| A | B |
|---|
| Asteroids | A small planet that revolves around the sun. The largest asteroid is only about six hundred miles in diameter.,  |
| Cleavage | The surface created by a rock or mineral when broken along a preferred (natural) direction, creating a bright reflective plane surface., 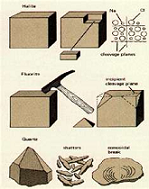 |
| Dark Matter | A hypothetical form of matter that is believed to make up 90 percent of the universe; it is invisible (does not absorb or emit light) and does not collide with atomic particles but exerts gravitational force.,  |
| Erosion | Is the process of weathering and transport of solids (sediment, soil, rock and other particles) in the natural environment or their source and deposits them elsewhere, 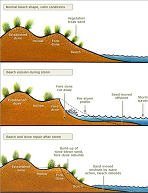 |
| Geocentric Model | That the earth is center of the universe and other objects orbit around it,  |
| Hydroelectricity | Is the term referring to electricity generated by hydropower; the production of electrical power through the use of the gravitational force of falling or flowing water. It is the most widely used form of renewable energy., 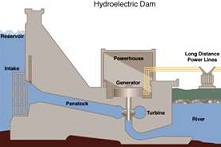 |
| Magma | Molten rock in the earths crust,  |
| Mountain | A feature on Earths surface that rises higher than the surrounding landscape.,  |
| Photosphere | The intensely luminous surface of a star., 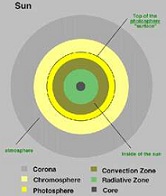 |
| Principle of superposition | The principle that in a series of stratified sedimentary rocks the lowest stratum is the oldest, 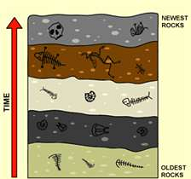 |
| Rock Strata | Distinguished layers of rock,,  |
| Solar Eclipse | Occurs when the moon passes between the sun and the Earth, and the Moon fully or partially covers the Sun as viewed from a location on Earth. This can only happen during a new moon, when the Sun and Moon are in conjunction as seen from Earth.,  |
| Sunspots | Any of the dark spots that appear at times on the sun's surface and are usually visible only through a telescope,  |
| Troposhpere | The lowest portion of Earth's atmosphere. It contains approximately 75% of the atmosphere's mass and 99% of its water vapor and aerosols., 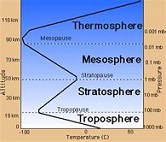 |
| Water Cycle | The process in which water moves back and forth between Earths surface and the atmosphere by means of evaporation, condensation, and precipitation., 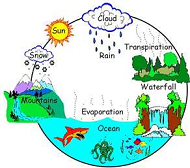 |