| A | B |
|---|
| Altitude | The height above sea level of a place,  |
| Cinder Cone Volcano | Cone build up by the accumulation of loose bits of magma (scoria) that fall around a vent or crater after being expelled into the air during moderately explosive activity. If still sufficiently hot they meld when they fall to the ground., 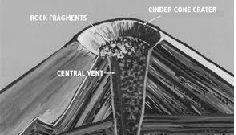 |
| Crust | The outermost rock layer of Earth, which contains all of Earth’s surface features, 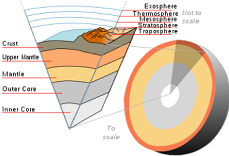 |
| Elastic Rebound | The bending and subsequent “catching up” of the crust, 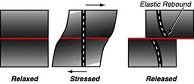 |
| Full Moon | The phase of the moon that occurs when Earth is between the sun and the moon, so that all of the moon’s lighted side can be seen from Earth,  |
| Humidity | The amount of moisture (water vapor) present in the atmosphere.,  |
| Low-Pressure System | A large area where air is rising, causing low surface air pressure; also called a low.,  |
| Moon | A natural satellite revolving around a planet.,  |
| Parent Rock | Original rock from which something else was formed. It is mainly used in the context of soil formation where the parent rock will have a large influence on the nature of the resulting soil.,  |
| Precipitation | Water, in the form of rain, snow, sleet, or hail, falling from clouds in the sky, 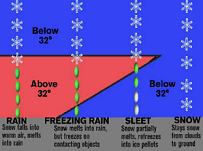 |
| Rift Valley | Elongated depression, trough, or graben in the earth's crust, bounded on both sides by normal faults and occurring on the continents or under the oceans., 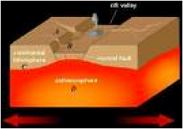 |
| Smog | A haze in the atmosphere produced by the reaction of sunlight with pollutants from cars and factories.,  |
| Subduction | A geological process in which one edge of a crustal plate is forced sideways and downward into the mantle below another plate,  |
| Transform Boundary | Also known as conservative plate boundary, is a fault which runs along the boundary of a tectonic plate. The relative motion of such plates is horizontal in either sinistral or dextral direction, 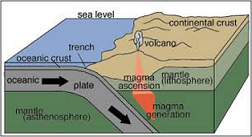 |
| Warm Front | The boundary formed when a warm air mass slides up and over a cool air mass., 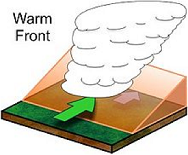 |