| A | B |
|---|
| Active site | The part of an enzyme that interacts with the substrate during catalysis., 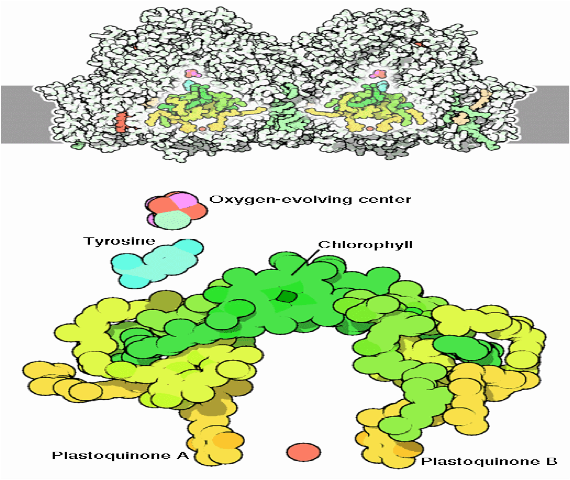 |
| Adenosine triphosphate | Is chemical compound that breaks down to release the energy responsible for muscle contraction. It is the only useable form of energy in the body., 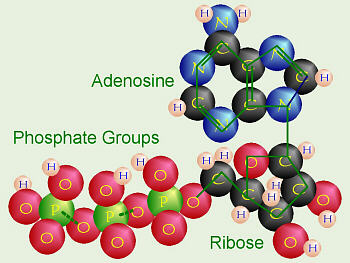 |
| amino acid | Organic compounds containing an amino group and a carboxylic acid group, 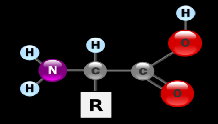 |
| Anabolism | The synthesis in living organisms of more complex substances, 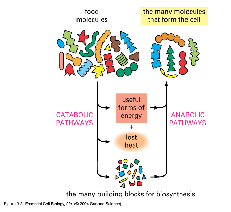 |
| Carbohydrates | Mainly sugars and starches, together constituting one of the three principal types of nutrients used as energy sources (calories) by the body,  |
| Catabolism | The metabolic breakdown of complex molecules into simpler ones, often resulting in a release of energy, 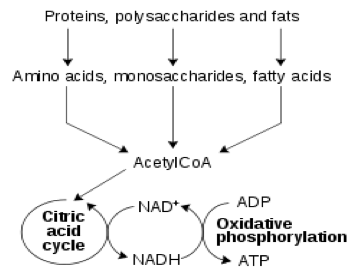 |
| Disaccharide | Any of a group of carbohydrates, as sucrose or lactose, that yield monosaccharides on hydrolysis., 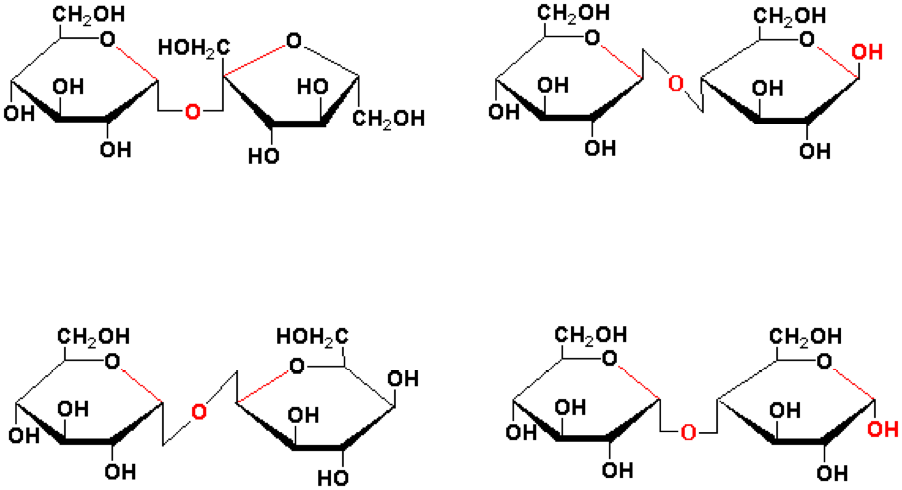 |
| Enzymes | Any of various proteins, as pepsin, originating from living cells and capable of producing certain chemical changes in organic substances by catalytic action, as in digestion., 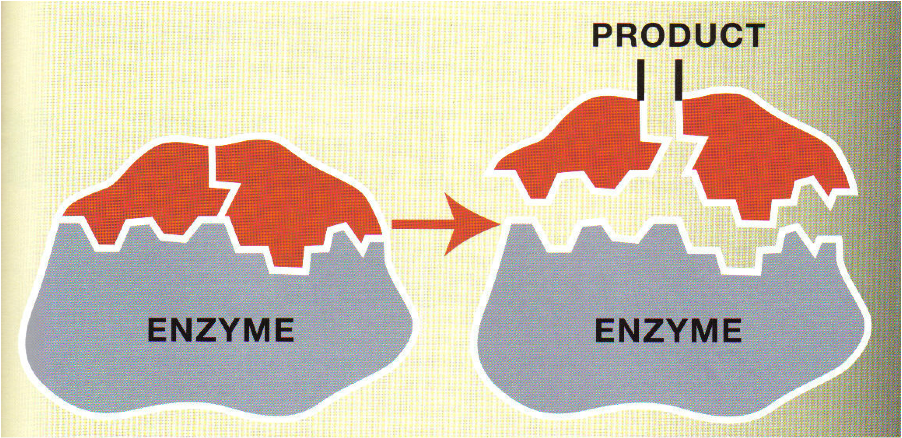 |
| Gene | A segment of DNA that is involved in producing a polypeptide chain,  |
| Lipids | Broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins, 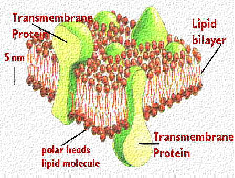 |
| Metabolism | The sum of the physical and chemical processes in an organism by which its material substance is produced, maintained, and destroyed, and by which energy is made available.,  |
| Monosaccharides | A sugar that constitutes the building blocks of a more complex form of sugars such as oligosaccharides and polysaccharides.,  |
