| A | B |
|---|
| Active Transport | Movement of materials in biological systems, particularly into and out of cells and across epithelial layers, 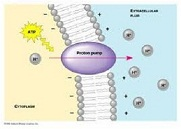 |
| Anticodon | A sequence of three nucleotides in a region of transfer RNA that recognizes a complementary coding triplet of nucleotides in messenger RNA during translation by the ribosome’s in protein biosynthesis., 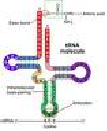 |
| Cartilage | A flexible tissue that acts as a cushion between bones and provides flexibility at the end of bones., 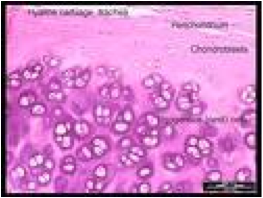 |
| Class | A taxonomic category of organisms ranking above an order and below a phylum or division., 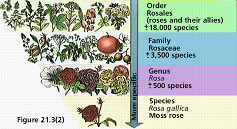 |
| Diffusion | The transmission of elements or features of one culture to another., 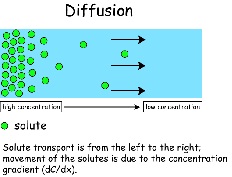 |
| Endocytosis | Is the process by which cells absorb molecules (such as proteins) by engulfing them., 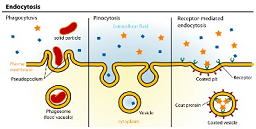 |
| Food Chain | A series of organisms interrelated in their feeding habits, the smallest being fed upon by a larger one, which in turn feeds a still larger one, etc.,  |
| Herbaceous | Having little or no woody tissue and persisting usually for a single growing season,  |
| Isotonic | Having the same (or equal) osmotic pressure and same water potential since the two solutions have an equal concentration of water molecules., 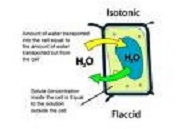 |
| Mesoderm | One of the three primary germ cell layers -- the other two are the ectoderm and endoderm -- in the very early embryo. The mesoderm is the middle layer. It differentiates to gives rise to a number of tissues and structures including bone, muscle, connective tissue, and the middle layer of the skin. Some cells in mesodermal tissues retain the capacity to differentiate in diverse directions. For example, some cells in the bone marrow (mesoderm) can become liver (endoderm).,  |
| Nerves | Thin strands of tissue, composed of neutrons, that carry impulses throughout the body, 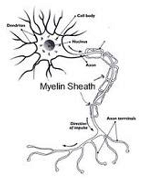 |
| Ovaries | The female reprodutive organs that produce egg cells., 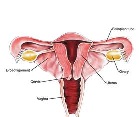 |
| Protein | Any of numerous, highly varied organic molecules constituting a large portion of the mass of every life form and necessary in the diet of all animals and other non photosynthesizing organisms, composed of 20 or more amino acids linked in a genetically controlled linear sequence into one or more long polypeptide chains, the final shape and other properties of each protein being determined by the side chains of the amino acids and their chemical attachments., .jpeg) |
| Saprophyte | Any organism that lives on dead organic matter, as certain fungi and bacteria.,  |
| Telephase | The final stage of meiosis when the chromosomes move toward opposite ends of the nuclear spindle, 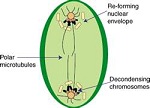 |
| Veins | Blood vessels that return blood to the heart., 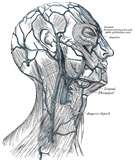 |