| A | B |
|---|
| Anode | The positive electrode in an electrolytic cell, toward which negatively charged particles are attracted.,  |
| Battery | A device containing an electric cell or a series of electric cells storing energy that can be converted into electrical power (usually in the form of direct current).,  |
| Cathode | A negatively charged electrode, as of a electrolytic cell, a storage battery, or an electron tube., 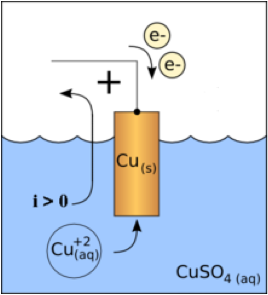 |
| Cell potential | Potential difference, Ecell, between oxidation and reduction half-cells under nonstandard conditions., 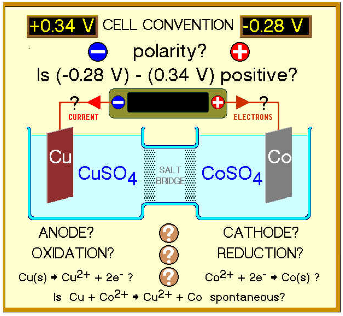 |
| Dry Cell (battery) | The dry cell battery is one of the most commonly used types of batteries. A, C, 9-volt, and watch batteries are dry cell batteries.,  |
| Electrical Potential | At a point in space is the electrical potential energy divided by charge associated with a static (time-invariant) electric field.,  |
| Electrochemical Cell | The weight of a substance (as an element) deposited or evolved during electrolysis by the passage of a specified quantity of electricity and usu., 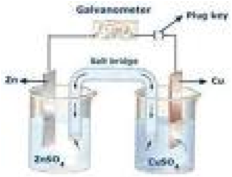 |
| Electrochemical process | A chemical change accompanying the passage of an electric current, especially as used in the preparation of commercially important quantities of certain chemical substances., 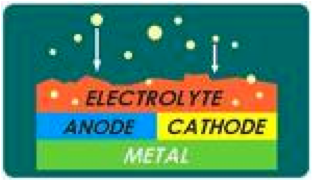 |
| Electrode | A conductor, not necessarily metallic, through which a current enters or leaves a nonmetallic medium, as an electrolytic cell, arc generator, vacuum tube, or gaseous discharge tube., 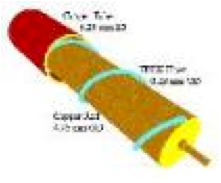 |
| Electrolysis | The passage of an electric current through an electrolyte with subsequent migration of positively and negatively charged ions to the negative and positive electrodes.,  |
| Electrolytic cell | A cell containing an electrolyte in which an applied voltage causes a reaction to occur that would not occur otherwise (such as the breakdown of water into hydrogen and oxygen),  |
| Fuel cell | cell that produces electricity by oxidation of fuel (hydrogen and oxygen or zinc and air); often used in electric cars,  |
| Half-cell | Half of an electrolytic or voltaic cell, where either oxidation or reduction occurs., 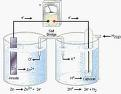 |
| Reduction potential | Is a measure of the tendency of a chemical species to acquire electrons and thereby be reduced.,  |
| Salt Bridge | Iis a laboratory device used to connect the oxidation and reduction half-cells of a galvanic cell (voltaic cell), a type of electrochemical cell., 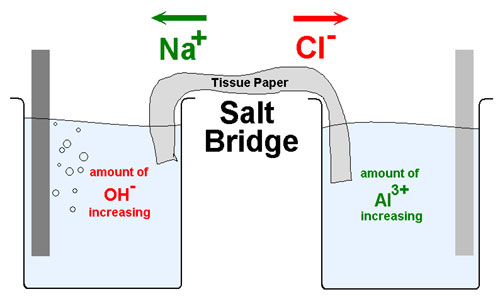 |
| Standard cell potential | This potential difference is created as a result of the difference between individual potentials of the two metal electrodes with respect to the electrolyte., 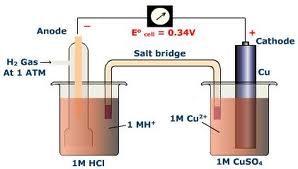 |
| Standard hydrogen electrode | Redox electrode which forms the basis of the thermodynamic scale of oxidation-reduction potentials, 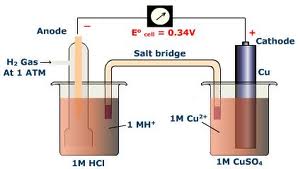 |
| Voltaic cell | Electric cell that generates an electromotive force by an irreversible conversion of chemical to electrical energy,  |