| A | B |
|---|
| Alloys | Mixtures composed of two or more elements.,  |
| Chemical Formula | It shows the kinds and numbers of atoms in the smallest representative unite of a substance., 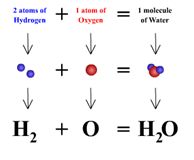 |
| Coordination number | Number of ions of opposite charge that surround each ion in a crystal.,  |
| Electron dot structure | A notation that depicts valence electrons as dots around the atomic symbol of the element; the symbol represents the inner electrons and atomic nucleus; also called Lewis dot structure., 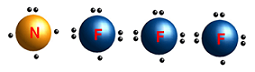 |
| Formula unit | The lowest whole-number ratio of ions on an ionic compound; in magnesium chloride, the ratio of magnesium ions to chloride ions is 1:2 and the formula unit is MgC12.,  |
| Halide ion | A negative ion formed when a halogen atom gains an electron,  |
| Ionic bonds | The electrostatic attraction that binds oppositely charged ions together, 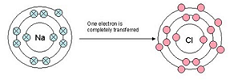 |
| Ionic compounds | A compound composed of positive and negative ions., 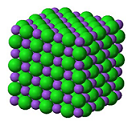 |
| Metallic bonds | The force of attraction that holds metals together; it consists of the attraction of free-floating valence electrons for positively charged metal ions., 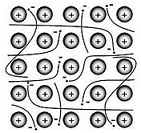 |
| Octet rule | Atoms react by gaining or losing electrons so as to acquire the stable electron structure of a noble gas, usually eight valence electrons., 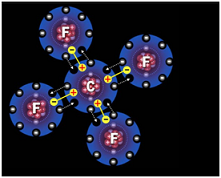 |
| Valence electron | An electron in the highest occupied energy level of an atom, 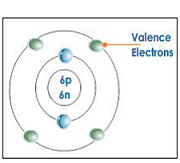 |