| Nucleic Acid | Biological molecules essential for life, and include DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid). Together with proteins, nucleic acids make up the most important macromolecules., 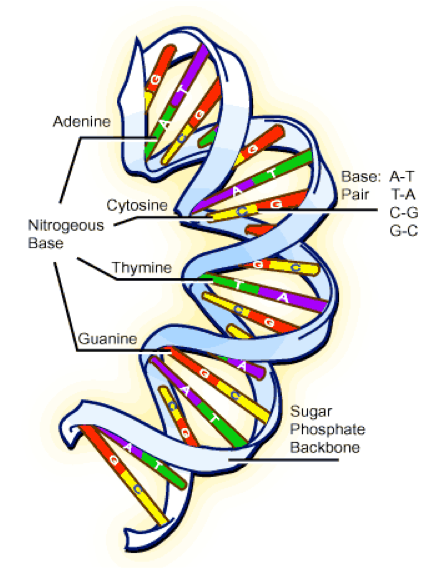 |
| Nucleotides | Molecules that, when joined together, make up the structural units of RNA and DNA. In addition, nucleotides play central roles in metabolism., 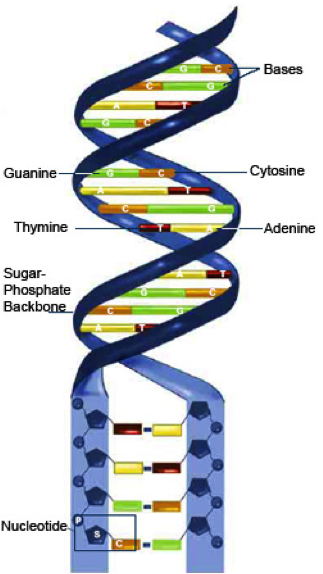 |
| Peptide | Short polymers formed from the linking, in a defined order, of ?-amino acids,  |
| Peptide bond | The primary linkage of all protein structures, 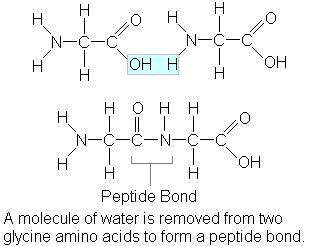 |
| Phospholipids | Class of lipids and are a major component of all cell membranes as they can form lipid bilayers, 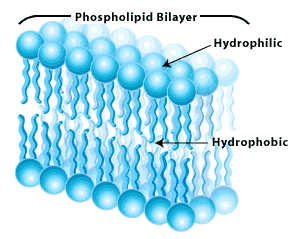 |
| Photosynthesis | The process by which plants and other photoautotrophs generate carbohydrates and oxygen from carbon dioxide, water, and light energy in chloroplasts,  |
| Polysaccharide | Any of a class of carbohydrates formed by repeating units linked together by glycosidic bonds.,  |
| Protein | A molecule composed of polymers of amino acids joined together by peptide bonds.,  |
| Saponification | Usually, a process by which triglycerides are reacted with sodium or potassium hydroxide to produce glycerol and a fatty acid salt, called 'soap'., 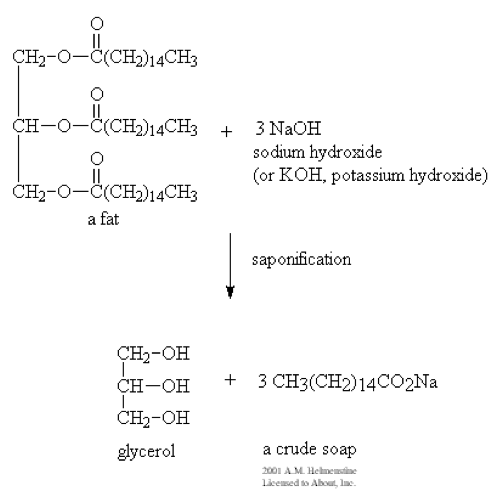 |
| Substrates | The material or substance on which an enzyme acts., 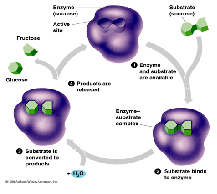 |
| Triglyceride | A naturally occurring ester of three fatty acids and glycerol that is the chief constituent of fats and oils., 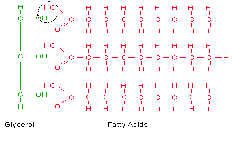 |
| Waxes | Any of various natural, oily or greasy heat-sensitive substances, consisting of hydrocarbons or esters of fatty acids that are insoluble in water but soluble in nonpolar organic solvents., 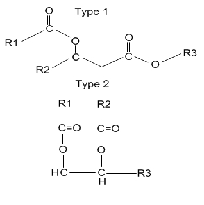 |