| A | B |
|---|
| Atom | The basic building blocks of matter that make up everyday objects.,  |
| Atomic Mass | Tells how many protons and neutrons are in its atom., 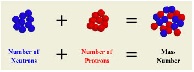 |
| Atomic Mass Unit | Unit of mass for expressing masses of atoms or molecules., 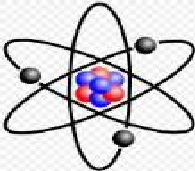 |
| Atomic Number | The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom., 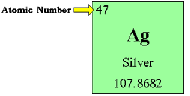 |
| cathode ray | beam of electrons emitted by the cathode of an electrical discharge tube, 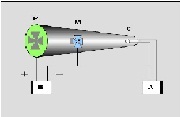 |
| Dalton's Atomic Theory | Theory stating that an element is composed of only one kind of atom, and a compound is composed of particles that are chemical combinations of different kinds of atoms.,  |
| Electron | A negatively charged subatomic particle, 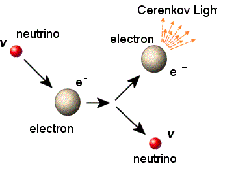 |
| Group | A vertical column of elements in the periodic table, 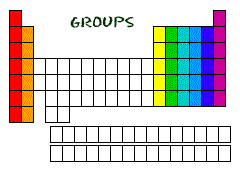 |
| Isotopes | Atoms of the same element that have the same atomic number but different atomic masses due to different number of nuetrons, 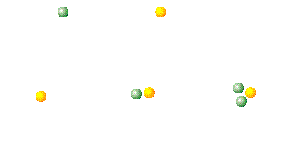 |
| Mass Number | The total number of protons and nuetrons in the nucleus of an atom,  |
| Nucleus | The tiny, dense central portion of an atom, composed of protons and nuetrons, 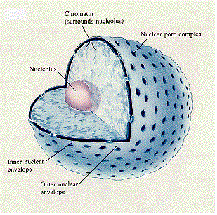 |
| Neutron | A subatomic particle with no charge and a mass of 1 amu, 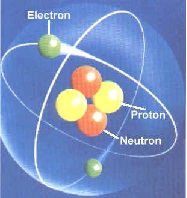 |
| Period | A horizontal row of elements in the periodic table, 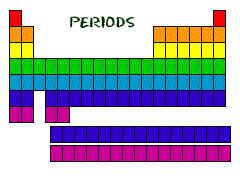 |
| Periodic Table | An arrangement of elements in which the elements are seperated into groups based on a set of repeating properties, 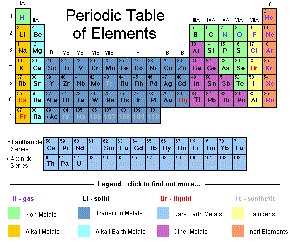 |
| Proton | A positively charged subatomic partical found in the nucleus of an atom, 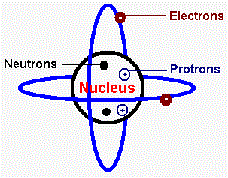 |