| A | B |
|---|
| Acid Dissociation Constant | Quantitative measure of the strength of an acid in solution., 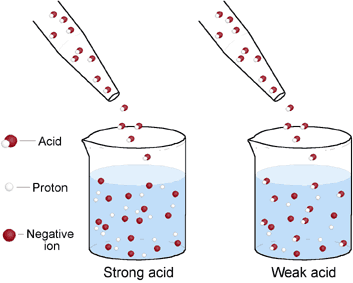 |
| Acidic Solution | A mixture, a solution, of water and various chemicals, some of which are able to release hydrogen ions (H +) into the mixture/solution, such that the pH of the solution is less than 7,  |
| Alkaline solutions | An alkaline solution is a mixture of a base solid dissolved in water.,  |
| Amphoteric | An amphoteric substance is one that can react as either an acid or base., 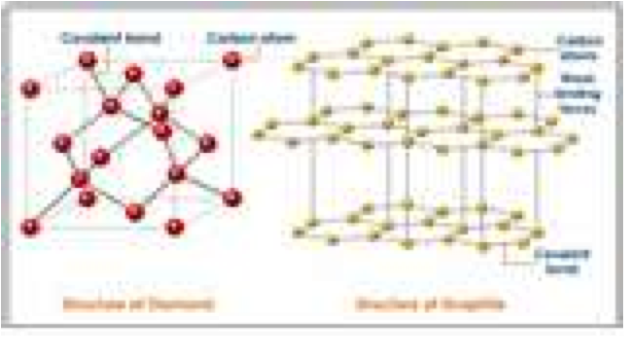 |
| Base dissociation constant | The equilibrium constant for the reaction of a base with water to produce the conjugate acid and the hydroxide ion,  |
| Basic Solution | A solution that has a higher concentration of hydroxide ions that hydrogen ions; a pH between 7 and 14.,  |
| Buffer Capacity | A buffer solution is an aqueous solution consisting of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. |
| Buffers | An ionic compound that resists changes in its pH,  |
| Conjugate acid base pairs | Two species related to one another by the presence of a hydrogen ion (in the acid part of the pair) or its absence (in the base part or the pair)., 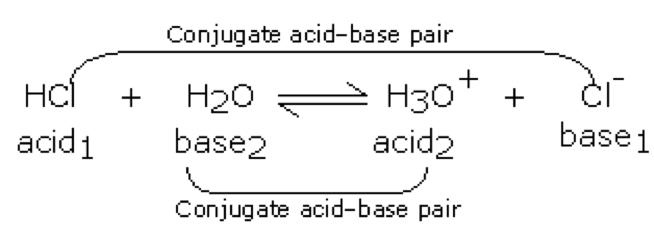 |
| Conjugate acids | Is the acid member, HX, of a pair of compounds that differ from each other by gain or loss of a proton. A conjugate acid can release or donate a proton.,  |
| Conjugate base | Any compound, of general formula X, which can be transformed into a conjugate acid HX by the gain of a proton, 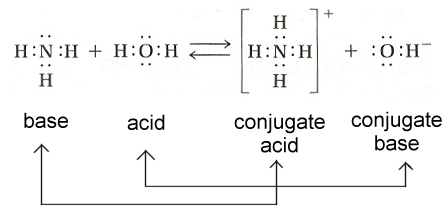 |
| Diprotic acid | A diprotic acid is an acid such as H2SO4 (sulfuric acid) that happens to contain within its molecular structure two hydrogen atoms per molecule capable of dissociating (i.e. ionizable) in water.,  |
| End Point | resultant: the final point in a process,  |
| Equivalence point | A chemical reaction when a titrant (in buret) is added and is stoichiometrically equal to the amount of moles of substance, 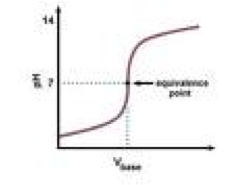 |
