| A | B |
|---|
| Line-Emission Spectrum | A diagram or graph that indicates the degree to which a substance emits radiant energy with respect to a wavelength |
| Atomic Orbital | a mathematical expression describing the probability of finding an electron at various locations, 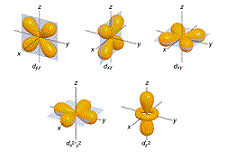 |
| Frequency | A number of cycles or vibrations per unit of time; also the number of waves produced in a given amount of time, 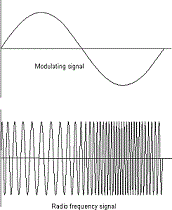 |
| Excited State | A state in which an atom has more energy than it does as its ground state |
| Photon | A unit or quantum of light; a particle of electromagnetic radiation that has zero rest mass & carries a quantum of energy |
| Electron Configurations | the arrangment of electrons of an atom in its ground state into various orbitals,  |
| Quantum | The basic unit of electromagnetic energy; it characterizes the wave properties of electrons |
| Wavelength | The distance from any point on a wave to an identical point on the next wave, 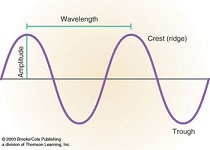 |
| Photoelectric Effect | The emission of electrons from a material when light of certain frequencies shines on the surface of the material |
| Electromagnetic Spectrum | The energy needed to remove an electron from a negative ion to form a neutral atom or molecule |
| Amplitude | the height of a wave's crest, 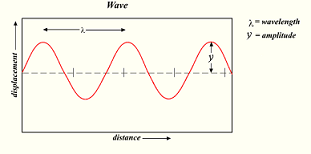 |
| Ground State | The lowest energy state of a quantized system, 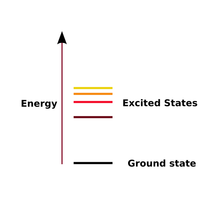 |
| Atomic Emission Spectrum | the pattern formed when light passes through a prism or diffraction grating to separate it into the different frequencies of light it contains, 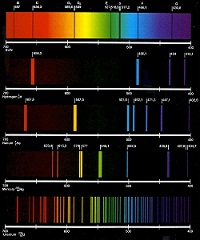 |
| Electromagnetic Radiation | The radiation associated with an electric & magnetic field; it varies periodically & travels at the speed of light |
| Aufbau Principle | the rule that electrons occupy the orbitals of lowest energy first, 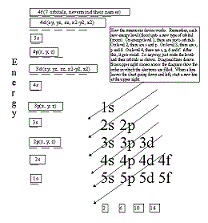 |
| Continuous Spectrum | The uninterrupted broad band of all colors (wavelength) emitted by incandescent solids |
| Energy Levels | The specific energies an electron in an atom or other system can have, 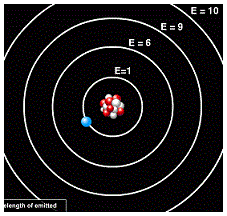 |
| Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle | It is impossible to know exactly both the velocity and the position of a particle at the same time, 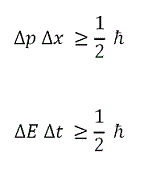 |
| Hertz | The unit of frequency, equal to one cycle per second, 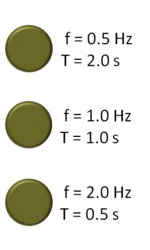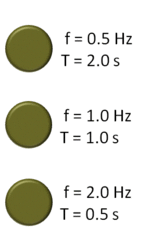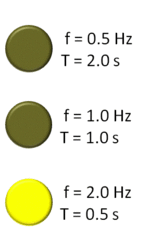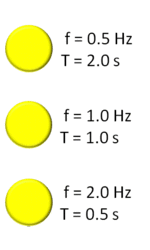 |
| Hund's Rule | Electron occupy orbitals of the same energyin a way that makes the number or electrons with the same spin direction as large as possible, 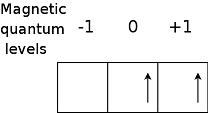 |
| Pauli Exclusion Principle | An atomic orbital may describe at most two electrons, each with opposite spin direction, 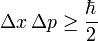 |
| Quantum Mechanical Model | The modern description, primarily mathematical, of the behavior of electrons in atoms, 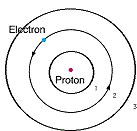 |
| Spectrum | Wavelengths of visible light that are separated when a beam of light passes through a prism; range of wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation, 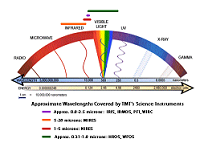 |