| A | B |
|---|
| Alpha Particle | Form of nuclear radiation consisting of two protons and two nuclear., 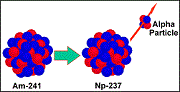 |
| Breaking | To separate the molecule,,  |
| Combustion | Rapid oxidation accompanied by heat and, usually, light., 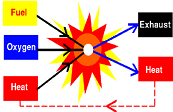 |
| Diffraction | Various phenomena which occur when a wave encounters an obstacle.,  |
| Electromagnetic Wave | A wave produced by the acceleration of an electric charge and propagated by the periodic variation of intensities of, usually, perpendicular electric and magnetic fields.,  |
| Friction | A force that surface exerts on another when the two rub against each other.,  |
| Hydrocarbon | An organic compound that contains only the elements carbon and hydrogen., 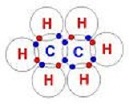 |
| Isotope | An atom with the same number of protons and different numbers of neutrons from other atoms of the same element, 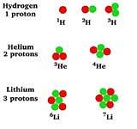 |
| Mass | Is the quantity of inertia possessed by an object or the proportion between force and acceleration referred to in Newton's Second Law of Motion., 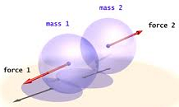 |
| Noise | Mixture of sound waves with no pleasing timbre and no identifiable pitch.,  |
| Photon | A quantum of electromagnetic radiation; an elementary particle that is its own antiparticle,  |
| Radio waves | Electromagnetic waves with the longest wavelengths and the lowest frequencies.,  |
| Solubility | Measure of how well a solute can dissolve in a solvent at a given temperature., 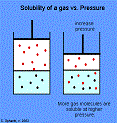 |
| Terminal | The part of an electrode above the surface of the electrolyte.,  |
| Virtual image | An upright image formed where rays of light appear to meet or come from., 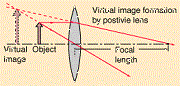 |