| A | B |
|---|
| Absolute Zero | Zero point on the kelvin temperature scale, equivalent to -273.15°C, 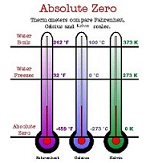 |
| Accepted Value | Quantity used by general agreement of the scientific community |
| Accuracy | Closeness of a measurement to the true value of what it is being measured,  |
| Calorie | Quantity of heat needed to raise the temperature of 1g of pure water 1° C |
| Celsius Scale | Temperature scale on which the freezing point of water is 0°C and the boiling point is 100°C, 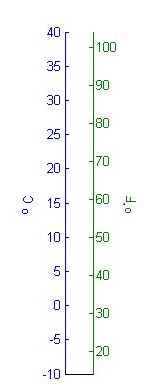 |
| Conversion Factor | Ratio of equivalent measurements use to convert a quantity from one unit to another, 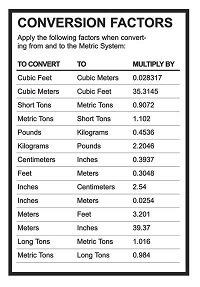 |
| Density | Ratio of the mass of an object to its volume,  |
| Dimensional Analysis | Technique of problem- solving that uses the units that are part of a measurement to help solve the problem, 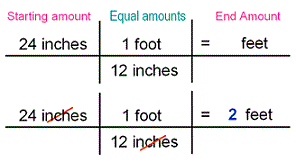 |
| Energy | Capacity for doing work or producing heat |
| Error | Difference between the accepted value and the experimental value |
| Experimental Value | Quantitative value measured during an experiment |
| Gram | Metric mass unit equal to the mass of 1 cm3 of water 4C,  |
| International System of Units | Revised version of the metric system, adopted by international agreement in 1960, 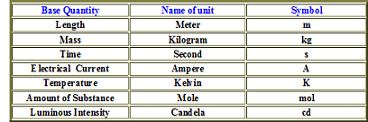 |
| Joule | SI unit of energy; 4.184 J equal one calorie, 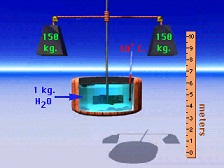 |
| Kelvin Scale | Temperature scale in which the freezing point of water is 273 K and the boiling point is 373 K; 0 K is absolute 0, 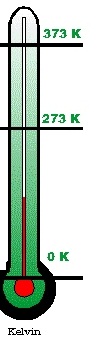 |
| Kilogram | The mass of 1 L of water at 4 C; it is the base unit of mass in SI,  |
| Liter | The volume of a cube measuring 10 centimeters on each edge (1000 cm3); it is the common unprefixed unit of the volume in the metric system,  |
| Measurement | Process of obtaining the magnitude of a quantity, such as length or mass, relative to a unit of measurement, such as a meter or a kilogram,  |
| Meter | Symbol m, is the base unit of length in the International System of Units (SI)., 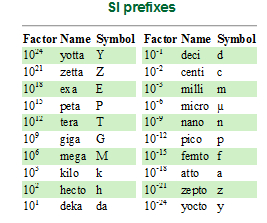 |
| Percent Error | Measure of how inaccurate a measurement is standerized to how large a measurement is., 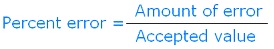 |
| Precision | Accuracy; exactness |
| Scientific Notation | Method of writing or displaying numbers in terms of a decimal number between 1 and 10 multiplied by a power of 10.,  |
| Significant Figures | All the digits that can be sknown precisely in a measurement, plus a last estimated digit. |
| Temperature | The degree of hotness or coldness of a body or environment,  |
| Weight | A force that measures the pull of gravity on a given mass.,  |