| A | B |
|---|
| Allotrope | A structurally different form of an element,  |
| Amorphous Solid | A solid in which there is no long-range order of the positions of the atoms,  |
| Atmospheric Pressure | The pressure exerted by the atmosphere at the earth's surface. It has an average value of 1 atmosphere., 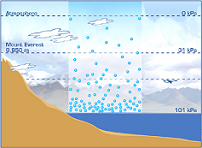 |
| Barometer | An instrument that measures atmospheric pressure., 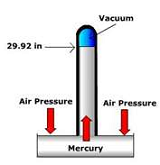 |
| Boiling Point | The temperature at which a liquid will start to become a gas, and boil., 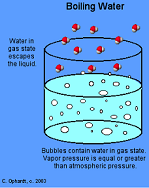 |
| Crystal | A solid formed by the solidification of a chemical and having a highly regular atomic structure,  |
| Evaporation | Is a type of vaporization of a liquid, that occurs only on the surface of a liquid., 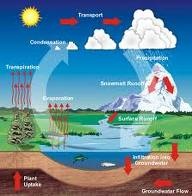 |
| Gas pressure | The pressure exerted by a gas,  |
| Glass | Any compound that has solidified from a molten state into a non-crystalline form.,  |
| Kinetic Energy | The energy of a body or a system with respect to the motion of the body or of the particles in the system., 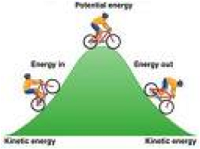 |
| Kinetic Theory | A theory that gases consist of small particles in random motion, 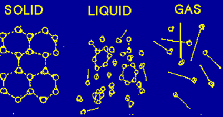 |
| Melting Point | The temperature below which a liquid turns into a solid,  |
| Normal Boiling Point | The boiling point of an element or a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the environmental pressure surrounding the liquid., 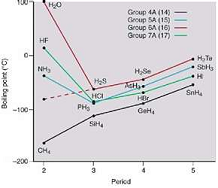 |
| Pascal | A unit of pressure equal to one newton per square meter,  |
| Phase Diagram | A phase diagram in physical chemistry, engineering, mineralogy, and materials science is a type of chart used to show conditions at which thermodynamically distinct phases can occur at equilibrium, 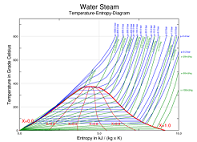 |
| Standard Atmosphere | A unit of pressure: the pressure that will support a column of mercury 760 mm high at sea level and 0 degrees centigrade,  |
| Sublimation | A change directly from the solid to the gaseous state without becoming liquid,  |
| Triple Point | A temperature point at which a substance can be either a solid, liquid, or gas, 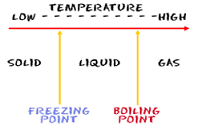 |
| Unit Cell | The simplest unit of a regular lattice., 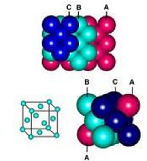 |
| Vacuum | A space entirely devoid of matter.,  |
| Vapor Pressure | The pressure exerted by the molecules of a vapor, esp. that part of the total pressure exerted by vapor in a mixture of gases, as by water vapor in air.,  |
| Vaporization | The rapid change of water into steam, esp. in a boiler., 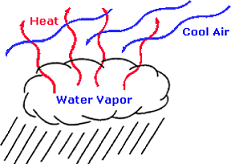 |
| Atmosphere Conversion Factors | Use these to convert between different atmospheric units.,  |