| Hydronium Ion (H3 O+) | The H 3 O + ion, which is formed by the combination of a proton with a water molecule. Its presence accounts for the properties of acids., 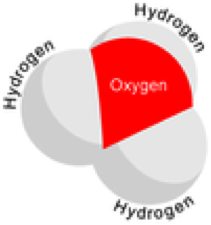 |
| Ion- product constant for water | Water molecules can function as both acids and bases. One water molecule (acting as a base) can accept a hydrogen ion from a second one (acting as an acid).,  |
| Lewis Acid | A substance that can accept an electron pair from a base; thus, AlCl3, BF3, and SO3 are acids., 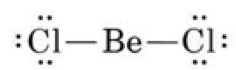 |
| Lewis Base | A substance capable of donating a pair of electrons to an acid to form a covalent bond,  |
| Monoprotic acid | A monoprotic acid is an acid that can only release one hydrogen ion into a solution.,  |
| Neutral solution | An aqueous solution with a pH of 7.0 and is neutral to any charges.,  |
| Neutralization Reactions | Refers to acid and base reaction producing salt and water, 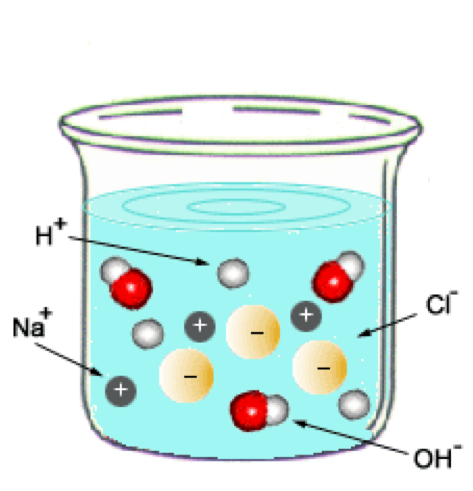 |
| pH | A measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. |
| Salt Hydrolysis | Dissolution is the process by which a solid or liquid forms a homogeneous mixture with a solvent, 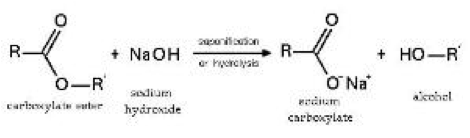 |
| Self-ionization | To give an atom or group of atoms a net electric charge by adding or removing one or more electrons., 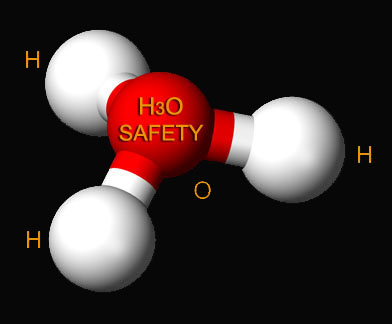 |
| Standard Solution | A chemical term which describes a solution of known concentration,  |
| Strong Acids | Is an acid that ionizes completely in an aqueous solution by losing one proton, 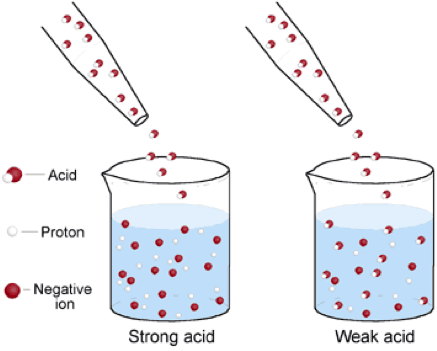 |
| Strong Bases | Substance that can accept hydrogen ions or more generally, donate electron pairs., 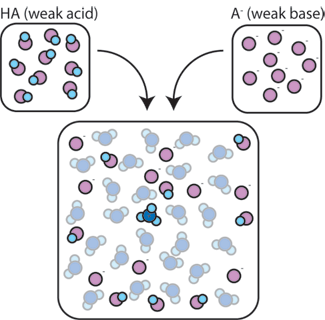 |
| Titration | Used to determine the unknown concentration of a known reactant, 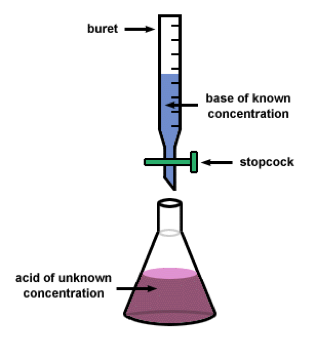 |
| Triprotic Acids | An acid that has three ionizable hydrogen atoms in each molecule.,  |
| Weak Acids | Is an acid that dissociates incompletely, 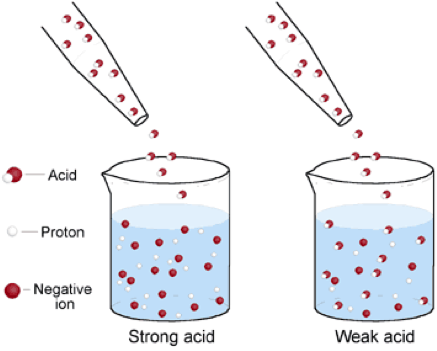 |
| Weak base | Weak base is a chemical base that does not ionize fully in an aqueous solution,  |