| A | B |
|---|
| Miscible | Capable of being mixed,  |
| Boiling-Point Elevation | Describes the phenomenon that the boiling point of a liquid (a solvent) will be higher when another compound is added, meaning that a solution has a higher boiling point than a pure solvent.,  |
| Colligative Property | Properties of solutions that depend on the number of particles in a volume of solvent and not on the mass of the particles., 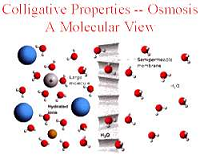 |
| Concentrated Solution | To concentrate a solution, one must add more solute (e.g. alcohol), or reduce the amount of solvent (e.g. water)., 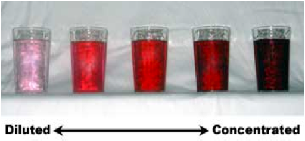 |
| Concentration | The act or process of concentrating, especially the fixing of close, undivided attention.,  |
| Dilute Solution | A solution (liquid mixture) that has a small amount of solute dissolved. As you add more water to a sugar solution the solution, becomes more and more dilute.,  |
| Freezing-Point Depression | The phenomenon in which the freezing point of a liquid (a solvent) is depressed when another compound is added, meaning that a solution has a lower freezing point than a pure solvent., 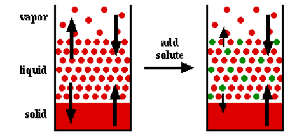 |
| Henry’s Law | At a constant temperature, the amount of a given gas dissolved in a given type and volume of liquid is directly proportional to the partial pressure of that gas in equilibrium with that liquid., 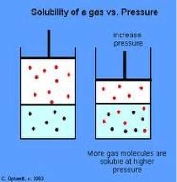 |
| Molal Boiling-Point Elevation | This is the phenomenon of increasing the temperature at which a liquid boils by dissolving another substance in the liquid,  |
| Molal Freezing Point Depression | Describes the phenomenon in which the freezing point of a liquid (a solvent) is depressed when another compound is added, meaning that a solution has a lower freezing point than a pure solvent.,  |
| Molality | Unit of concentration, defined to be equal to the number of moles of solute divided by the number of kilograms of solvent., 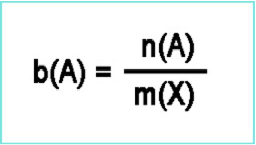 |
| Molarity | Is the number of moles of solute dissolved in one liter of solution.,  |
| Mole Fraction | In chemistry, mole fraction x is a way of expressing the composition of a mixture.,  |
| Saturated Solution | A solution in which the maximum amount of solvent has been dissolved. Any more solute added will sit as crystals on the bottom of the container., 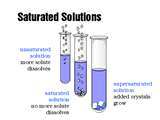 |
| Supersaturated Solution | A solution that contains more solute than it normally would at a given temperature., 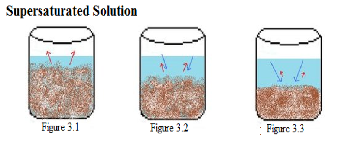 |
| Unsatured Solution | A solution in which more solute can be dissolved at a given temperature is called an unsaturated solution. A given solution that is saturated at a particular temperature may become unsaturated when the temperature is increase.,  |
| Immiscible | Incapable of mixing,  |
| Henry's Law Equation | 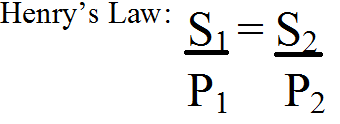 |
| Molarity (M) Equation | 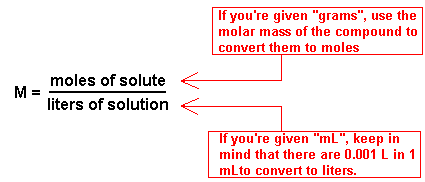 |
| Percent by Volume Equation | 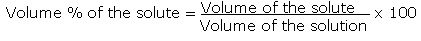 |
| Percent by Mass Equation |  |
| Molality Equation | 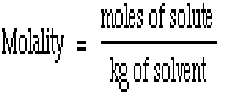 |
| Mole Fractions Equation | 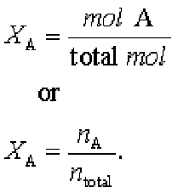 |
| Freezing-Point Depression Equation |  |
| Boiling-Point Elevation Equation | 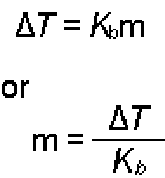 |
| Moles of Solute Equation | 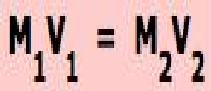 |