |
| Molar Heat of Vaporization | The quantity of energy required to evaporate 1 mole, or a unit mass, of a liquid, at constant pressure and temperature. Also known as enthalpy of vaporization; heat of evaporation; latent heat of vaporization.,  |
| Specific Heat | The heat required to raise the temperature of one gram of a substance one degree centigrade,  |
| Standard Heat of Formation | The standard enthalpy of formation "standard heat of formation" of a compound is the change of enthalpy that accompanies the formation of 1 mole of a substance in its standard state from its constituent elements in their standard states (the most stable form of the element at 1 bar of pressure,  |
| System | An integrated whole, composed of diverse, interacting, specialized structures and subfunctions.,  |
| Thermochemical Equation | Is a balanced stoichiometric chemical equation that includes the enthalpy change, ?H.,  |
| Thermochemistry | The branch of chemistry concerned with the study and measurement of the heat evolved or absorbed during chemical reactions, 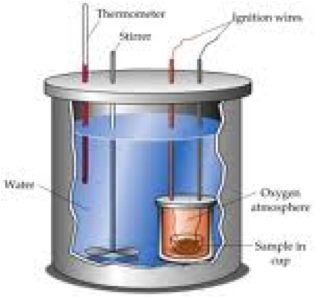 |