| A | B |
|---|
| Activated Complex | Any chemical species formed from the collision of energetic particles which is capable of reacting to form intermediates or products.,  |
| Activation Energy | The minimum amount of energy required to initiate a reaction and is denoted by Ea., 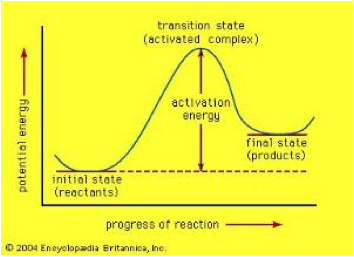 |
| Chemical Equilibrium | Is the distribution of interverting chemical compounds, 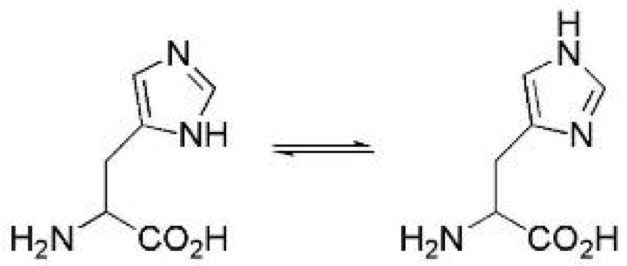 |
| Collision Theory | Theory of reaction rates that states that effective collisions between reactant molecules must occur in order for the reaction to occur., 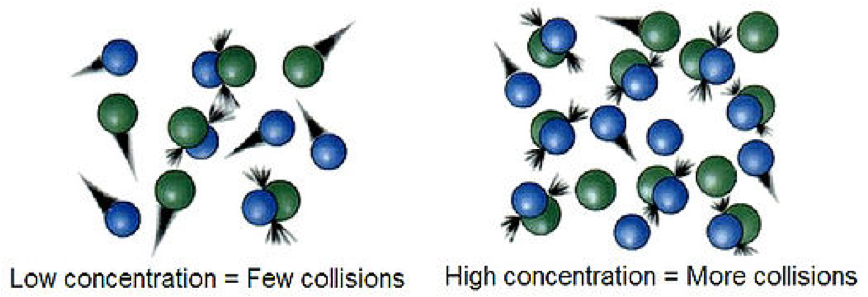 |
| Common Ion | An ion that is common to two or more components in a mixture, 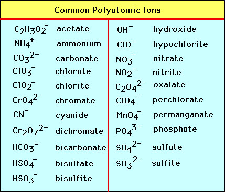 |
| Common Ion Effect | Term used to describe the effect on a solution of two dissolved solutes that contain the same ion or ions. |
| Elementary Reaction | A chemical reaction in which one or more of the chemical species react directly to form products in a single reaction step and with a single transition state, 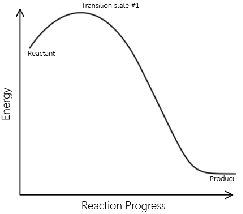 |
| Entropy | A thermodynamic property that is a measure of the energy not available for useful work in a thermodynamic process,  |
| Equilibrium Constant | The ratio of concentrations when equilibrium is reached in a reversible reaction (when the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction), 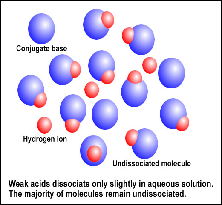 |
| Equilibrium position | Is determined mostly by the concentration of products and the concentration of reactants.,  |
| First order reaction | Is one where the rate depends on the concentration of the species to the first power, 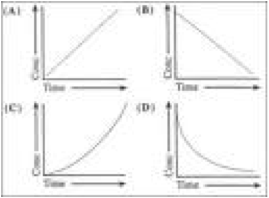 |
| Free energy | A thermodynamic quantity that is the difference between the internal energy of a system and the product of its absolute temperature and entropy,  |
| Gibbs free- energy change | Thermodynamic potential that measures the "useful" or process-initiating work obtainable from an isothermal, isobaric thermodynamic system,  |
| Inhibitor | Substance that retards or stops an activity,  |
| Intermediate | lying between two extremes in time or space or state, 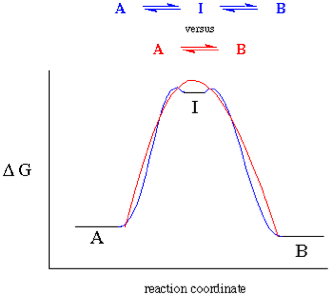 |
| Law of disorder | A measure of the loss of information in a transmitted message.,  |
| Le Chateliers principal | the principle that if any change is imposed on a system that is in equilibrium then the system tends to adjust to a new equilibrium counteracting the change, 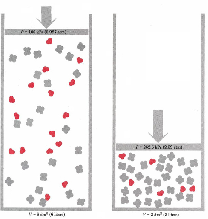 |
| Nonspontaneous reaction | A reaction which cannot occur without the input of work from an external source. ?G > 0 for nonspontaneous reactions at T and P., 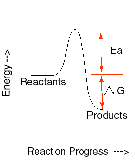 |
| Rate | a certain quantity or amount of one thing considered in relation to a unit of another thing and used as a standard or measure: at the rate of 60 miles an hour.,  |
| Rate Law | The rate law or rate equation for a chemical reaction is an equation which links the reaction rate with concentrations or pressures of reactants and constant parameters (normally rate coefficients and partial reaction order)., 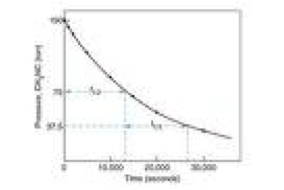 |
| reaction mechanism | is the step by step sequence of elementary reactions by which overall chemical change occurs.,  |
| reversible reaction | is a chemical reaction that results in an equilibrium mixture of reactants and products.,  |
| Solubility Product Constant | Any type of chemical equilibrium relationship between solid and dissolved states of a compound at saturation, 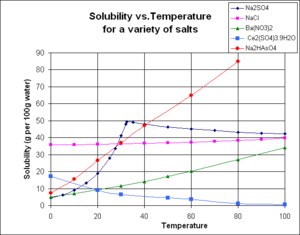 |
| Specific rate constant | An experimentally determined (proportionality) constant, which is different for different reactions and which changes only with temperature,  |
| Spontaneous reaction | The time-evolution of a system in which it releases free energy (most often as heat) and moves to a lower, more thermodynamically stable, energy state,  |
| Transition state | Particular configuration along the reaction coordinate,  |