| A | B |
|---|
| Accuracy | Correctness of a single measurement. Accuracy is determined by comparing the measurement against the true or accepted value.,  |
| Bit | Each 1 and 0 in the binary system.,  |
| Computer | An electric device that stores, processes, and retrieves information.,  |
| Controlled Experiment | An experiment in which all variables except one are kept constant,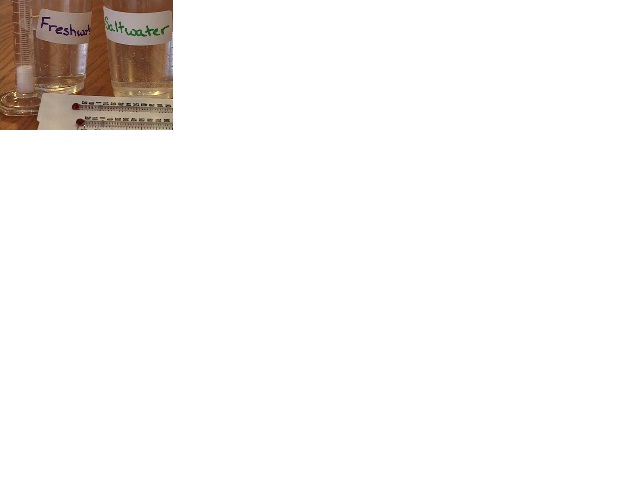  |
| Evidence | Tends to prove or disprove something; ground for belief; proof.,  |
| Global Positioning System (GPS) | A system of satellites, computers, and receivers that is able to determine the latitude and longitude of a receiver on Earth by calculating the time difference for signals from different satellites to reach the receiver.,  |
| Incandescent Lights | Lights that glow when a filament inside them get hot.,  |
| Laboratory Glassware | A shallow glass dish used as an evaporating surface or to cover a beaker,  |
| Melting Point | The temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid. It is equal to the freezing point,  |
| Patterns | Decoration or ornament having such a design,  |
| Radar | A system of detecting reflected radio waves.,  |
| Satellite | An object that travels around another object in space,  |
| Society | An organized group of persons associated together for religious, benevolent, cultural, scientific, political, patriotic, or other purposes.,  |
| Theory | The analysis of a set of facts in their relation to one another,  |
| Variable | Any factor that can change in an experiment.,  |