| A | B |
|---|
| Adenine | A purine base, C5H5N5, one of the fundamental components of nucleic acids, as DNA, in which it forms a base pair with thymine, and RNA, in which it pairs with uracil.,  |
| Binomial | Nomenclature involves organizing an organism's scientific name into a combination of two terms. These terms are the genus name and the species. Both of these terms are italicized and the genus name is also capitalized.,  |
| Cell Nucleus | Acts like the brain of the cell. It helps control eating, movement, and reproduction. If it happens in a cell, chances are the nucleus knows about it., 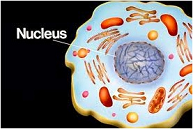 |
| Commensalism | The relation between two different kinds of organisms when one receives benefits from the other without damaging it,  |
| DNA Deoxyribonucleic Acid | Complex compound that carries information about cell activities from one generation to another, 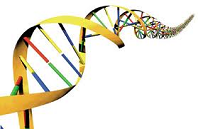 |
| Energy Transfer | When energy is being move from one place to another,  |
| Gene | The basic physical unit of heredity; a linear sequence of nucleotides along a segment of DNA that provides the coded instructions for synthesis of RNA, which, when translated into protein, leads to the expression of hereditary character., 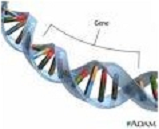 |
| Hibernate | To enter a sleeplike state of reduced body activity; how some animals survive the winter,  |
| Larynx | Two folds of tissue that make up the human voice box, .jpg) |
| Migrate | Is to move from one environment to another, where conditions are more favorable.,  |
| Noninfectious Disease | A disease that cannot be transmitted from one individual to another.,  |
| Pasteurization | The process of heating milk, and some other foods, to kill bacteria that cause spoilage and disease., 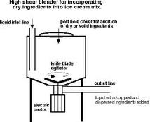 |
| Radiation Therapy | Process in which radioactive elements are used to destroy unhealthy cells., 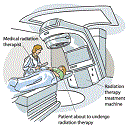 |
| Skin | The organ that covers and protects the body, and excretes wastes by perspiring., 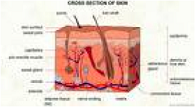 |
| Tissues | A cellular organizational level intermediate between cells and a complete organism, 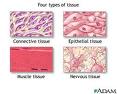 |
| Vitamin | An organic compound that serves as a helper molecule in a variety of chemical reactions in the body, 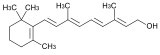 |