| A | B |
|---|
| Aquifer | Any geological formation containing or conducting ground water, esp. one that supplies the water for wells, springs, etc., 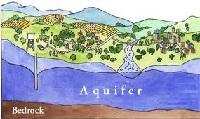 |
| Clast | A fragment of rock that was broken from a larger rock or rock unit,  |
| Dark Energy | In physical cosmology, astronomy and celestial mechanics, dark energy is a hypothetical form of energy that permeates all of space and tends to increase the rate of expansion of the universe.,  |
| Equinox | The time or date (twice each year) at which the sun crosses the celestial equator, when day and night are of equal length (about September 22 and March 20)., 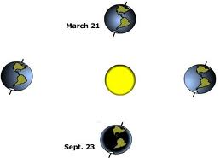 |
| Galaxy | A large system of stars held together by mutual gravitation and isolated from similar systems by vast regions of space.,  |
| Hurricane | A huge, rotating storm that forms over the ocean in the tropics, with strong winds and heavy rains.,  |
| Lunar Eclipse | An eclipse in which the moon appears darkened as it passes into the earth's shadow., 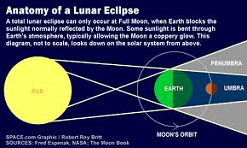 |
| Moon Phase | A lunar phase or phase of the moon refers to the appearance of the illuminated portion of the Moon as seen by an observer, usually on Earth.,  |
| Phases | The changing apparent shape of the moon as seen from the Earth,  |
| Prevailing Winds | The winds that commonly blow in the same direction at a given latitude., 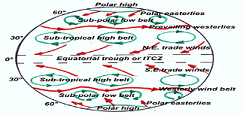 |
| Rock | A natural, stony material composed of one or more minerals.,  |
| Soil | A mixture of small rock fragments and decayed organic material that covers much of Earth’s land surface., 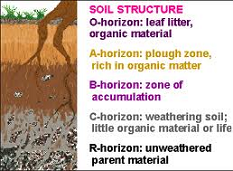 |
| Subtropical High | A significant belt of high pressure situated around the latitudes of 30°N in the Northern Hemisphere and 30°S in the Southern Hemisphere., 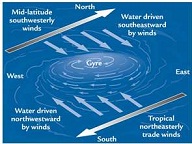 |
| Transport | To carry, move, or convey from one place to another., 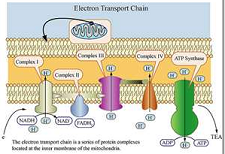 |
| Water Cycle | The natural sequence through which water passes into the atmosphere as water vapor, precipitates to earth in liquid or solid form, and ultimately returns to the atmosphere through evaporation., 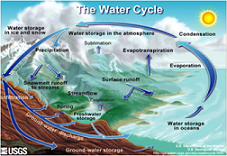 |