| A | B |
|---|
| Amino Acid | Any of a class of organic compounds that contains at least one amino group, –NH2, and one carboxyl group, –COOH, 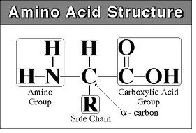 |
| Biome | A complex biotic community characterized by distinctive plant and animal species and maintained under the climatic conditions of the region, esp. such a community that has developed to climax.,  |
| Cellulose | A complex carbohydrate with which plants build strong stems and roots., 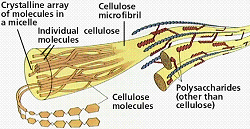 |
| Convergent Evolution | Describes the process whereby organisms not closely related independently acquire similar characteristics,  |
| Ear Canal | Is a tube running from the outer ear to the middle ear., 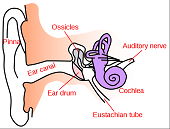 |
| Exocytosis | A process of cellular secretion or excretion in which substances contained in vesicles are discharged from the cell., 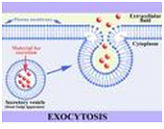 |
| Glucose | A sugar found in the body; the monomer of many complex carbohydrates., 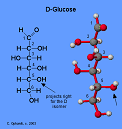 |
| Hydrogen Bond | A type of chemical bond in which a hydrogen atom that has a covalent link with one of the electronegative atoms (F, N, O) forms an electrostatic link with another electronegative atom in the same or another molecule., 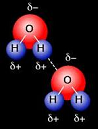 |
| Lungs | A pair of organs, located in the chest, that contain millions of tiny air sacs, in which the exchange of respiratory gases between the blood and the environment takes place,  |
| Monera | The lowest division of rhizopods, including those which resemble the amoebas, but are destitute of a nucleus.,  |
| Nucleus | The structure within the cell that controls cell activity and contains genetic material. The center of an atom., 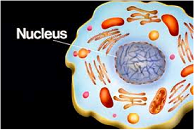 |
| Phylogenic Trees | Is a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological species or other entities that are known to have a common ancestor,  |
| Respiration | The process of taking in oxygen from the environment and releasing carbon dioxide and water vapor., 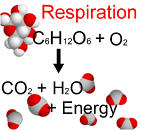 |
| Spinal Cord | The thick cord of nerve tissue that extends from the brain down through the spinal column., 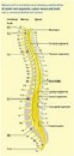 |
| Transmutation | To change or alter in form, appearance, or nature and to a higher form., 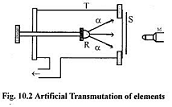 |